8 EtherCAT Communications
8 - 2
NX-series EtherCAT Coupler Unit User’s Manual (W519)
8-1 Structure of CAN Application Proto-
col over EtherCAT (CoE)
EtherCAT allows the use of multiple protocols for communications. However, the EtherCAT Slave Ter-
minal uses the CAN application protocol over EtherCAT (CoE) as the device profile for the CAN appli-
cation protocol. The CoE is a communications interface that is designed to provide compatibility with
EtherCAT devices. The CAN application protocol is an open network standard.
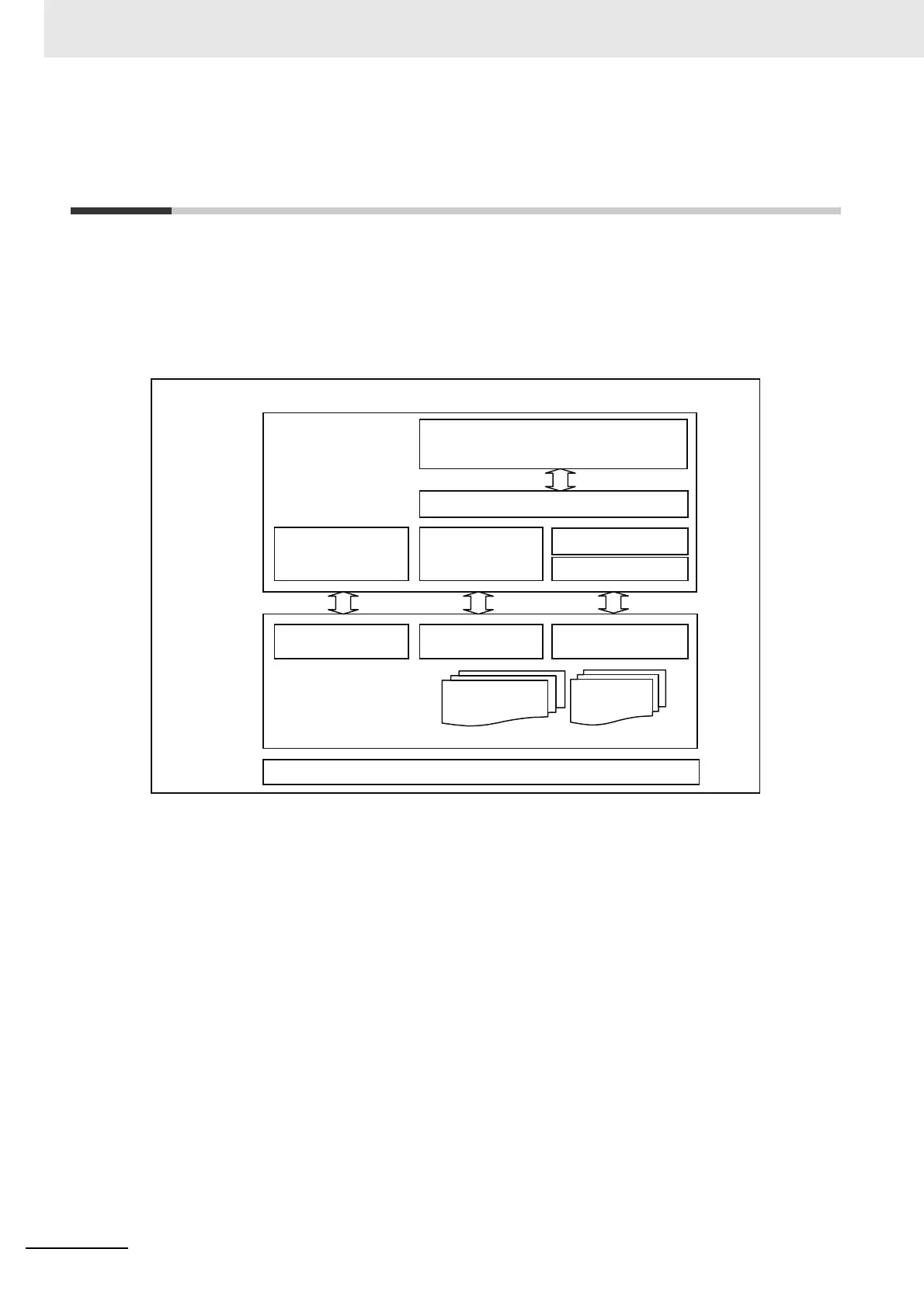
The following figure shows how the CoE is structured for an EtherCAT Coupler Unit.
The object dictionary for the CAN application protocol is broadly divided into PDOs (process data
objects) and SDOs (service data objects).
PDOs are contained in the object dictionary. The PDOs can be mapped in the object dictionary. The
process data is defined by the PDO mappings. PDOs are used in PDO communications for periodic
exchange of process data.
SDOs are the objects that can be read and written. SDOs are used in non-periodic SDO communica-
tions (event-driven message communications).
If you use the CoE interface to set the object dictionary for PDOs and SDOs, you can provide EtherCAT
devices with the same device profiles as the CAN application protocol.
EtherCAT Coupler Unit
EtherCAT physical layer
SDO (mailbox)
NX Unit application
Object dictionary
PDO mappings
PDO communications (cyclic)
EtherCAT data link layer
Registers
Mailbox
Process data
FMMUSyncManager
Application layer
Transitions of
communications
states

 Loading...
Loading...











