96
REAC applications and settings
REAC applications and settings
REAC applications
This chapter explains more advanced ways to use REAC.
For basic information about REAC, refer to “Basic knowledge
about REAC” (p. 11) .
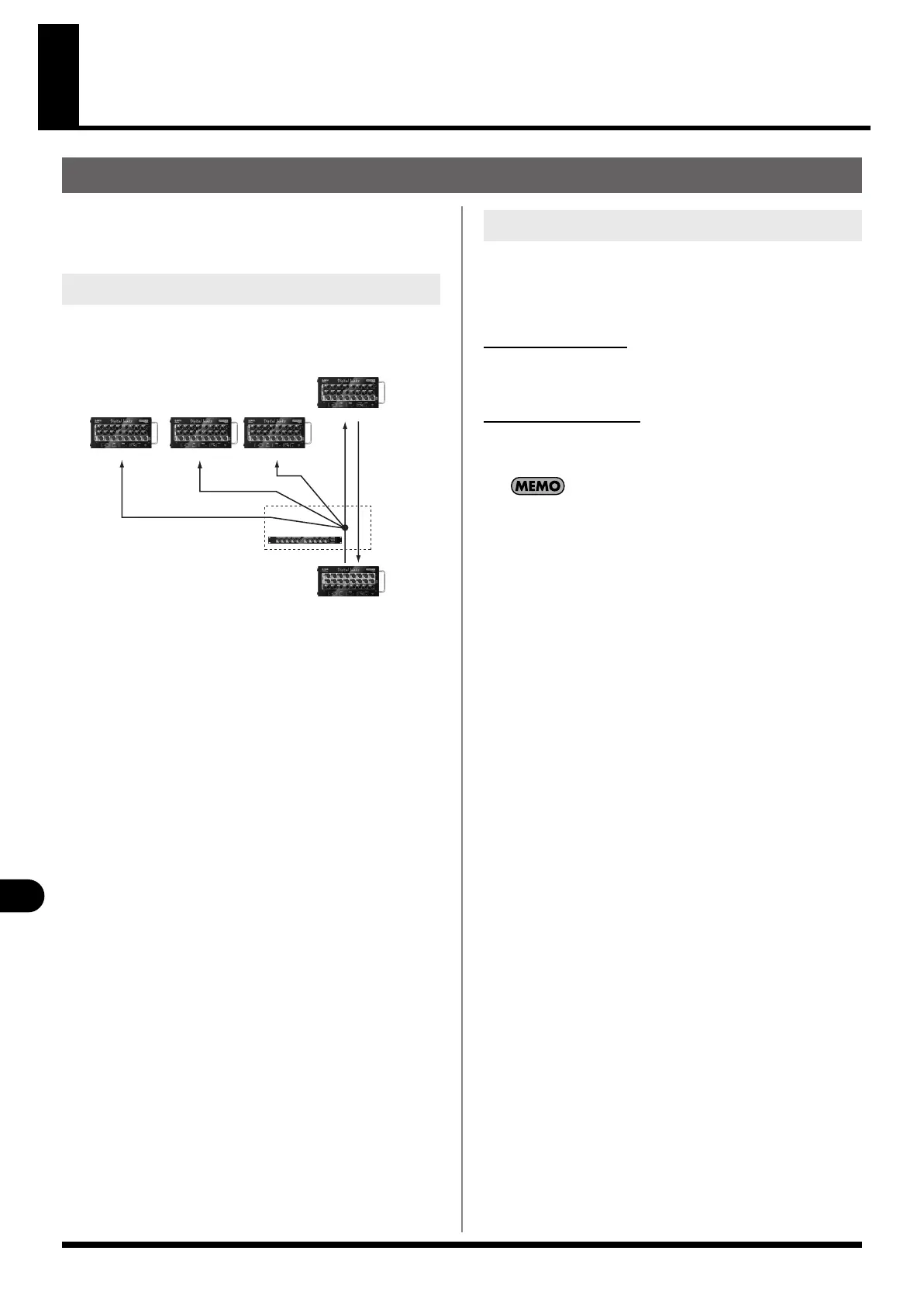
By connecting a REAC splitter between the REAC master and
slave, you can split the output from the REAC master device and
distribute it to multiple REAC split devices.
fig.REACsplit.eps
To assign a REAC device to operate in split mode, you must set its
REAC mode to Split. The REAC split device will function solely to
receive signals from the REAC master device.
Caution when using a REAC splitter
For a REAC splitter, you can use the S-4000-SP, S-4000D, or an
Ethernet switching hub. Switching hubs that meet the following
conditions can be used with the M-200i:
•
1000BASE-T compatible device (IEEE 802.3ab, Gigabit
Ethernet) that supports 100 BASE-TX (IEEE 802.3u, Fast
Ethernet)
•
Full duplex communication (simultaneous bidirectional
communication)
The network transmission time between REAC devices is
approximately 375 microseconds, but if the signal passes
through a REAC splitter (S-4000-SP, S-4000D, or an Ethernet
switching hub), approximately 200 microseconds of delay will
occur for each device. A maximum of four REAC splitters can be
connected in series.
fi
The REAC port on the M-200i operates as the REAC master, the
REAC slave, or the REAC split. For information on how to make
REAC settings, refer to “REAC settings” (p. 98).
REAC port input
Input signals from the REAC port rises at the input patchbay.
REAC port output
The 40 channels from the output patchbay are output to the
REAC port.
Output cannot be made to the REAC port on the M-200i when it
has been set to be a REAC split device.
REAC splitting
SPLIT SPLIT SPLIT
REAC SPLITTER
MASTER
SLAVE
About the M-200i's REAC functionality
M-200i_e.book 96 ページ 2013年1月16日 水曜日 午後4時9分

 Loading...
Loading...