MB95630H Series
MN702-00009-2v0-E FUJITSU SEMICONDUCTOR LIMITED 461
CHAPTER 22 UART/SIO
22.5 Interrupts
22.5 Interrupts
The UART/SIO has six interrupt-related bits: receive error flag bits (PER, OVE,
FER), receive data register full flag bit (RDRF), transmit data register empty flag
bit (TDRE), and transmission completion flag bit (TCPL).
■ Interrupts of UART/SIO
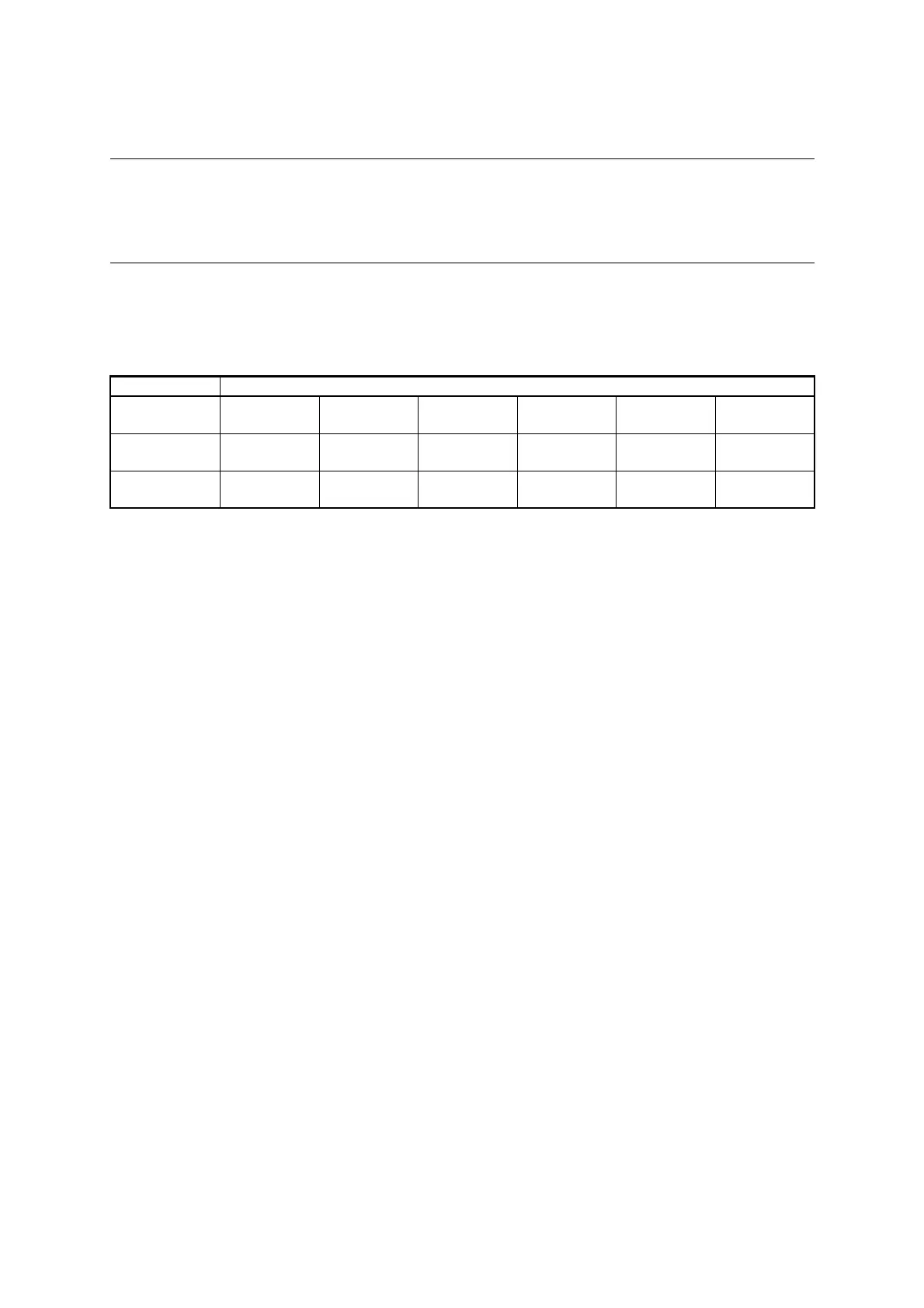
Table 22.5-1 lists the UART/SIO interrupt control bits and interrupt sources.
■ Transmit Interrupt
When transmit data is written to the UART/SIO serial output data register ch. n (TDRn), the
data is transferred to the transmission shift register. When the next piece of data can be written,
the TDRE bit is set to "1". At this time, an interrupt request to the interrupt controller occurs
when transmit data register empty interrupt enable bit has been enabled (SMC2n:TEIE = 1).
The TCPL bit is set to "1" upon completion of transmission of all pieces of transmit data. At
this time, an interrupt request to the interrupt controller occurs when transmission completion
interrupt enable bit has been enabled (SMC2n:TCIE = 1).
■ Receive Interrupt
If the data is input successfully up to the stop bit, the RDRF bit is set to "1". If an overrun
error, a parity error, or a framing error occurs, the corresponding error flag bit (PER, OVE, or
FER) is set to "1".
These bits are set when a stop bit is detected. If receive interrupt enable bit has been enabled
(SMC2n:RIE = 1), an interrupt request to the interrupt controller will be generated.
Table 22.5-1 UART/SIO Interrupt Control Bits and Interrupt Sources
Item Description
Interrupt request
flag bit
SSRn:TDRE SSRn:TCPL SSRn:RDRF SSRn:PER SSRn:OVE SSRn:FER
Interrupt request
enable bit
SMC2n:TEIE SMC2n:TCIE SMC2n:RIE SMC2n:RIE SMC2n:RIE SMC2n:RIE
Interrupt source
Transmit data
register empty
Transmission
completion
Receive data full Parity error Overrun error Framing error
 Loading...
Loading...