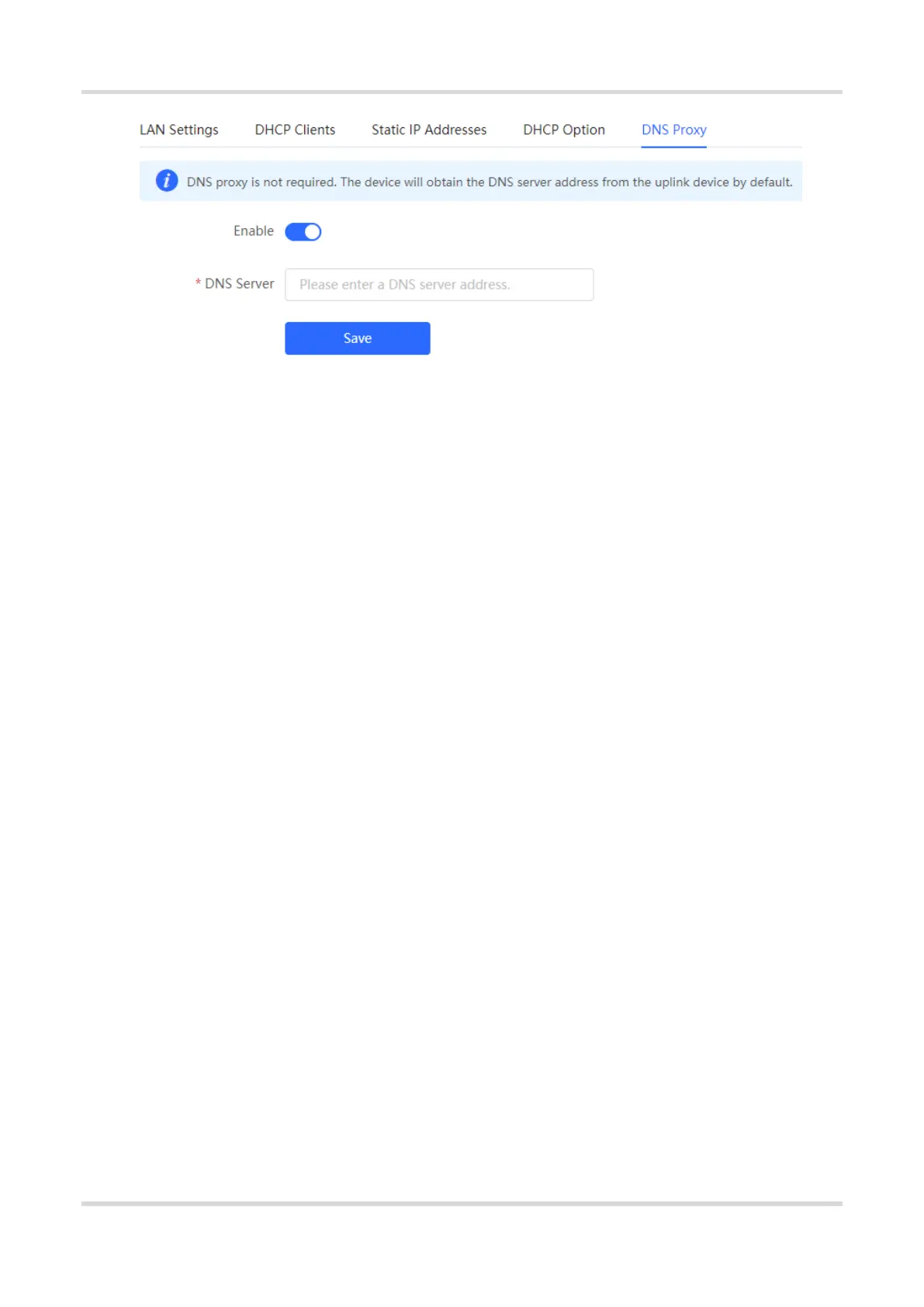
Web-based Configuration Guide 1 Network Settings
48
3.7 Configuring IPv6
3.7.1 IPv6 Overview
Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6) is the next-generation IP protocol designed by Internet Engineering Task Force
(IETF) to substitute IPv4. It is used to compensate insufficient IPv4 network addresses.
3.7.2 IPv6 Basics
1. IPv6 Address Format
IPv6 extends 32-bit IPv4 address into 128 bits, providing wider address space than IPv4.
The basic format of an IPv6 address is X:X:X:X:X:X:X:X. It is represented as eight groups of four hexadecimal
digits (0-9, A-F), each group representing16 bits. The groups are separated by colons (:). In this format, each X
represents a group of four hexadecimal digits.
Samples of IPv6 addresses are 2001:ABCD:1234:5678:AAAA:BBBB:1200:2100, 800:0:0:0:0:0:0:1, and
1080:0:0:0:8:800:200C:417A.
The digit 0 in an IPv6 address can be suppressed as follows:
Leading zeros in each 16-bit field are suppressed. For example, 2001:00CD:0034:0078:000A:000B:1200:2100
can be suppressed to 2001:CD:34:78:A:B:1200:2100.
The long sequence of consecutive all-zero fields in some IPv6 addresses can be replaced with two colons (::).
For example, 800:0:0:0:0:0:0:1 can be represented as 800::1. The two colons (::) can be used only when all
the 16 bits in a group are 0s, and it can appear only once in an IPv6 address.
2. IPv6 Prefix
IPv6 addresses are typically composed of two logical parts:
Network prefix: n bits, corresponding to the network ID in IPv4 addresses
interface ID: (128 – n) bits, corresponding to the host ID in IPv4 addresses
A slash (/) is used to separate the length of network prefix from an IPv6 address. For example,
12AB::CD30:0:0:0:0/60 indicates that the 60-bit network prefix in the address is used for route selection. IPv6
prefixes can be obtained from the IPv6 DHCP server, along with IPv6 addresses. A downlink DHCP server can
also automatically obtain IPv6 prefixes from its uplink DHCP server.

 Loading...
Loading...








