RL78/G13 CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
R01UH0146EJ0100 Rev.1.00 121
Sep 22, 2011
3.1.6 Data memory addressing
Addressing refers to the method of specifying the address of the instruction to be executed next or the address of the
register or memory relevant to the execution of instructions.
Several addressing modes are provided for addressing the memory relevant to the execution of instructions for the
RL78/G13, based on operability and other considerations. For areas containing data memory in particular, special
addressing methods designed for the functions of the special function registers (SFR) and general-purpose registers are
available for use. Figures 3-12 to 3-21 show correspondence between data memory and addressing. For details of each
addressing, see 3.4 Addressing for Processing Data Addresses.
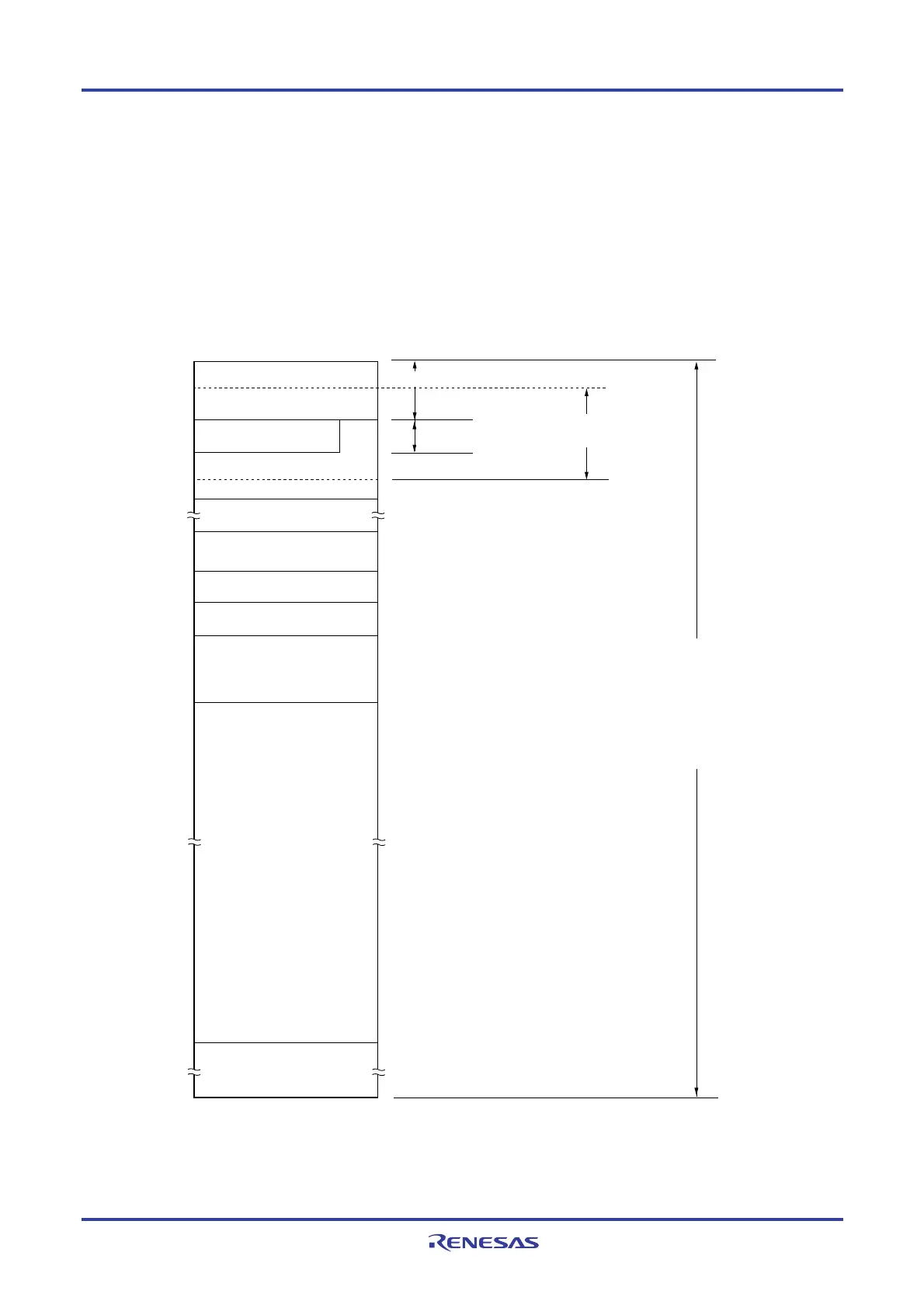
Figure 3-12. Correspondence Between Data Memory and Addressing (R5F100xA, R5F101xA(x = 6 to 8, A to C, E to G))
Special function register (SFR)
256 bytes
General-purpose register
32 bytes
RAM
2 KB
Reserved
Special function register (2nd SFR)
2 KB
Reserved
Code flash memory
16 KB
00000H
EFFFFH
F0000H
F0FFFH
F1000H
Data flash memory
Note
4 KB
F1FFFH
F2000H
FF6FFH
FF700H
FFEDFH
FFEE0H
FFEFFH
FFF00H
FFFFFH
03FFFH
04000H
F07FFH
F0800H
Direct addressing
Register indirect addressing
Based addressing
Based indexed addressing
Short direct
addressing
SFR addressing
Register addressing
FFE1FH
FFE20H
FFF1FH
FFF20H
Mirror
8 KB
F3FFFH
F4000H
Reserved
Note R5F100xA only.
Caution When executing instructions from the RAM area while RAM parity error resets are enabled (RPERDIS
= 1), be sure to initialize the used RAM area + 10 bytes.
<R>

 Loading...
Loading...











