User's Manual 574 Document #: LTRT-27045
Mediant 1000B Gateway & E-SBC
languages such as German. An example of such a character is the umlaut (or diaeresis),
which consists of two dots placed over a letter, as in ä. The importance of this conversion
feature is that it allows PSTN entities that do not support accented characters, to receive
ASCII characters. For example, the device can convert the Unicode character ä into the
ASCII character "ae".
Note:
The table works in conjunction with the ISO8859CharacterSet parameter.
When the parameter is set to [0] (Latin only), it converts accented characters into
ASCII (e.g., ä to "a"). However, the table can be used to overwrite these "basic"
conversions and customize them (e.g., ä to "ae" instead of the default "a").
The following procedure describes how to configure Character Conversion rules through
the Web interface. You can also configure it through ini file (CharConversion) or CLI
(configure voip > gateway dtmf-supp-service dtmf-and-dialing > char-conversion).
To configure a Character Conversion rule:
1. Open the Char Conversion table (Setup menu > Signaling & Media tab > Gateway
folder > DTMF & Supplementary > Char Conversion).
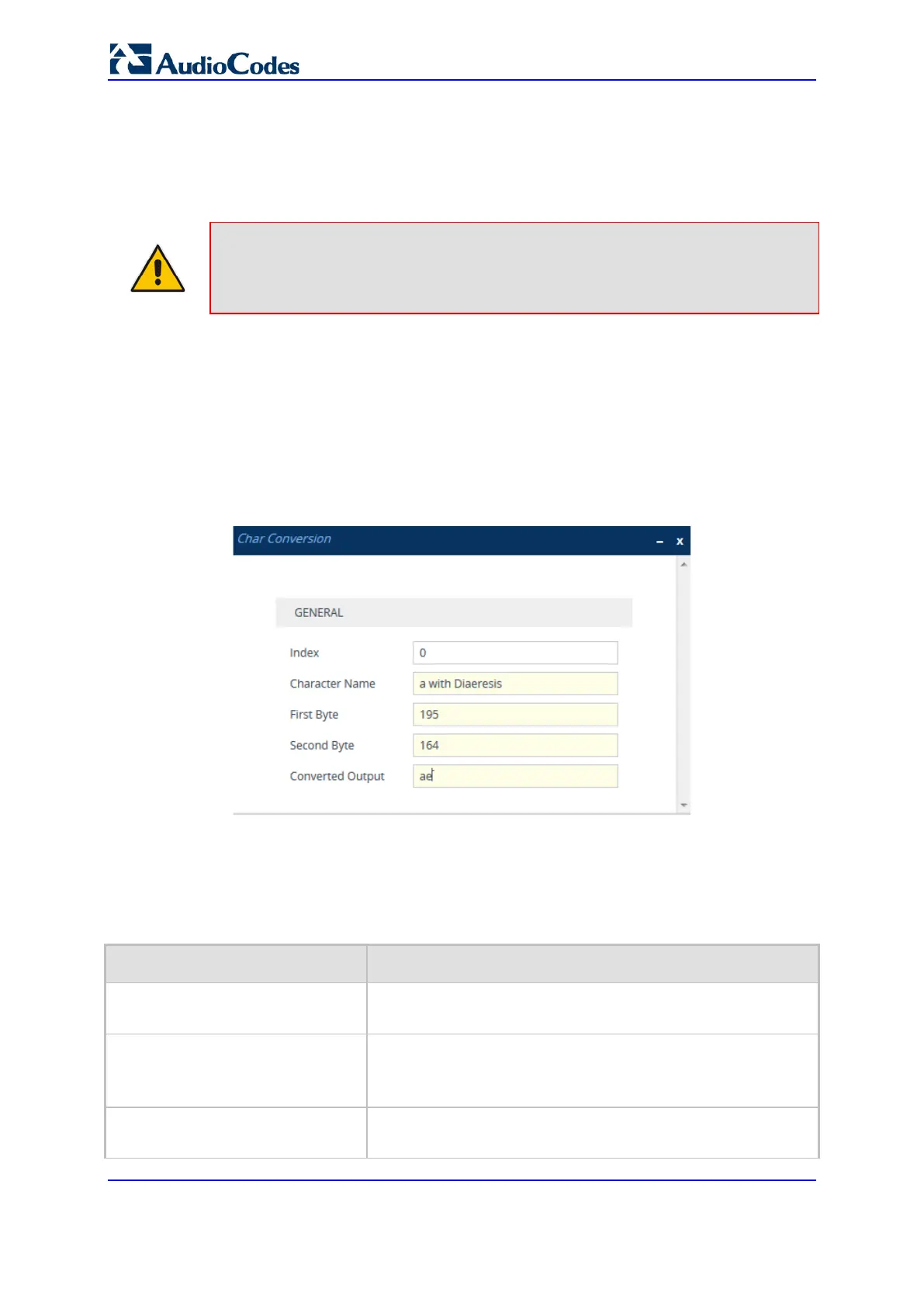
2. Click New; the following dialog box appears:
Figure 26-17: Char Conversion Table - Add Dialog Box
The figure above shows a configuration example where ä is converted to ae.
3. Configure a Character Conversion rule according to the parameters described in the
table below.
4. Click Apply.
Table 26-8: Char Conversion Table Parameter Descriptions
Parameter Description
Index
[CharConversion_Index]
Defines an index number for the new table row.
Note: Each row must be configured with a unique index.
Character Name
char-name
[CharConversion_CharName]
Defines an arbitrary name to easily identify the row.
The valid value is a string of up to 40 characters.
Note: Each row must be configured with a unique name.
First Byte
first-byte
Defines the first byte of the Unicode character (e.g., 195).
The default is 194.

 Loading...
Loading...



















