EM–4
2GR-FE ENGINE MECHANICAL – ENGINE
EM
(h) Install the 6 ignition coils.
Torque: 10 N*m (102 kgf*cm, 7 ft.*lbf)
(i) Install the intake air surge tank. (See page FU-17).
10. INSPECT CO/HC
(a) Start the engine.
(b) Run the engine at 2,500 rpm for approximately 180
seconds.
(c) Insert the CO/HC meter testing probe at least 40 cm
(1.3 ft) into the tailpipe during idling.
(d) Check CO/HC concentration at idle and/or 2,500
rpm.
HINT:
Check regulations and restrictions in your area
when performing 2 mode CO/HC concentration
testing (engine check at both idle speed and at
2,500 rpm).
If the CO/HC concentration does not comply with
regulations, perform troubleshooting in the order
given below.
(1) Check A/F sensor and heated oxygen sensor
operation.
(2) See the table below for possible causes, and
then inspect and repair.
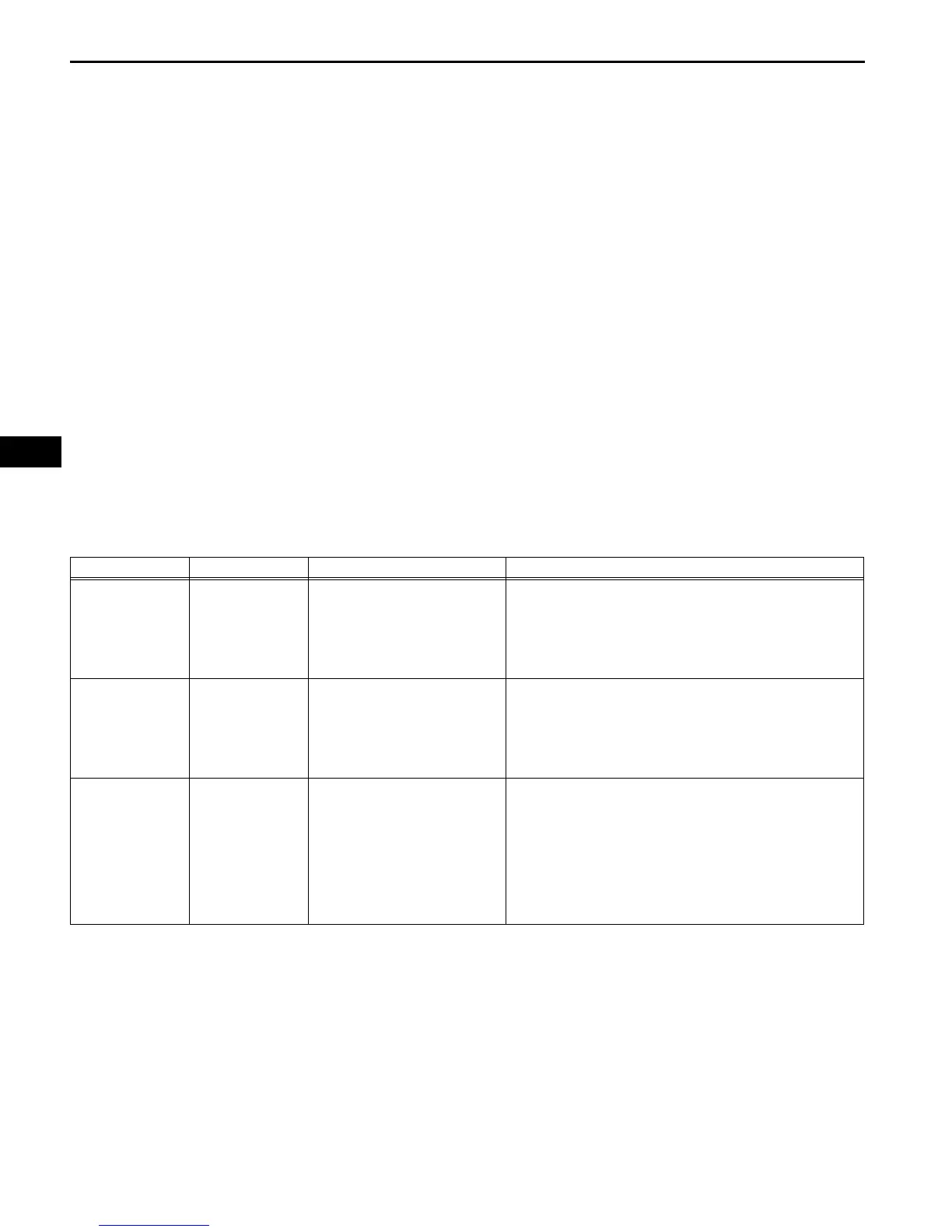
CO HC Problems Causes
Normal High Rough idle
1. Faulty ignitions:
– Incorrect timing
– Fouled, shorted or improperly gapped plugs
2. Incorrect valve clearance
3. Leaks in intake and exhaust valves
4. Leaks in cylinders
Low High
Rough idle
(fluctuating HC reading)
1. Vacuum leaks:
– PCV hoses
– Intake manifold
– Throttle body
– Brake booster line
2. Lean mixture causing misfire
High High
Rough idle
(black smoke from exhaust)
1. Restricted air filter
2. Plugged PCV valve
3. Faulty SFI system:
– Faulty fuel pressure regulator
– Defective ECT sensor
– Defective MAF meter
–Faulty ECM
– Faulty injectors
– Faulty throttle position sensor

 Loading...
Loading...