4.3.4.3 Call Forwarding (CF)—by QSIG
Description
The PBX forwards the call to a destination extension in another PBX in QSIG network. The destination can be
set on your own PBX on an extension basis as the forward destination of trunk calls (® 2.3.2 Call Forwarding
(FWD)).
If the same trunk group is used for the incoming call and the forwarded call, the following situation will be
possible.
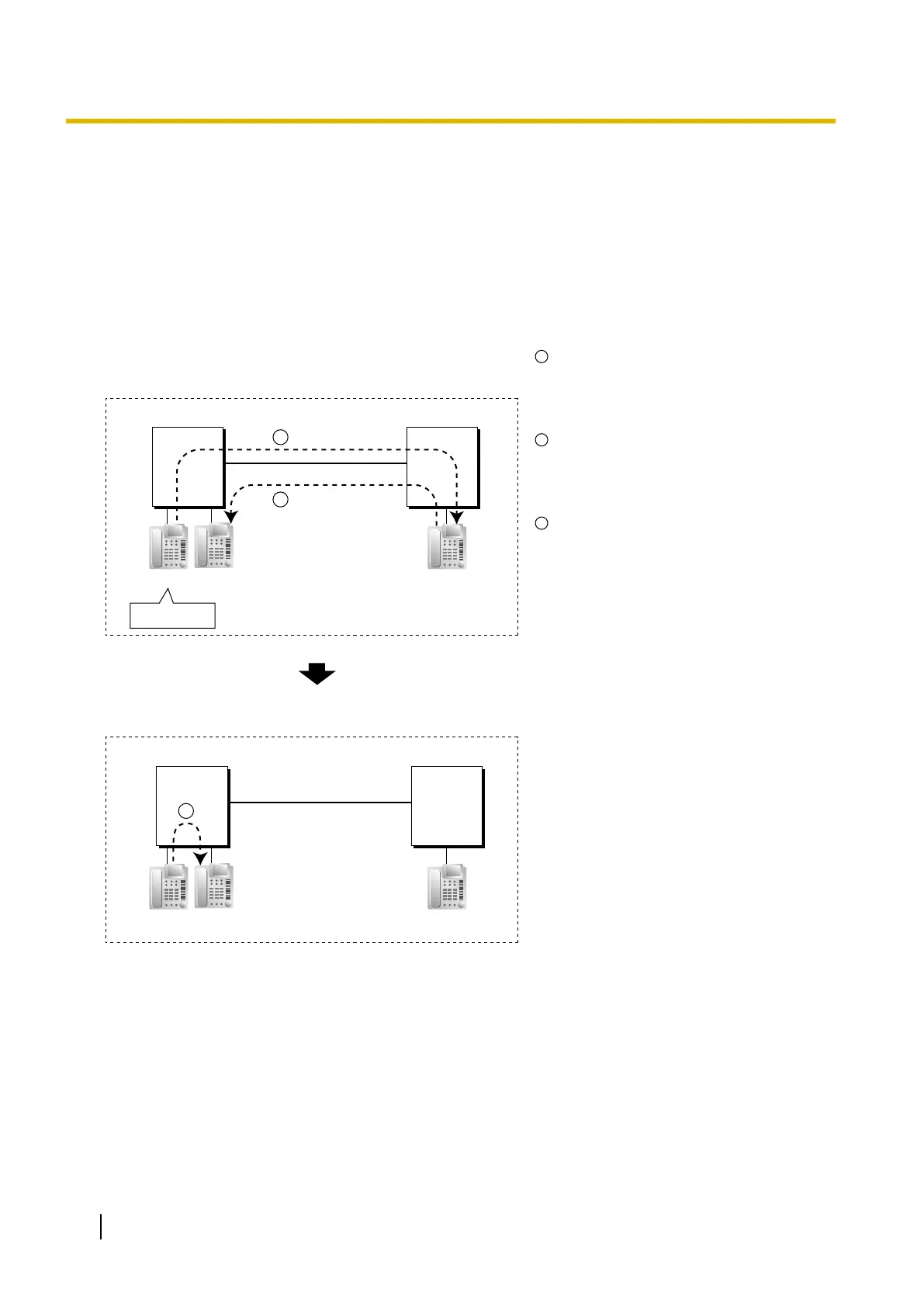
[Example]
PBX-1
QSIG
PBX-2
Dials "2000".
PBX-1
QSIG
PBX-2
Extn. 1001 Extn. 2000
Extn. 1001 Extn. 2000
(Forward Destination
of Trunk Calls: 1001)
Call to 2000
1
Forwarded
to 1001
2
3
Extn. 1000
Extn. 1000
Extension 1000 of PBX-1 dials
extension number
"2000", and the call
is sent to extension "2000" of PBX-2
through QSIG network.
The call is forwarded to the forward
destination of trunk calls of extension
2000, which is extension
"1001" of
PBX-1.
The call between PBX-1 and PBX-2 is
released, and the call is connected
directly to the forward destination of
extension 2000.
Conditions
• This feature complies with European Telecommunication Standard
(ETS) specification ETS 300 257,
Diversion supplementary services.
• This feature can be enabled or disabled on each ISDN (QSIG) port of the PBX.
442 Feature Guide
4.3.4 QSIG Standard Features

 Loading...
Loading...

















