Power Distribution Guidelines
R
230 Intel
®
Pentium
®
4 Processor / Intel
®
850 Chipset Family Platform Design Guide
12.2.1 ACPI Hardware Model
The Intel 850 chipset-based desktop supports both legacy and ACPI operations, which involves
sequencing the platform between the various global system states (G0–G3). Figure 171 depicts
global states and the transitions. For complete detail of the mechanisms involved in transition from
any of the global states refer to the ACPI Interface Specification 1.0a, Section 4.5.
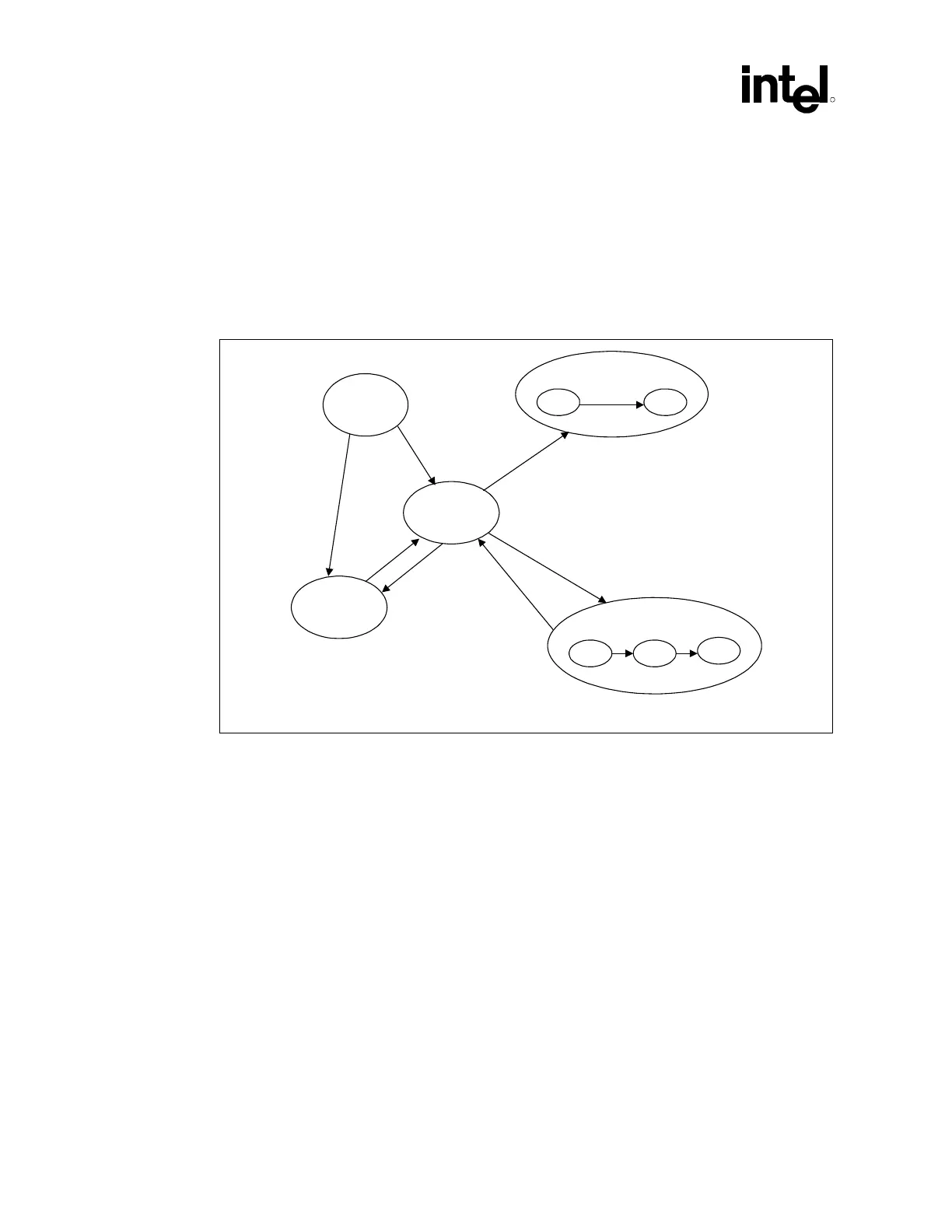
Figure 171. Global System Power States and Transition
PWR_Global_State_Trans
Processor Power State
C1 C2
G3-Mech
Off
G0(S0,C0)-
Working
G2(S5)-
Soft Off
G1 (Sleep State)
S3
S4
S1
12.2.2 Thermal Design Power
The thermal design power numbers are estimation of the maximum expected power generated by a
component in a realistic application. It is based on extrapolations in both hardware and software
technology over the product life. It does not represent the expected power generated by a power
virus. The ICC max sustained (WCRA) numbers are estimation of the maximum expected current
generated within a die section in a realistic application such as an application that executes
extensive memory reads/writes.
Refer to the Intel
850 Chipset: Thermal Considerations Application Note (AP-720) and the Intel
®
850 Chipset: 82850 Memory Controller Hub (MCH) Datasheet for additional thermal package
characteristics.

 Loading...
Loading...











