System modules
CANaux3_IO (node number 36)
Outputs_CANaux3
13
318
EDBCSXA064 EN 3.2
13.14.2 Outputs_CANaux3
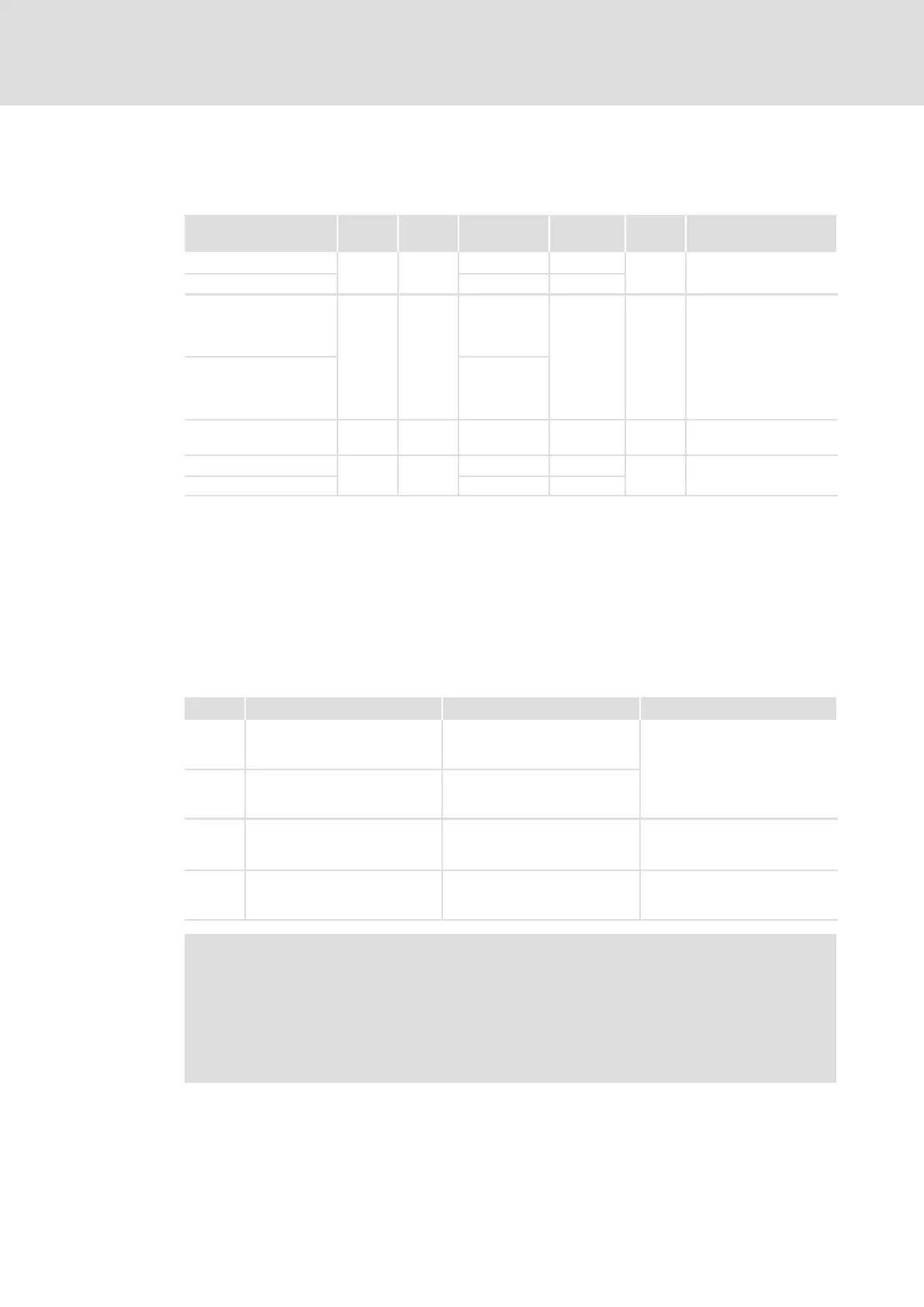
System variables
Variable Data
type
Signal
type
Address Display
code
Display
format
Comments
CANaux3_nOutW1_a
integer
analog
%QW36.0 C2493/8
dec [%]
CANaux3_nOutW2_a %QW36.1 C2493/9
CANaux3_bFDO0_b
BOOL binary
%QX36.0.0
˘ ˘
... ...
CANaux3_bFDO15_b %QX36.0.15
CANaux3_bFDO16_b %QX36.1.0
... ...
CANaux3_bFDO31_b %QX36.1.15
CANaux3_dnOutD1_p double
integer
position %QD36.0 ˘ ˘
CANaux3_nOutW3_a
integer analog
%QW36.2 C2493/10
dec [%]
CANaux3_nOutW4_a %QW36.3 C2493/11
User data
The first 4 bytes of the 8 bytes user data to be sent can be written via several variables of
different data types. According to requirements, data can therefore be transferred from
the PLC program as
ƒ binary information (1 bit)
ƒ status word/quasi−analog value (16 bit)
ƒ angle information (32 bit)
Byte Variable (1 bit) Variable (16 bit) Variable (32 bit)
1, 2 CANaux3_bFDO0_b
...
CANaux3_bFDO15_b
CANaux3_nOutW1_a
CANaux3_dnOutD1_p
3, 4 CANaux3_bFDO16_b
...
CANaux3_bFDO31_b
CANaux3_nOutW2_a
5, 6
CANaux3_nOutW3_a
7, 8
CANaux3_nOutW4_a
Note!
Avoid simultaneous overwriting via different variable types to ensure data
consistency.
If you want to describe e.g. the bytes 1 and 2, either use only the variable
CANaux3_dnOutD1_p, or only the variable CANaux3_nOutW1_a or only the
variables CANaux3_bFDO0_b ... CANaux3_bFDO15_b!
 Loading...
Loading...