Web-based Configuration Guide 1 Network Settings
44
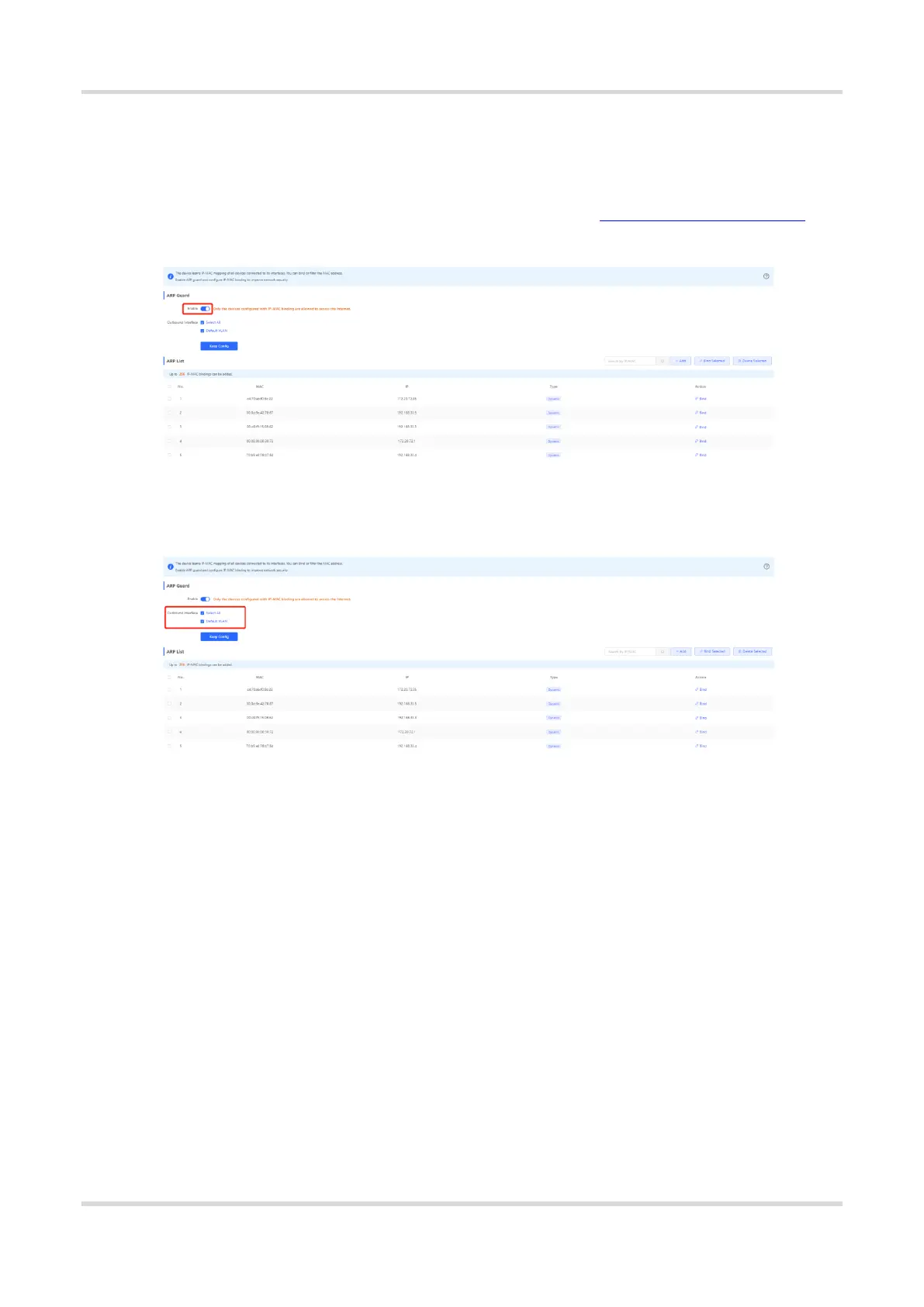
3.4.3 Configuring ARP Guard
After ARP guard is enabled, only devices configured with IP-MAC binding on the LAN are allowed to access the
external network.
Before enabling ARP guard, configure ARP binding. For specific steps, see 3.11.2 Configuring ARP Binding.
(1) Enable ARP guard.
(2) Select an effective port.
If you select Select All, the configuration will take effect on all clients on the LAN. If you select a specified
port, the configuration will take effect only on clients connected to the port.
3.5 Configuring VLAN
3.5.1 VLAN Overview
Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) is a communication technology that divides a physical LAN into multiple logical
broadcast domains. Each VLAN has independent broadcast domains. Hosts in the same VLAN can directly
communicate with each other, while hosts in different VLANs cannot as they are isolated at Layer 2. Compared
with traditional Ethernet, VLAN has the following advantages:
Control broadcast storms: Broadcast packets can only be forwarded inside a VLAN. This saves bandwidth as
the performance of a VLAN is not affected by broadcast storms of other VLANs.
Enhance LAN security: As a VLAN is divided into multiple broadcast domains, packets of different VLANs in a
LAN are isolated. Different VLAN users cannot directly communicate, enhancing network security.
Simplify network management: The VLAN technology can be used to divide the same physical network into
different logical networks. When the network topology changes, you only need to modify the VLAN
configuration, simplifying network management.

 Loading...
Loading...








