Chapter 3 Featured Functions
DHCP Relay Statistics
Description Factory Default
No of Packets inserted Circuit-Id option
The amount of Packets which inserted Circuit-Id option. 0
No of Packets inserted Remote-Id suboption
The amount of Packets which inserted Remote-Id suboption. 0
No of Packets dropped
The amount of Packets which dropped. 0
No of Packets which did not inserted RAI option
The amount of Packets which did not insert RAI (Relay Agent
Information) option.
0
3.1.5.3 DHCP L2Relay
In some networks, DHCP servers rely on Relay Agent Information option appended by Relay Agents
for IP address and other parameter assignment policies. This works fine when end hosts are directly
connected to Relay Agents. In some network configurations, one or more Layer 2 devices may
reside between DHCP clients and a Relay agent. In these network scenarios, it is difficult to use the
Relay Agent Information option for an IP address and other parameter assignment policies
effectively. So there is a requirement for the device that is closest to the end hosts to append a
Relay Agent Information option in DHCP messages. These devices are typically known as Layer 2
Relay Agents.
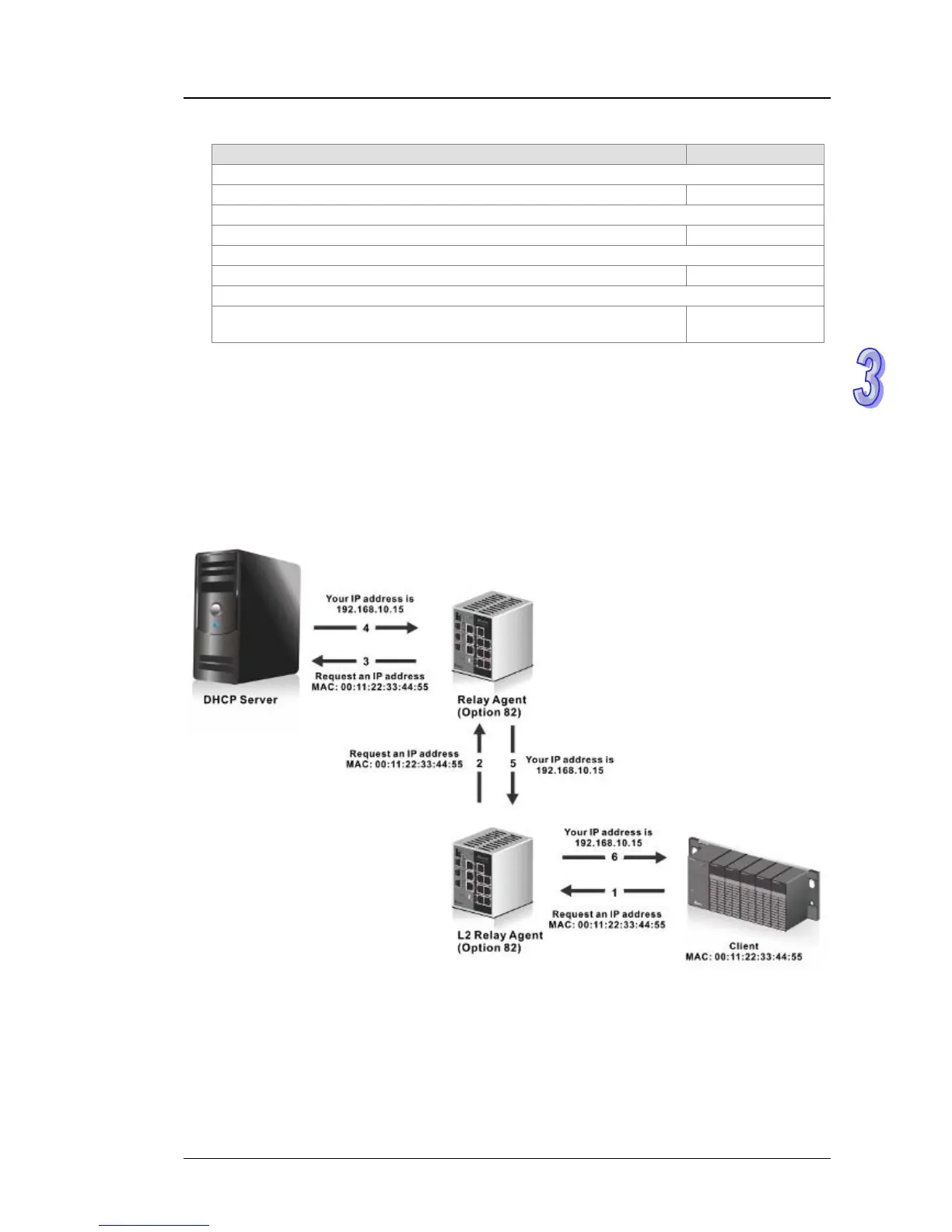
DHCP snooping steps:
1. A DHCP client sends a DHCP request via broadcast.
2. When a switch (relay agent) receives the DHCP request, it will add DHCP option-82 to the
packet. DHCP option-82 includes the MAC address of the host which sends a DHCP request
(remote-ID sub-option) and the interface ID on the switch which connects to the host (circuit-ID
sub-option).
3-17
 Loading...
Loading...