RL78/F13, F14 CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
R01UH0368EJ0210 Rev.2.10 184
Dec 10, 2015
3.3 Instruction Address Addressing
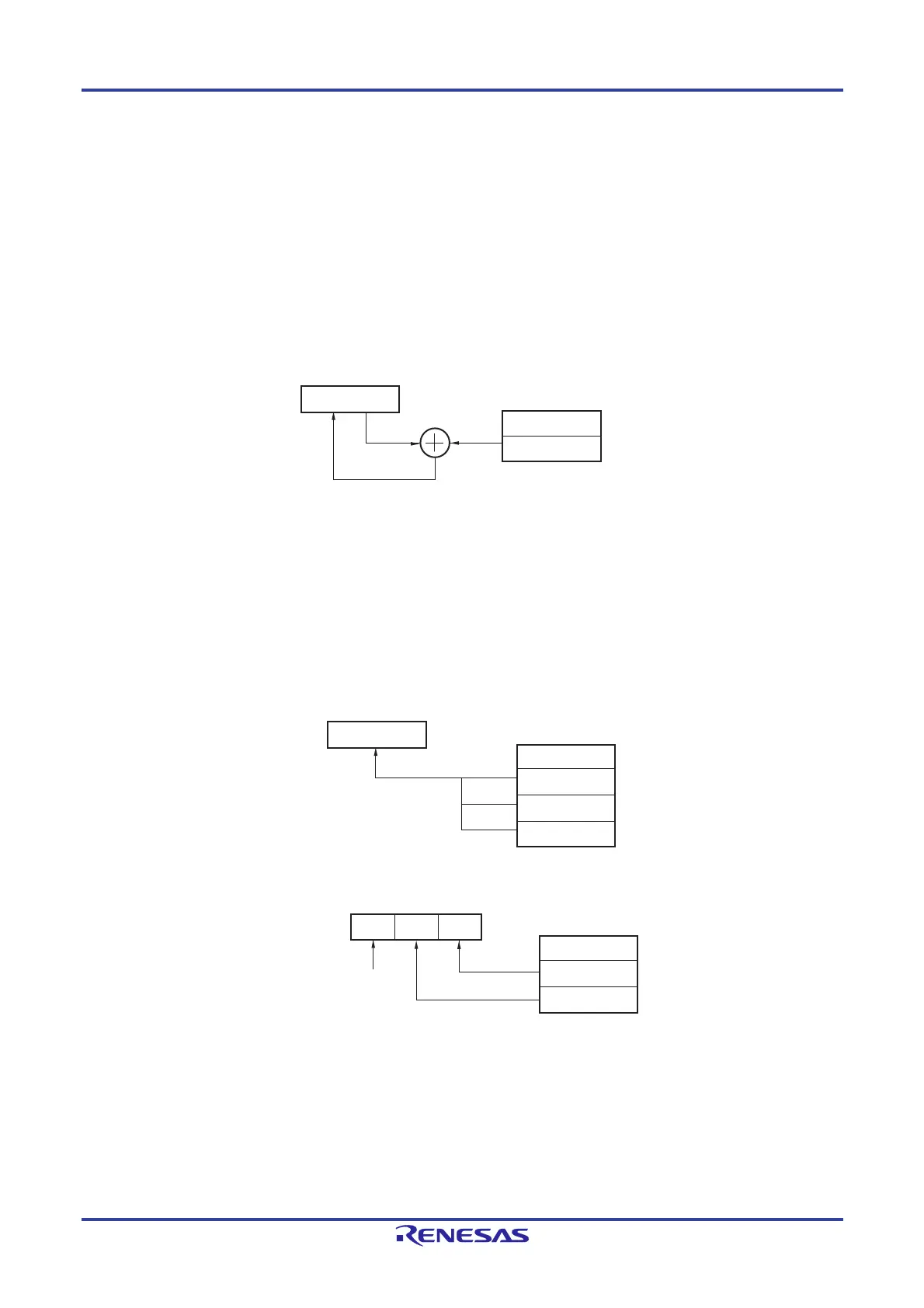
3.3.1 Relative addressing
[Function]
Relative addressing stores in the program counter (PC) the result of adding a displacement value included in the
instruction word (signed complement data: –128 to +127 or –32768 to +32767) to the program counter (PC)’s value
(the start address of the next instruction), and specifies the program address to be used as the branch destination.
Relative addressing is applied only to branch instructions.
Figure 3-42. Outline of Relative Addressing
3.3.2 Immediate addressing
[Function]
Immediate addressing stores immediate data of the instruction word in the program counter, and specifies the program
address to be used as the branch destination.
For immediate addressing, CALL !!addr20 or BR !!addr20 is used to specify 20-bit addresses and CALL !addr16 or
BR !addr16 is used to specify 16-bit addresses. 0000 is set to the higher 4 bits when specifying 16-bit addresses.
Figure 3-43. Example of CALL !!addr20/BR !!addr20
Figure 3-44. Example of CALL !addr16/BR !addr16
OP code
Instruction code
PC
DISPLACE
8/16 bits
OP code
PC
Low Addr.
High Addr.
Seg Addr.
Instruction code
OP code
PCS
Low Addr.
High Addr.
PC PCH PCL
0000
Instruction code

 Loading...
Loading...











