For individual windings, you set the Monit
oredWinding setting to to HV, LV, TV accordingly. If you wish to
protect the transformer as a whole set the MonitoredWinding setting to Biased Current, which provides an
overall loading picture of the transformer.
The device provides two 3-stage Definite Time delayed trip elements; one element for Hotspot temperature and
one for Top Oil temperature. Top Oil temperature can be calculated, or measured directly using CLIO or RTD
methods, but Hotspot temperature is always calculated.
A pre-trip alarm can be configured in the tPre-trip Set setting. This alarm indicates that thermal overload will trip
after the set time if the load level remains unchanged.
Four cooling modes are available. You can set the oil exponent constant and winding exponent constant
independently for each mode. You can set the cooling mode automatically in the PSL or manually in the setting file.
For the latter, you will need to configure two opto-inputs as CM Select 1X and CM Select X1, and you must wire the
contacts to energise or de-energise these inputs. The selected cooling mode would then be as follows:
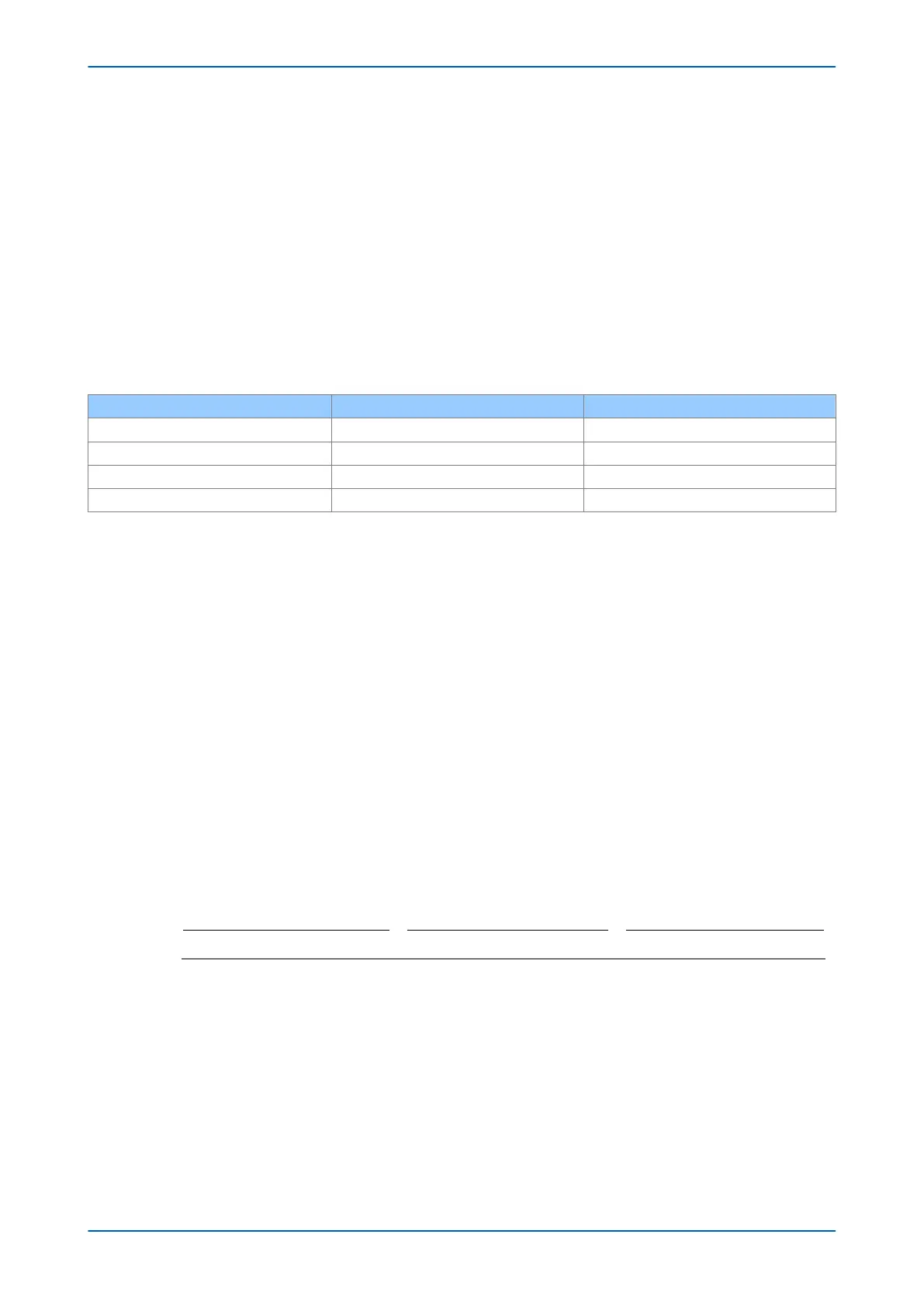
CM Select 1X CM Select X1 Selected Cooling Mode
0 0 1
0 1 2
1 0 3
1 1 4
To calculate the Top Oil and hotspot winding temperature, the device takes into consideration the ratio of the
actual load to the rated load. If the monitored winding is set to HV, LV, or TV, the rated load is determined by the
HV rating, LV rating, or TV rating settings respectively and the Irated setting. If the monitored winding is set as
the the biased current, the rated load is calculated using the Sref power rating setting in the SYSTEM CONFIG
column and the Irated setting in the THERMAL PROTECTION column.
The thermal overload model is executed once every power cycle. The thermal overload trip can be based on either
hot spot temperature or top oil temperature, or both.
The device has up to three hot spot stages and up to three top oil stages. The tripping signal, Top Oil T>x Trip, is
asserted when the top oil (measured or calculated) temperature is above the setting, Top Oil>x Set, and the time
delay, tTop Oil>x Set has elapsed. Also, the tripping signal, Hotspot>x Trip, is asserted when the hottest-spot
(calculated only) temperature is above the setting, Hotspot>x Set, and the time delay, tHotspot>x Set has elapsed.
2.1.1 THERMAL OVERLOAD BIAS CURRENT
The biased current used by the thermal protection is not the same as the biased current used by the differential
pr
otection. No vector correction or zero sequence filtering is performed. To calculate the bias current, the thermal
element considers the maximum RMS current on a per winding basis. Note that the bias current calculation
performed by the thermal element is not on a per-phase basis. The thermal bias current calculation is as follows:
I
Max I I I
HV FLC
Max I I
bias
HVArms HVBrms HVCrms
Sref
LVArms L
=
[ ]
+
, ,
_
,
VVBrms LVCrms
Sref
TVArms TVBrms TVCrms
I
LV FLC
Max I I I
TV
,
_
, ,
_
[ ]
+
[ ]
FFLC
Sref
2
where:
● HV_FL
C
Sref
= HV full load current at the reference power
● LV_FLC
Sref
= LV full load current at the reference power
● TV_FLC
Sref
= TV full load current at the reference power
P64x Chapter 7 - Transformer Condition Monitoring
P64x-TM-EN-1.3 145
 Loading...
Loading...