Table
16.
Operational
Status Byte (Register
Ru
1)
(cont.)
Bit
Position
Significance
14
lOP
Halt.
This
bit
is
set
to
1 if
an
error
con-
dition
is
detected
which causes
the
lOP
to
issue a
halt
order to
the
addressed
I/O
de-
vice.
Error conditions which may
cause
an
lOP
halt
(independent of
the
HTE
flag
within
the
I/o
command doubleword)
are:
1.
Bus
check
fault
that
occurs
while
fetch-
ing a command
2. Control
check
fault
3. Memory address error
4.
lOP
memory error
5.
lOP
contfol error
Table
16.
Operational Status Byte (Register
Ru1)
(cont.)
Bit
Position
14
(cont.)
15
Significance
Error conditions which may cause an
lOP
halt
only
if
the
HTE
flag is
coded
with a 1 are:
1.
Bus
check
fault
that
occurs
whi
Ie
fetch-
ing
data
2.
Transmission memory error
3.
Transmission
data
error
4.
Incorrect length conditi on occurri
ng
while
the
SIL
flag is coded with a
O.
An
lOP
halt
condition causes the current
operation to terminate immediately as
an
II
unusua I end
ll
•
This
bit
is set to a 1 if a Write Lock Violation
(WL
V)
occurs.
Table
17.
Status Response
Bits
for
I/O
Instructions
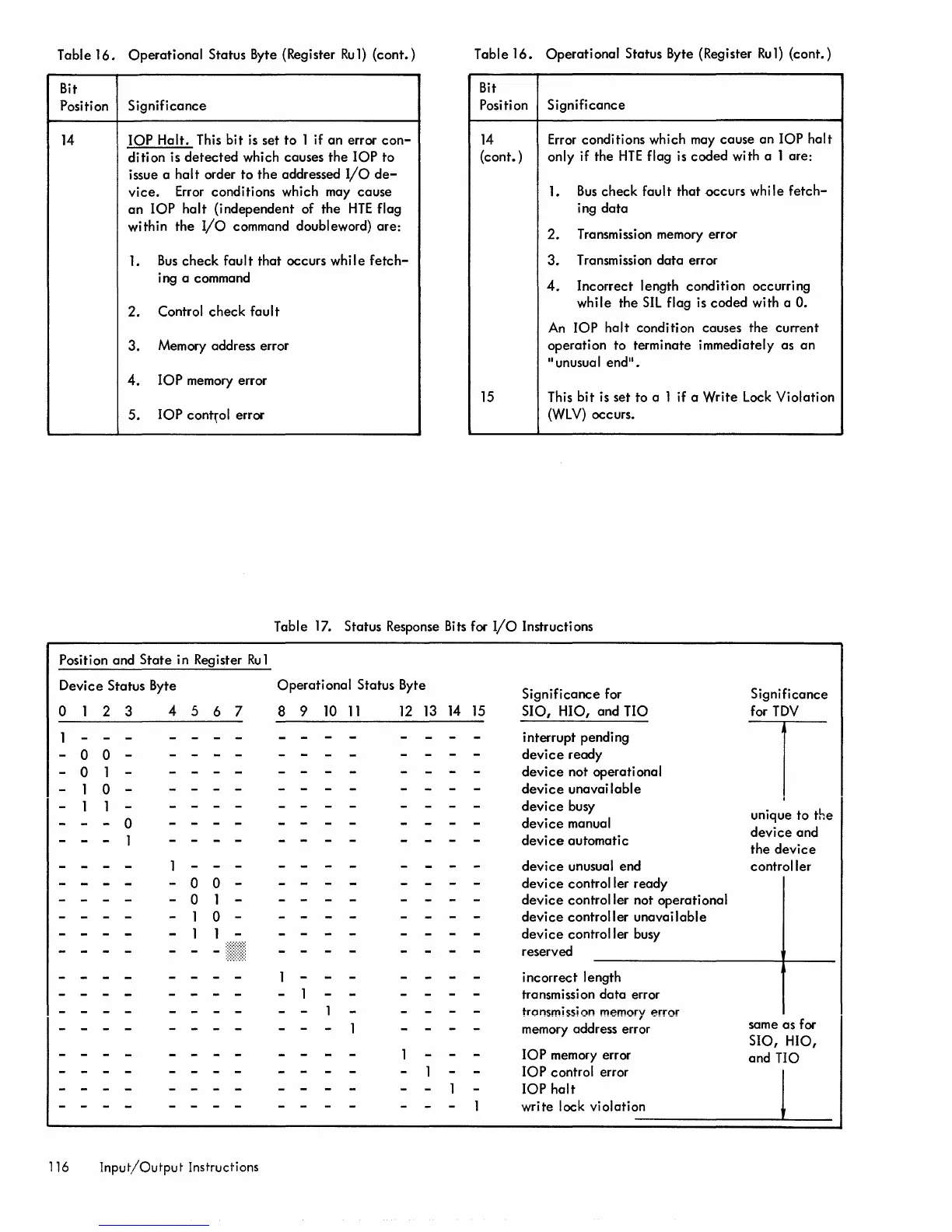
Position and
State
in Register
Ru
1
Device Status Byte
o
2 3
- 0 0 -
- 0 1
10-
1 1
- - - 0
- - - 1
4 5 6 7
- 0 0 -
- 0 1
10-
1 1
116
Input/Output
Instructions
Operational
Status Byte
8 9
10
11
12 13 14 15
Significance for
SIO,
HIO, and TIO
interrupt pending
device
ready
device
not operational
device
unavai lable
device
busy
device
manual
devi
ce
automati c
device
unusual end
device
controller ready
device
controller not operational
device
controller
unavailable
device
controller busy
reserved
incorrect length
transmission
data
error
tronsmission memory
error
memory address error
lOP
memory error
lOP
control error
lOP
halt
write lock violation
Significance
for
TDV
T
unique to the
device
and
the
device
controller
same as for
SIO,
HIO,
and TIO
I
 Loading...
Loading...











