4 HARMONIC BLOCKING
4.1 2ND HARMONIC BLOCKING
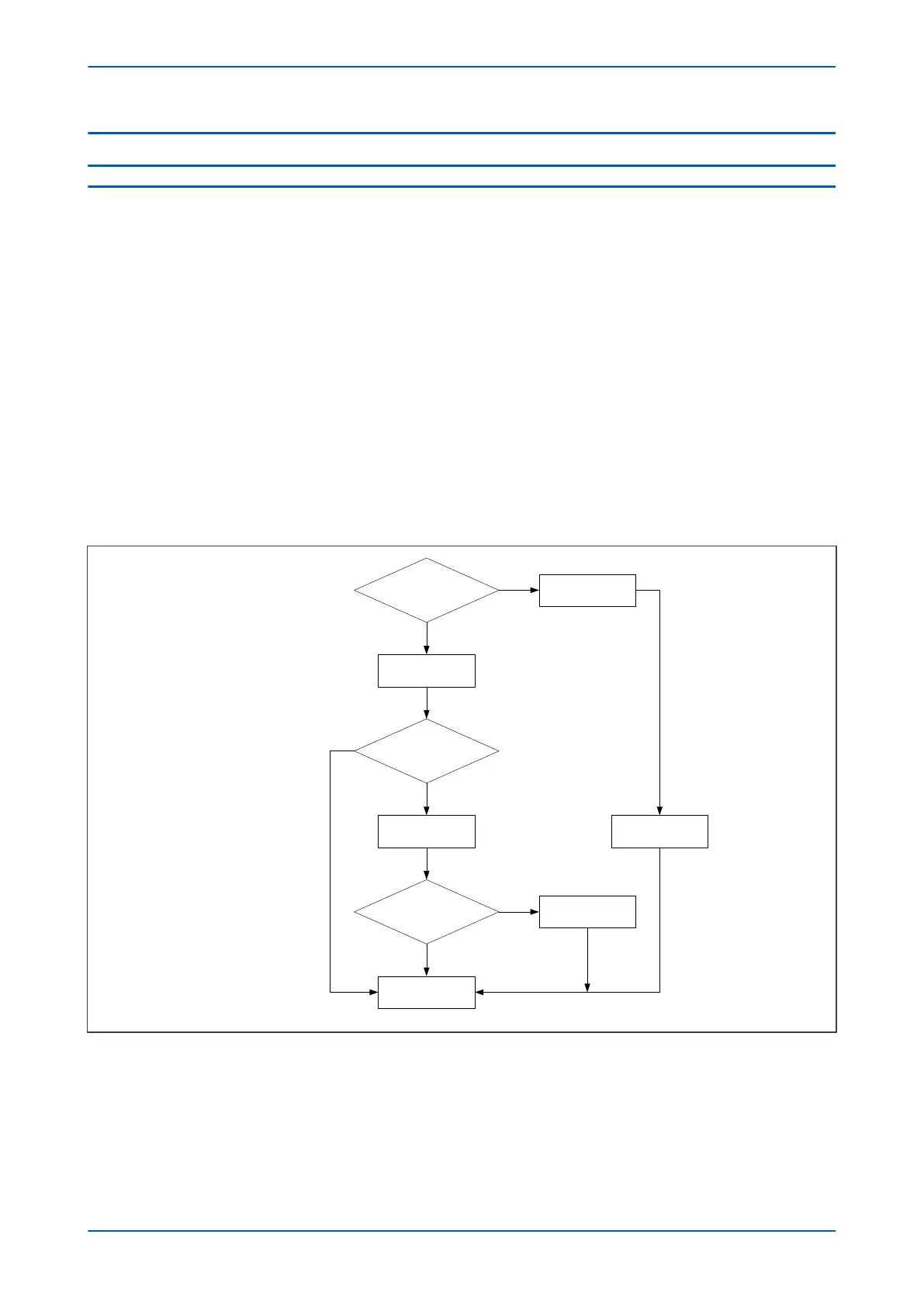
The IED filters the differential current to determine the fundamental (Idiff(fn)) and second harmonic (Idiff(2fn)
curr
ent components. The device uses these quantities to produce a blocking signal, which will block the protection
in the event that the second harmonic component exceeds a certain level.
Second harmonic blocking is phase segregated. If the ratio of the second harmonic component to fundamental
component exceeds an adjustable threshold (set by I2H Diff Set) in two consecutive calculations, a second
harmonic blocking signal is issued for the relevant phase. These are:
IA2H Diff Start (blocking signal for phase A)
IB2H Diff Start (blocking signal for phase B)
IC2H Diff Start (blocking signal for phase C)
If the Cross Blocking setting in the DIFF PROTECTION column is enabled, any one of the phase blocking signals will
block all three phases.
No blocking signal is asserted if the differential current exceeds the set thresholds Is-HS1 or Is-HS2.
The following flow diagram summarises the 2nd harmonic blocking procedure:
V03111
Any phase
Idiff(2 fn)/Idiff(fn) > Setting
Y
N
Counter + = 1
Counter = 0
Counter >= 2
Y
Block 1-phase
Low-set diff
Cross Block enabled
Y
N
N
Return
Block 3-phase
Low-set diff
Drop-off
Figure 47: 2nd harmonic blocking process
P64x Chapter 6 - Transformer Differential Protection
P64x-TM-EN-1.3 117

 Loading...
Loading...