87
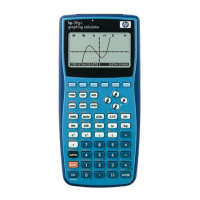
This can be solved by changing the
x axis scale to -6.4 to 6.4, which
gives table values of 0.2.
Using -3.2 to 3.2 is even better since it makes
the graph ‘square’ again, with both axes
proportional. Another good choice of scale for
the Plot-Table view is -8 to 8, giving table
values of 0.25. Basically any power of 2 is a
good choice. Again, adding or subtracting a
constant from each end of the axes will produce a graph where the y axis is
not centred.
Use of brackets in functions
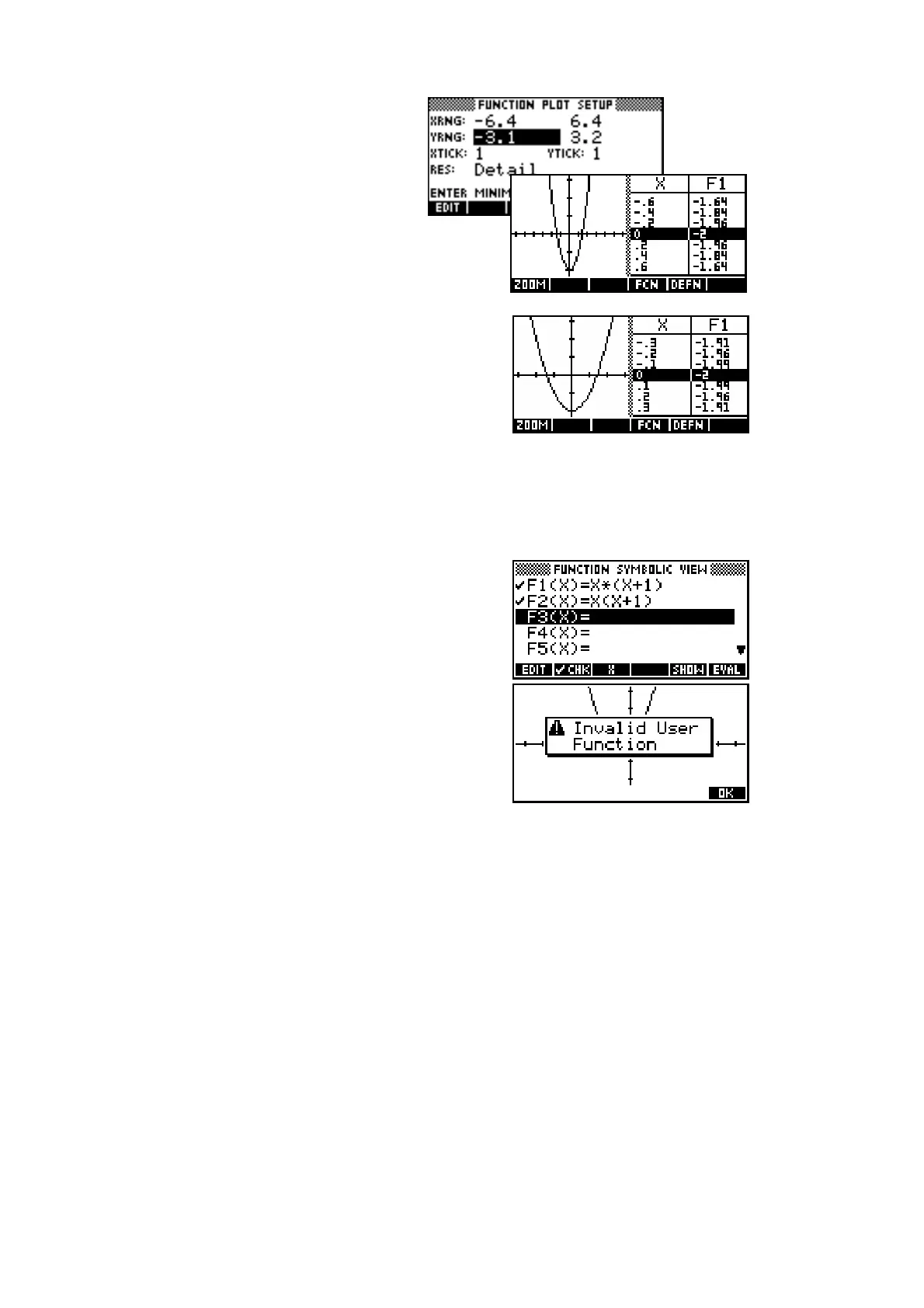
One problem commonly encountered by new
users is misinterpretation of brackets. The
hp 39g+ will correctly interpret
F1(X) = X
2
(X+1) as X
2
*(X+1) but will not
understand F(X)=X(X+1). When used in either
Function or Solve, it will result in the error
message of “Invalid User Function”.
Similarly if you want to use the sum to n terms formula for a GP in the Solve
aplet and enter it as S=A(1-R^N)/(1-R) then you will see a similar message
until you change it to read S=A*(1-R^)/(1-R).
The reason for this apparent ‘error’ is that all of the built-in functions such as
SIN(....) and COS(....) and ROUND(....) work with brackets. When the
calculator encounters X(X+1) it interprets this as asking it to evaluate a
function called X(....) at the value X+1. Since there is no such function it
returns the error message that you are trying to use a function that is
unknown.
The solution is simple: just remember to put the * sign in when you use
letters immediately before a bracket.
 Loading...
Loading...