I/O Controller Hub 2
R
150 Intel
®
Pentium
®
4 Processor / Intel
®
850 Chipset Family Platform Design Guide
9.6 SMBus/SMLink Interface
The SMBus interface on the ICH2 is the same as that on the ICH2. It uses two signals SMBCLK
and SMBDATA to send and receive data from components residing on the bus. These signals are
used exclusively by the SMBus Host Controller. The SMBus Host Controller resides inside the
ICH2. If the SMBus is used only for the RAMBUS SPD EEPROMs (one on each RIMM
connector), both signals should be pulled up with a 4.7 kΩ resistor to 3.3 V.
The ICH2 incorporates a new SMLink interface supporting AOL*, AOL2* and a slave
functionality. It uses two signals SMLINK[1:0]. SMLINK[0] corresponds to an SMBus clock
signal and SMLINK[1] corresponds to an SMBus data signal. Internally the SMLINK signals are
connected to the following:
• ICH2 Slave Interface
• ICH2 TCO Host Controller
• ICH2 Integrated LAN Slave Interface
For Alert on LAN* (AOL*) functionality, the TCO Host Controller transmits heartbeat and event
messages over the interface. When using the 82562EM LAN Connect Component, the ICH2’s
integrated LAN Controller will claim the SMLink heartbeat and event messages and send them out
over the network. An external, AOL2-enabled LAN Controller (i.e., 82550) will connect to the
SMLink signals to receive heartbeat and event messages, as well as access the ICH2 SMBus Slave
Interface. The slave interface function allows an external microcontroller to perform various
functions. For example, the slave write interface can reset or wake a system, generate SMI# or
interrupts, and send a message. The slave read interface can read the system power state, read the
watchdog timer status, and read system status bits.
Both the SMBus Host Controller and the TCO Host Controller obey the SMBus protocol, so the
two interfaces can be externally wire-OR’d together to allow an external management ASIC
(e.g., 82550) to access targets on the SMBus as well as the ICH2 Slave interface. This is done by
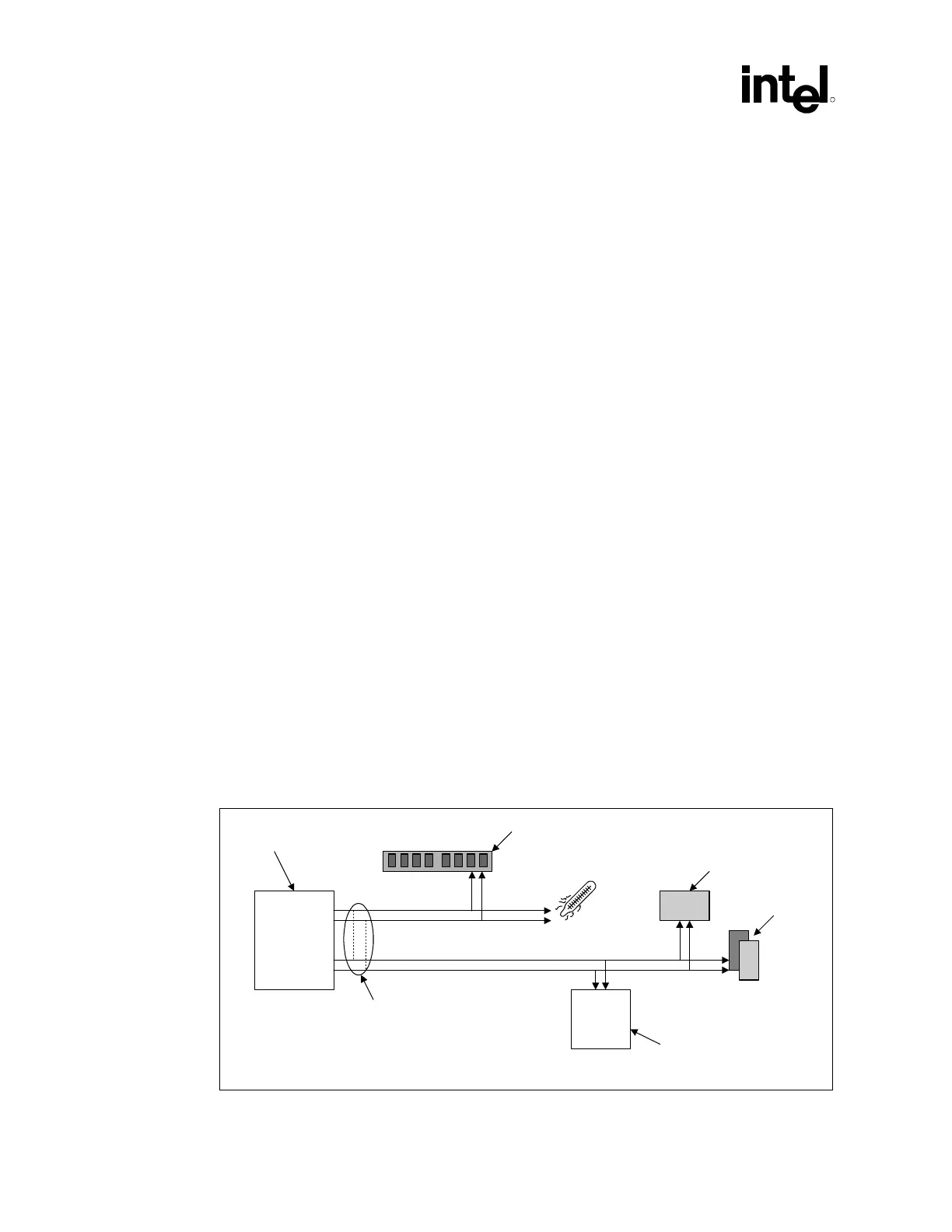
connecting SMLink[0] to SMBCLK and SMLink[1] to SMBDATA. See Figure 105.
Figure 105. SMBUS/SMLink Interface
ICH2
Host controller and
slave interface
SMBus
SMBCLK
SPD data
Temperature on
thermal sensor
Network
interface
card on PCI
Microcontroller
82850
Motherboard
LAN controller
Wire OR
(optional)
SMLink0
SMLink1
SMLink
SMBDATA
SMbus-SMlink_IF

 Loading...
Loading...











