325
E.g. 5 Solving a simultaneous integration
A continuous random variable X, has a probability
distribution function given by:
()
2
14
9
0
abxx
for x
fx
elsewhere
++
≤
=
Given that
()
5
2
27
Px≤=
, find the values of a and b.
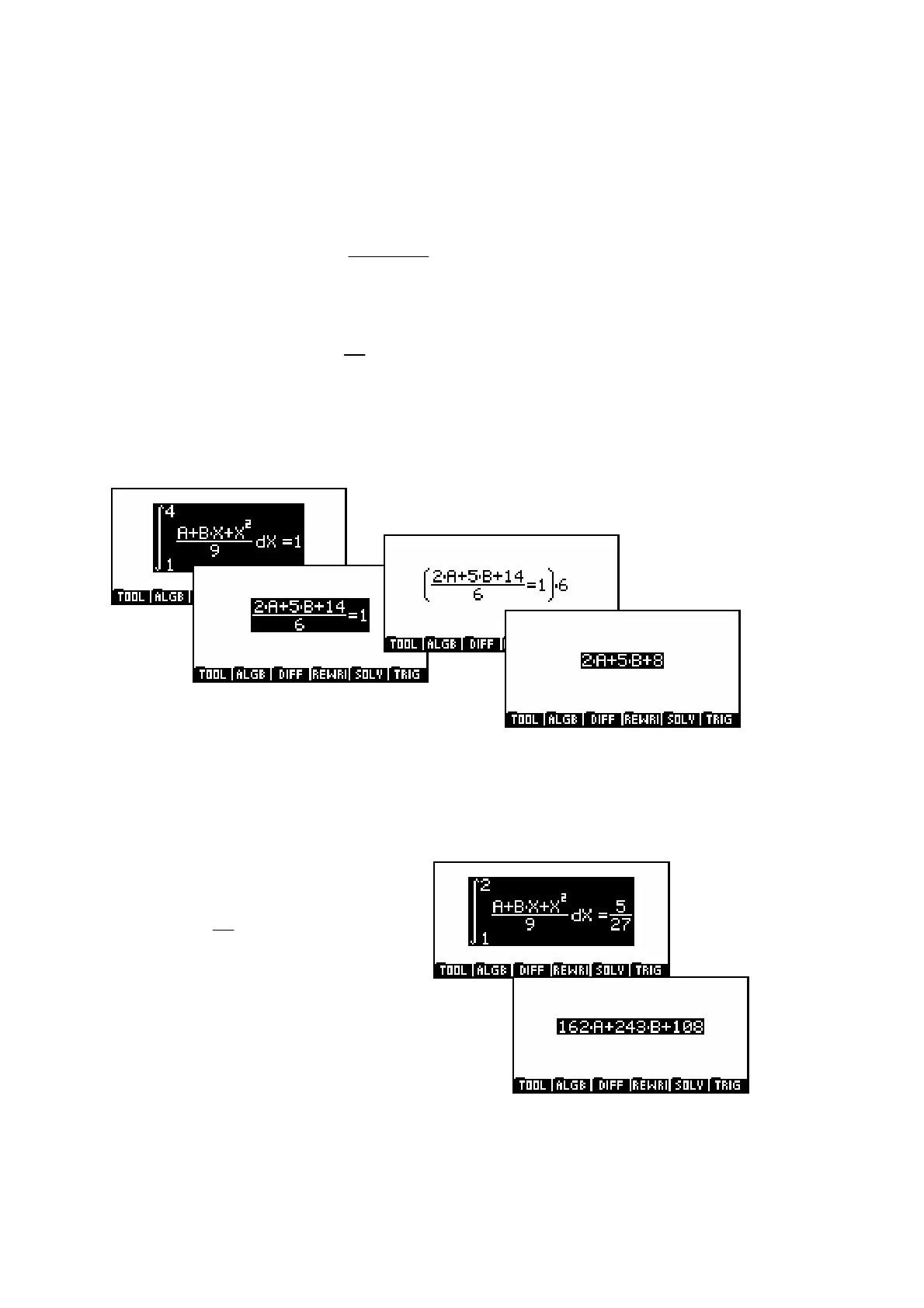
From the fact that it is a p.d.f. we know that
()
4
1
1
xdx
∫
. We can use this to
get the first expression in terms of a and b.
As can be seen above, the initial integration gives an equation involving a
fraction. This can be simplified by multiplying both sides by 6, highlighting the
entire equation first. Notice that when the final simplification is equal to zero,
the calculator does not bother to include the ‘=0’.
The second probability tells us that
()
2
1
5
27
fxdx=
∫
and this gives the
second of the pair of simultaneous
equations in exactly the same
fashion.
 Loading...
Loading...