14.9 Command: Direction
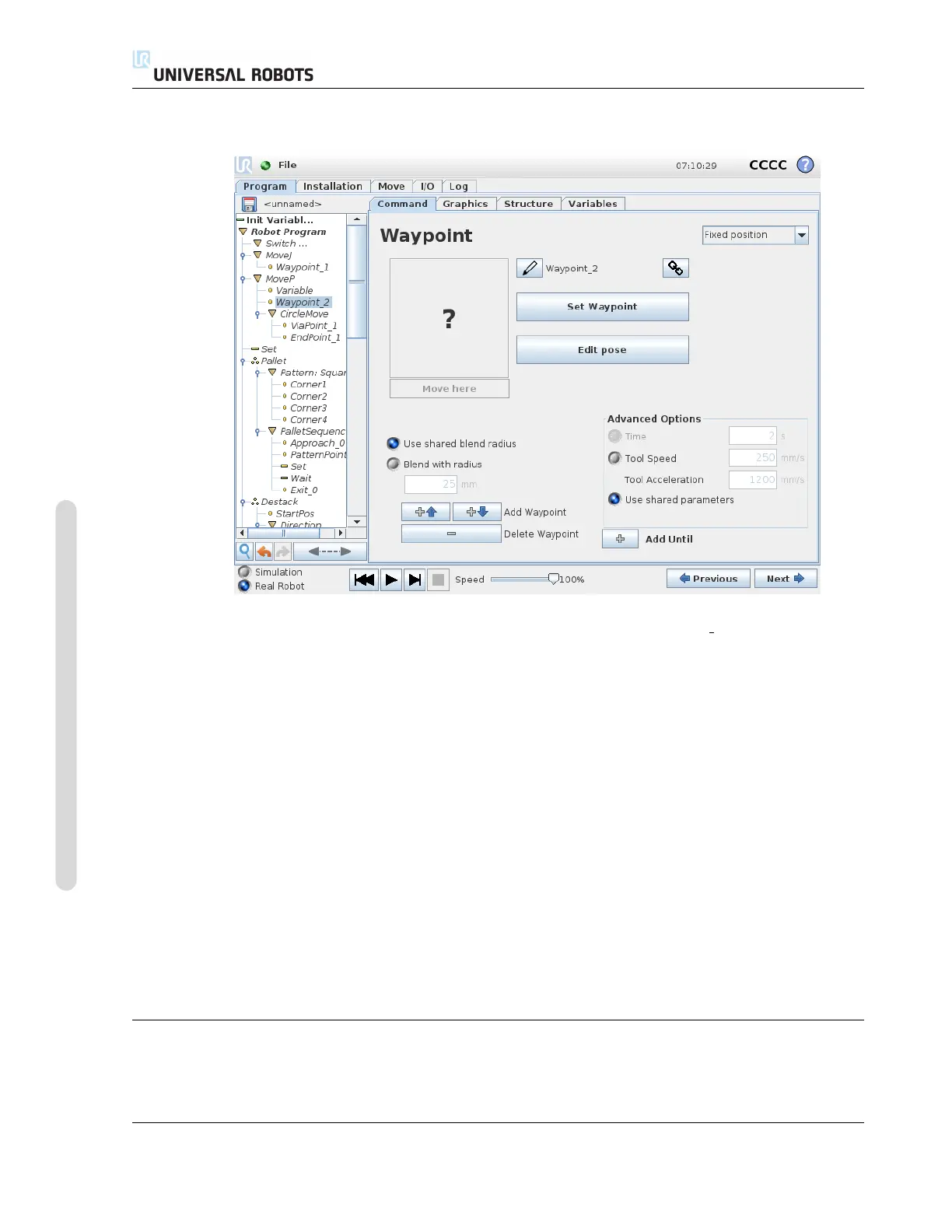
14.8 Command: Variable Waypoint
A waypoint with the position given by a variable, in this case calculated pos. The variable has
to be a pose such as
var=p[0.5,0.0,0.0,3.14,0.0,0.0]. The first three are x,y,z and the last three are the orien-
tation given as a rotation vector given by the vector rx,ry,rz. The length of the axis is the angle to be
rotated in radians, and the vector itself gives the axis about which to rotate. The position is always
given in relation to a reference frame or coordinate system, defined by the selected feature. If a
blend radius is set on a fixed waypoint and the waypoints preceding and succeeding it are variable
or if the blend radius is set on a variable waypoint, then the blend radius will not be checked for
overlap (see 14.6). If, when running the program, the blend radius overlaps a point, the robot
will ignore it and move to the next one.
For example, to move the robot 20 mm along the z-axis of the tool:
var_1=p[0,0,0.02,0,0,0]
Movel
Waypoint_1 (variable position):
Use variable=var_1, Feature=Tool
14.9 Command: Direction
The program node Direction specifies a motion relative to feature axes or TCPs. The robot moves
in along the path specified by the Direction Program Node until that movement is stopped by an
CB3 II-84 Version 3.10
Copyright © 2009–2019 by Universal Robots A/S. All rights reserved.
 Loading...
Loading...