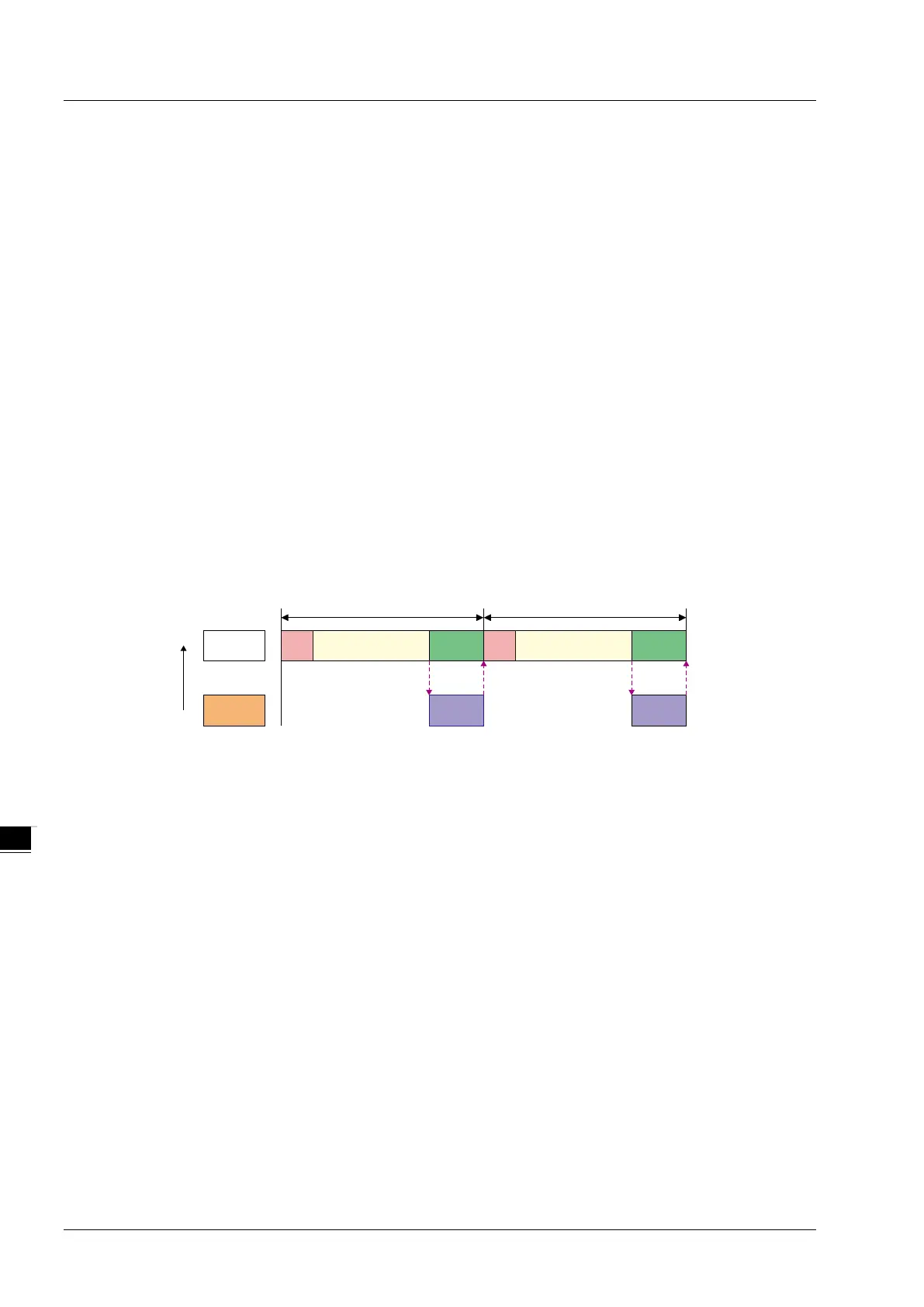DVP15MC11T Operation Manual
7.1 Tasks
Tasks are a series of functions of processing specified execution conditions and execution sequences for
I/O refresh and user program execution.
A task is defined with a name, priority level and type. Tasks can be classified into three types, the cyclic
task, freewheeling task and event-triggered task.
For every task, a group of POUs which are triggered by the task can be specified. If the task is executed
in current period, the POUs will be processed within a period of time.
The priority level and task type determine the execution sequence of the task.
A watchdog can be assigned for every task.
7.1.1 Task Types
Three task types that DVP15MC11T supports
1. Cyclic
2. Freewheeling
3. Triggered by event
Maximum 24 tasks that DVP15MC11T supports are respectively described below.
Cyclic task
The cyclic task will be executed cyclically according to the set time interval.
The way the cyclic task is executed
IO User program
Remaining
interval
Time interval b etween tasks
Cyclic
task
System
processing
Priority
High
Low
System
processing
IO User program
Remaining
interval
Time interval between tasks
System
processing
IO: IO means I/O refresh. I/O includes local I/O points and left-side and right-side extension
module data and CANopen data. The data can be specified to refresh before the set task is
executed. If not specified, the data will be refreshed during the system processing.
User Program: User Program stands for user program execution which is based on the
execution sequences of programs assigned in a task.
Remaining interval:
When the controller is to perform system processing, the low-priority task is executed first if any
and then the system processing is performed.
System processing:
The controller will perform the system processing which includes Ethernet, RS232 and RS485
communication processing after all task requests are completed.
The four terms mentioned above have the same meanings as those in the following sections.
Note: If the cycle set for a cyclic task is too short, after the user program execution is finished, the
task execution will be repeated immediately and no low-priority task or no system processing
will be executed. In this case, the execution of all tasks will be affected. If the watchdog is set for
the task, the watchdog timeout will occur, the controller will enter Error status and user program
execution will stop. If the watchdog is not set for the task, the controller will not be able to
perform system processing and the problems such as communication timeout will take place.
7-2
 Loading...
Loading...