4 OUT OF STEP PROTECTION
Out-of-Step detection is based on the speed and trajectory of measured positive sequence impedance passing
through a particular characteristic. During power system disturbances such as faults and power swings, measured
impedance moves away from normal load values. Power swings, where the system voltage angles change relative
to each other, can be either stable (recoverable) or unstable (non-recoverable). It is the unstable power swings that
result in an Out-of-Step condition.
For stable power swings the relative phase angles will oscillate, but these oscillations will fade and synchronism
between generating sources will be maintained. Detecting stable power swings is necessary to prevent unwanted
tripping of impedance measuring protection elements if the swing impedance transiently passes through the fault
impedance zone.
Unstable power swings (which can be destructive) result in sources of generation losing synchronism. This is called
pole slipping. Detecting unstable power swings allows controlled tripping to split the systems into stable areas so
that synchronism is maintained in each area. This is called Out-of-Step tripping (OOS or OST).
As well as tripping for Out-of-Step conditions, it is possible to predict OST conditions. This allows controlled tripping
and consequent splitting of the system to recover stable operation before pole slipping occurs. This is called
Predictive Out-of-Step tripping (Predictive OST).
Out-of-Step and Predictive Out-of-Step protection is based on changing impedance measurements, and uses a
pair of configurable quadrilateral characteristics in the impedance plane (Zone 5 and Zone 6).
Out of Step protection is used to split the power system into more stable areas of generation and load balance
during unstable power oscillations. The points at which the system should be split are determined by detailed
system stability studies.
4.1
OUT OF STEP DETECTION
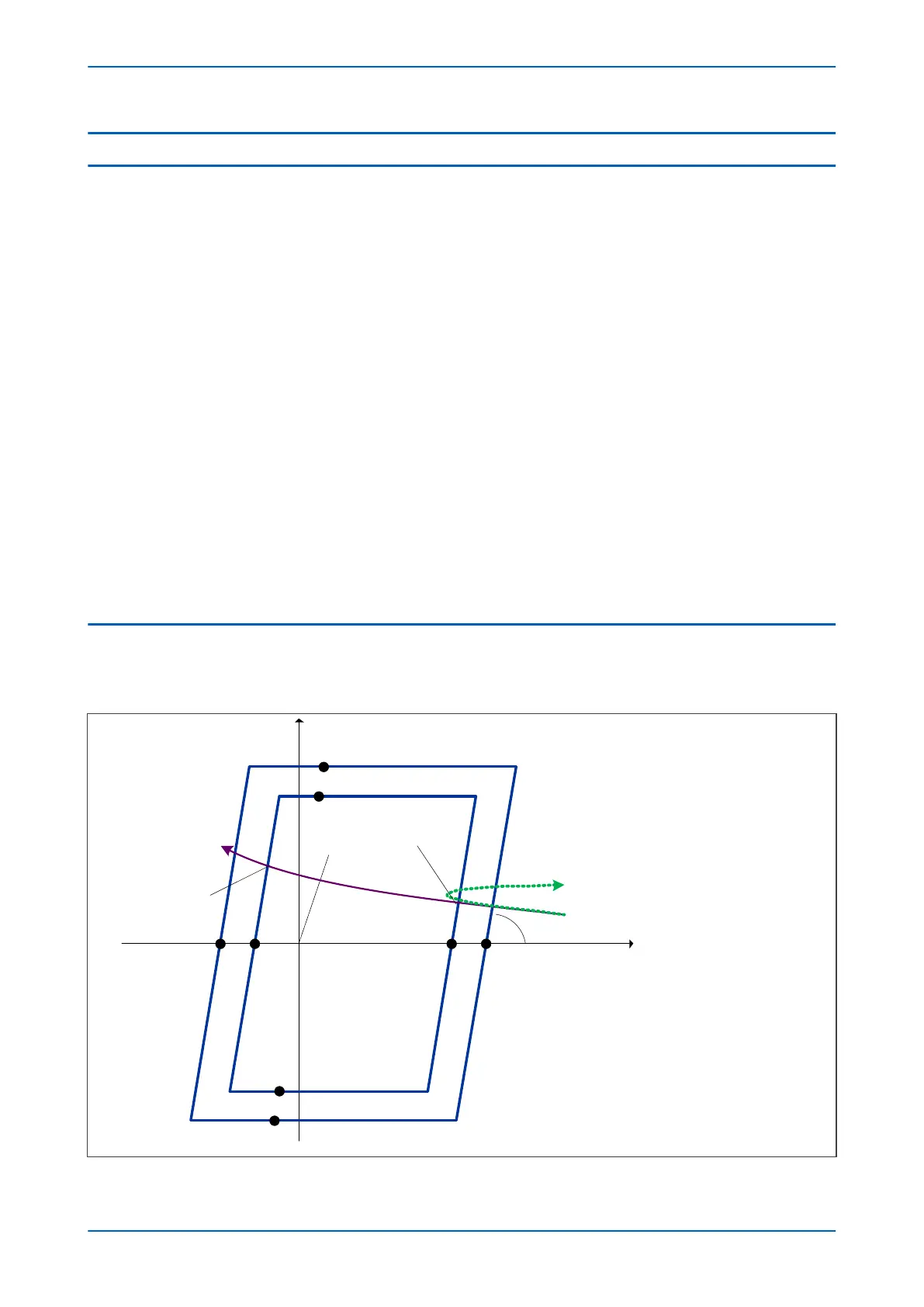
The Out of Step detection is based on the well proven ∆Z/∆t principle associated with two concentric polygon
characteristic, as shown below:
V02760
Zone 6
Zone 5
Resistive forward (+R)Resistive reverse (R’)
α
OST Z5'
OST R6
OST R5OST R5'OST R6'
+jX
ZL
OST Z6'
OST Z6
OST Z5
Recoverable swing
OST trip
Predictive OST trip
Figure 158: Out of Step detection characteristic
P543i/P545i Chapter 10 - Power Swing Functions
P54x1i-TM-EN-1 283

 Loading...
Loading...











