14.6 Command: Fixed Waypoint
evaluated before we actually reach WP 2 which is somewhat counter-intuitive when looking at the
program sequence. If a waypoint is a stop point and followed by conditional expressions to deter-
mine the next waypoint (e.g. the I/O command) it is executed when the robot arm has stopped at
the waypoint.
MoveL
WP_I
WP_1 (blend)
WP_2 (blend)
if (digital_input[1]) then
WP_F_1
else
WP_F_2
WP_I
WP_1
WP_2
WP_F_1
WP_F_2
*
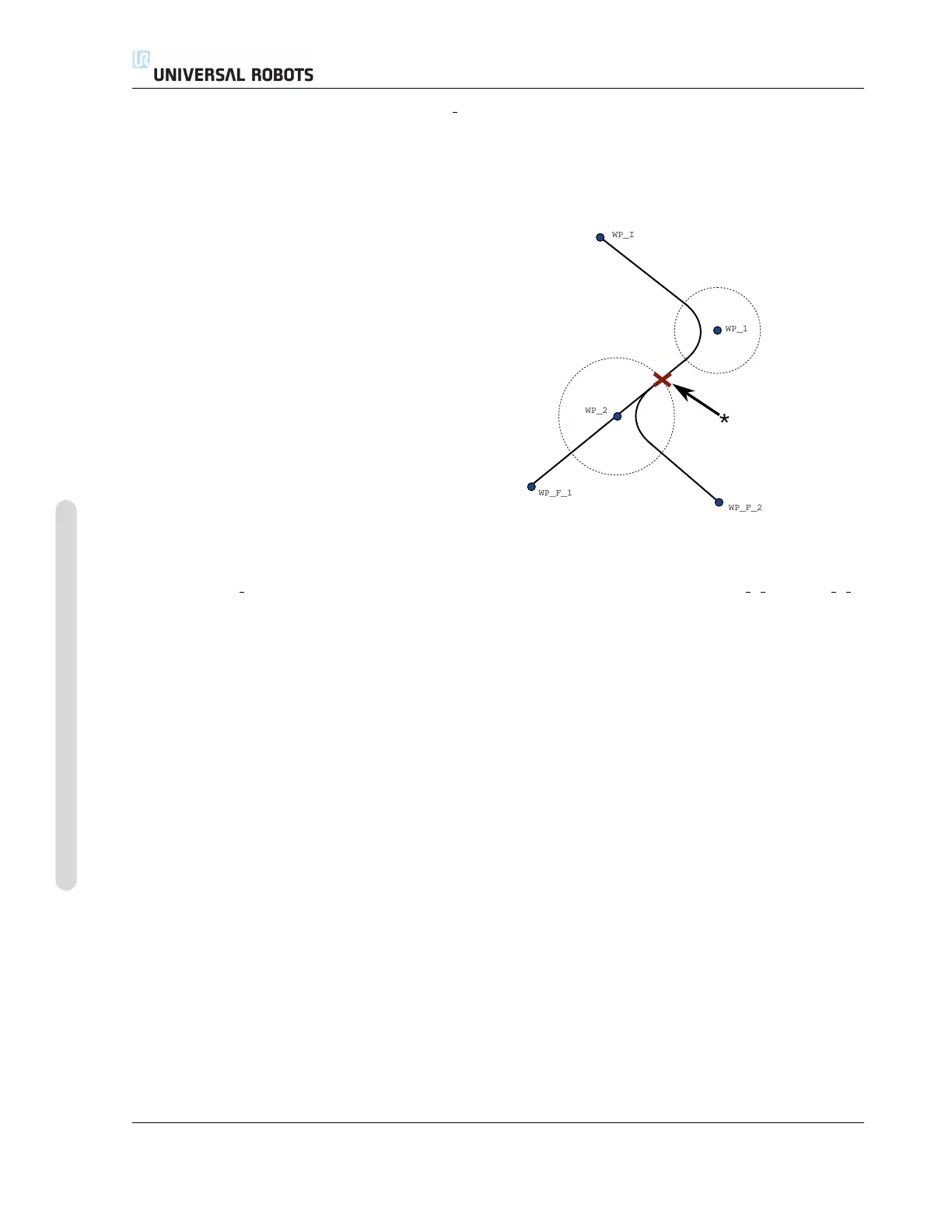
Figure 14.5: WP I is the initial waypoint and there are two potential final waypoints WP F 1 and WP F 2,
depending on a conditional expression. The conditional if expression is evaluated when the robot arm
enters the second blend (*).
Trajectory type combinations It is possible to blend between all four combinations of trajectory
types of MoveJ and MoveL, but the specific combination will affect the computed blend trajectory.
There are 4 possible combinations:
1. MoveJ to MoveJ (Pure Joint space blend)
2. MoveJ to MoveL
3. MoveL to MoveL (Pure Cartesian space blend)
4. MoveL to MoveJ
Pure joint space blending (bullet 1) vs. pure Cartesian space blending (bullet 3) is compared in
figure 14.6. It shows two potential paths of the tool for identical sets of waypoints.
Of the different combinations, bullets 2, 3 and 4 will result in trajectories that keep within the
boundaries of the original trajectory in Cartesian space. An example of a blend between different
trajectory types (bullet 2) can be seen in figure 14.7.
Pure joint space blends (bullet 1), however, may behave in a way that is less intuitive, since the
robot will try to achieve the smoothest possible trajectory in Joint space taking velocities and time
requirements into account. Due to this, they may deviate from the course specified by the way-
points. This is especially the case if there are significant differences in a joint’s velocity between the
CB3 II-80 Version 3.10
Copyright © 2009–2019 by Universal Robots A/S. All rights reserved.
 Loading...
Loading...