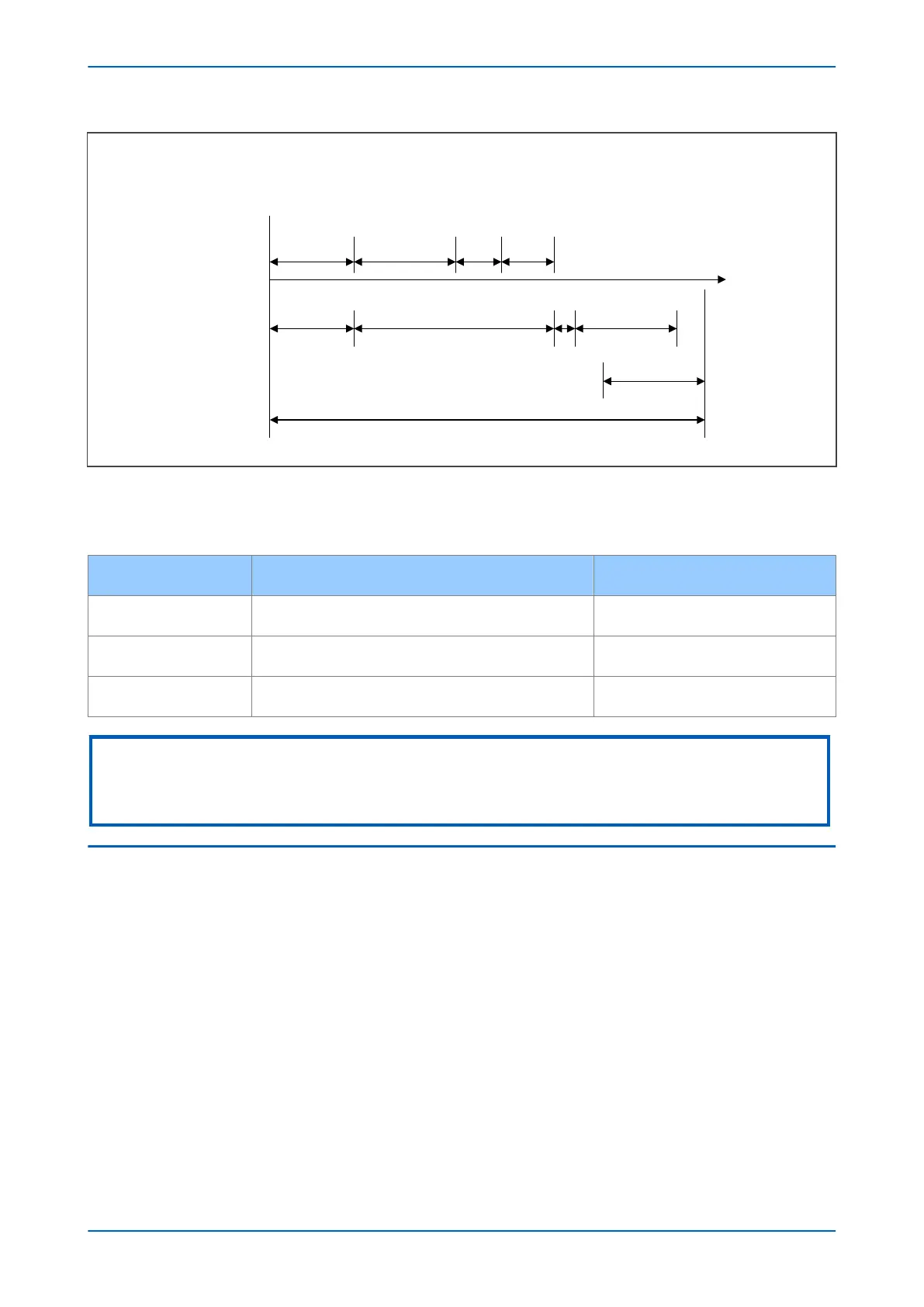
t
Breaker failure
operation
Normal
operation
Protection
operating time
Maximum breaker
clearing time
CBF
reset
time
Safety
margin
time
Fault occurs
Protection
operating time
CBF back-up trip time delay
Local Bks clearing
time
Remote CB
clearing time
Local 86
operating
time
Maximum fault clearing time
CBF resets:
1. Undercurrent element asserts
2. Undercurrent element asserts and the
breaker status indicates an open position
3. Protection resets and the undercurrent
element asserts
Fault occurs
V00693
Figure 109: CB Fail timing
The following examples consider dir
ect tripping of a 2-cycle circuit breaker. Typical timer settings to use are as
follows:
CB Fail Reset Mechanism tBF Time Delay
Typical Delay For 2 Cycle Circuit
Br
eaker
Initiating element reset
CB interrupting time + element reset time (max.) + error in tBF
timer + safety mar
gin
50 + 50 + 10 + 50 = 160 ms
CB open
CB auxiliary contacts opening/ closing time (max.) + error in tBF
timer + safety mar
gin
50 + 10 + 50 = 110 ms
Undercurrent elements
CB interrupting time + undercurrent element (max.) + safety
mar
gin operating time
50 + 25 + 50 = 125 ms
Note:
All CB Fail r
esetting involves the operation of the undercurrent elements. Where element resetting or CB open resetting is
used, the undercurrent time setting should still be used if this proves to be the worst case.
Where auxiliary tripping relays are used, an additional 10-15 ms must be added to allow for trip relay operation.
5.3 SETTING GUIDELINES (UNDERCURRENT)
The phase undercurrent settings (I<) must be set less than load current to ensure that I< operation correctly
indicates that the cir
cuit breaker pole is open. A typical setting for overhead line or cable circuits is 20%In. Settings
of 5% of In are common for generator CB Fail.
The earth fault undercurrent elements must be set less than the respective trip. For example:
IN< = (IN> trip)/2
Chapter 10 - CB Fail Protection P64x
234 P64x-TM-EN-1.3

 Loading...
Loading...