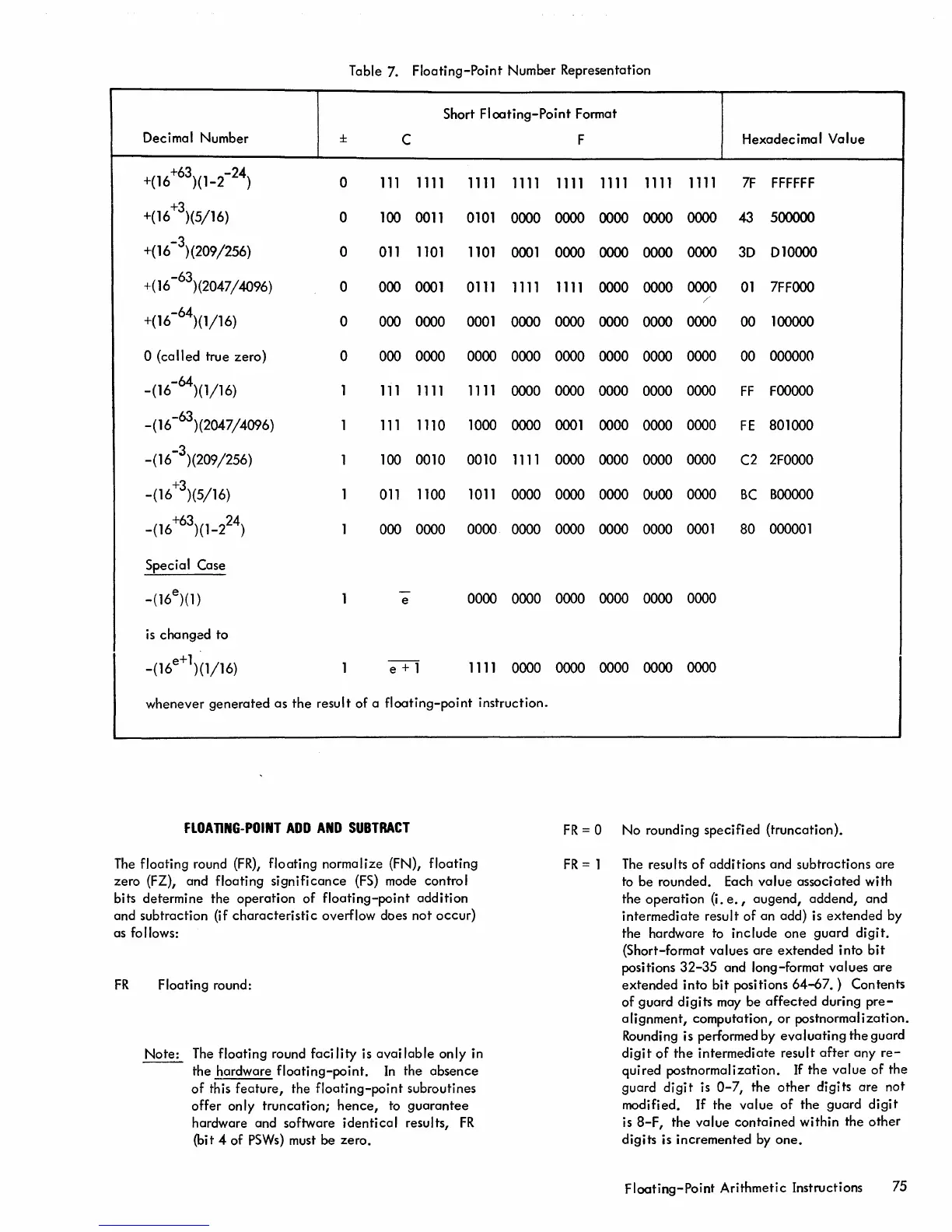
Table 7. Floating-Point Number Representation
Short Floating-Point Format
Decimal Number
±
C
+(16 +63)(1_2-
24
)
0
111
1111
1111
1111
+(16 +3)(5/16)
0 100
0011 0101
0000
+(16-
3
)(209/256)
0
011
1101
1101
0001
+(16 -63)(2047/4096)
0 000 0001 0111
1111
+(16-
64
)(1/16)
0
000 0000 0001 0000
o (called true zero)
0 000 0000 0000 0000
-(16-
64
)(1/16)
1
111
1111
1111
0000
-(16
-63)(2047/4096)
1
111
1110 1000
0000
-(
16-
3
)(209/256)
1
100 0010 0010
1111
-(16+
3
)(5/16)
1
011
1100
1011
0000
-(16
+63)(1_2
24
)
1
000 0000
0000
0000
Special Case
-(16
e
)(1
)
1
-
0000 0000
e
is
changed to
_(16
e
+
1
)(1/16)
1 e + 1
1111
0000
whenever generated as the result of a floating-point instruction.
FLOAllNG-POINT
ADD
AND
SUBTRACT
The
floating round
(FR),
floating normalize (FN), floating
zero
(FZ), and floating significance
(FS)
mode control
bits determine the operation of floating-point addition
and subtraction (if characteristic overflow does not occur)
as follows:
FR
Floating round:
Note:
The
floating round faci lity is avai lable only in
--
the hardware floating-point.
In
the absence
of
this feature, the floating-point subroutines
offer
on
Iy
truncation; hence, to guarantee
hardware and software identical results,
FR
(bit 4 of
PSWs)
must be zero.
F
Hexadecimal Value
1111
1111
1111
1111
7F
FFFFFF
0000
0000
0000
0000
43
500000
0000
0000
0000
0000
3D
Dl0000
1111
0000
0000
0000
01
7FFooo
/
0000 0000
0000
0000
00
100000
0000 0000
0000
0000 00 000000
0000
0000 0000
0000
FF
FOOooO
0001 0000
0000
0000
FE
801000
0000 0000
0000
0000 C2
2
FOooO
0000 0000 0000
0000
BC
BooooO
0000 0000
0000
0001
80
000001
0000 0000 0000
0000
0000 0000 0000
0000
FR
= 0 No rounding specified (truncation).
FR
= 1
The
results
of
additions and subtractions are
to
be rounded. Each value associated with
the operation (i.
e.,
augend, addend, and
intermediate result
of
an add)
is
extended by
the hardware
to
include one guard digit.
(Short-format values are extended into
bit
positions
32-35
and long-format values are
extended into bit positions
64-67.)
Contents
of
guard digits
may
be
affected
during
pre-
alignment, computation,
or
postnormalization.
Rounding is performed by evaluating the guard
digit
of
the
intermediate result
after
any
re-
quired postnormalization.
If
the value
of
the
guard
digit
is
0-7,
the other digits are not
modified.
If the value
of
the guard
digit
is
8-F,
the value contained within the other
digits is incremented
by
one.
Floating-Point Arithmetic Instructions 75
 Loading...
Loading...











