6.12 COPROCESSOR BOARD
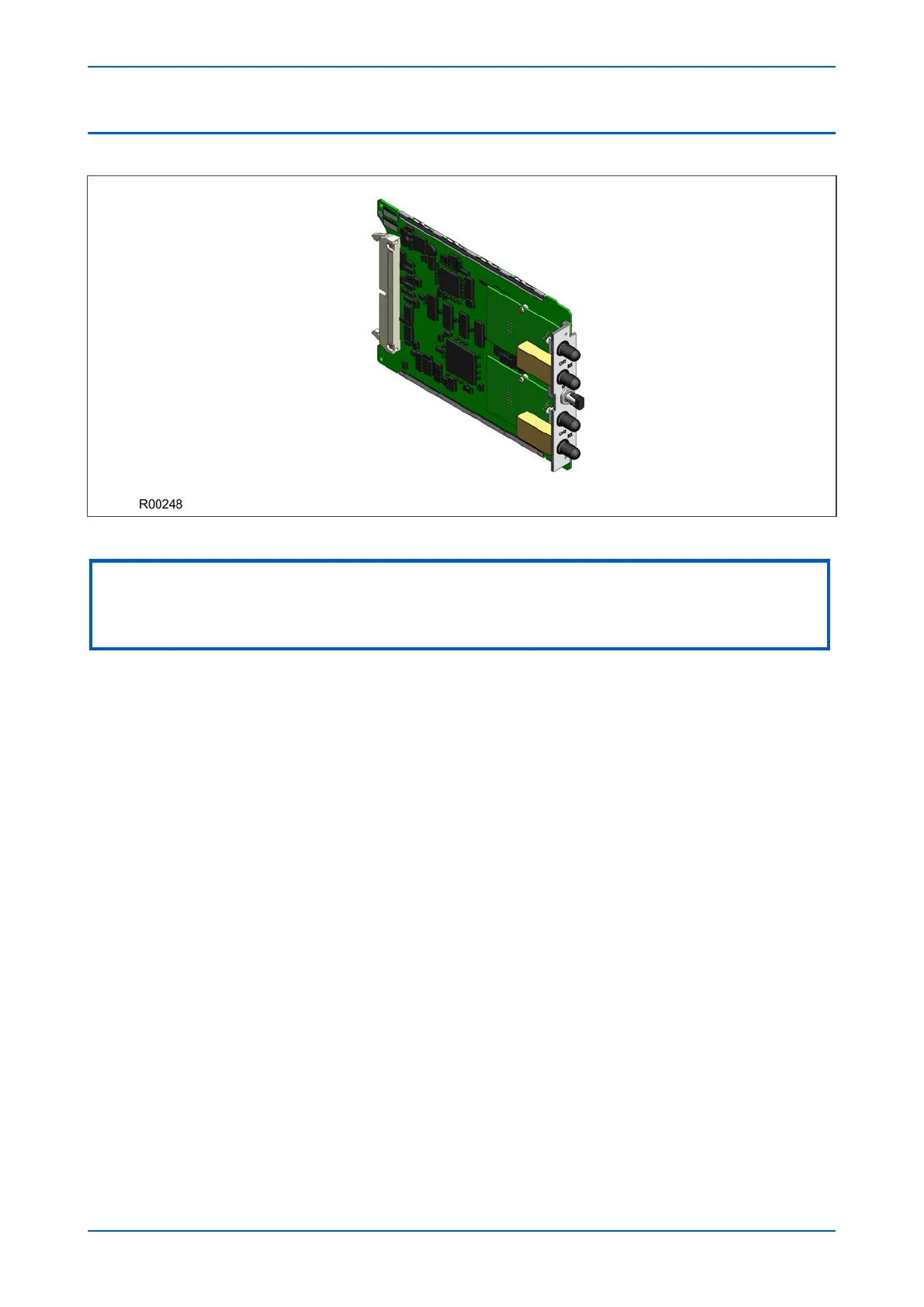
Figure 26: Fully populated Coprocessor board
Not
e:
The above figure shows a coprocessor complete with GPS input and 2 fibre-optic serial data interfaces, and is not necessarily
representative of the product and model described in this manual. These interfaces will not be present on boards that do not
require them.
Where applicable, a second processor board is used to process the special algorithms associated with the device.
This second pr
ocessor board provides fast access (zero wait state) SRAM for use with both program and data
memory storage. This memory can be accessed by the main processor board via the parallel bus. This is how the
software is transferred from the flash memory on the main processor board to the coprocessor board on power
up. Further communication between the two processor boards is achieved via interrupts and the shared SRAM.
The serial bus carrying the sample data is also connected to the co-processor board, using the processor’s built-in
serial port, as on the main processor board.
There are several different variants of this board, which can be chosen depending on the exact device and model.
The variants are:
● Coprocessor board with current differential inputs and GPS input
● Coprocessor board with current differential inputs only
● Coprocessor board with GPS input only
6.12.1 CURRENT DIFFERENTIAL INPUTS
Where applicable, the coprocessor board can be equipped with up to two daughter boards, each containing a
fibr
e-optic interface for a serial data link. BFOC 2.5 ST connectors are used for this purpose. One or two channels
are provided, each channel comprising a fibre pair for transmitting and receiving (Rx Tx). These channels are
labelled Ch1 and Ch2. These serial data links are used to transfer information between two or three IEDs for
current differential applications.
6.12.2 COPROCESSOR BOARD WITH 1PPS INPUT
In some applications, where the communication links between two remote devices are provided by a third party
telecommunications par
tner, the transmit and receive paths associated with one channel may differ considerably
in length, resulting in very different transmission and receive times.
Chapter 3 - Hardware Design P54A/B/C/E
58 P54xMED-TM-EN-1
 Loading...
Loading...