7.4.6 Monitored data
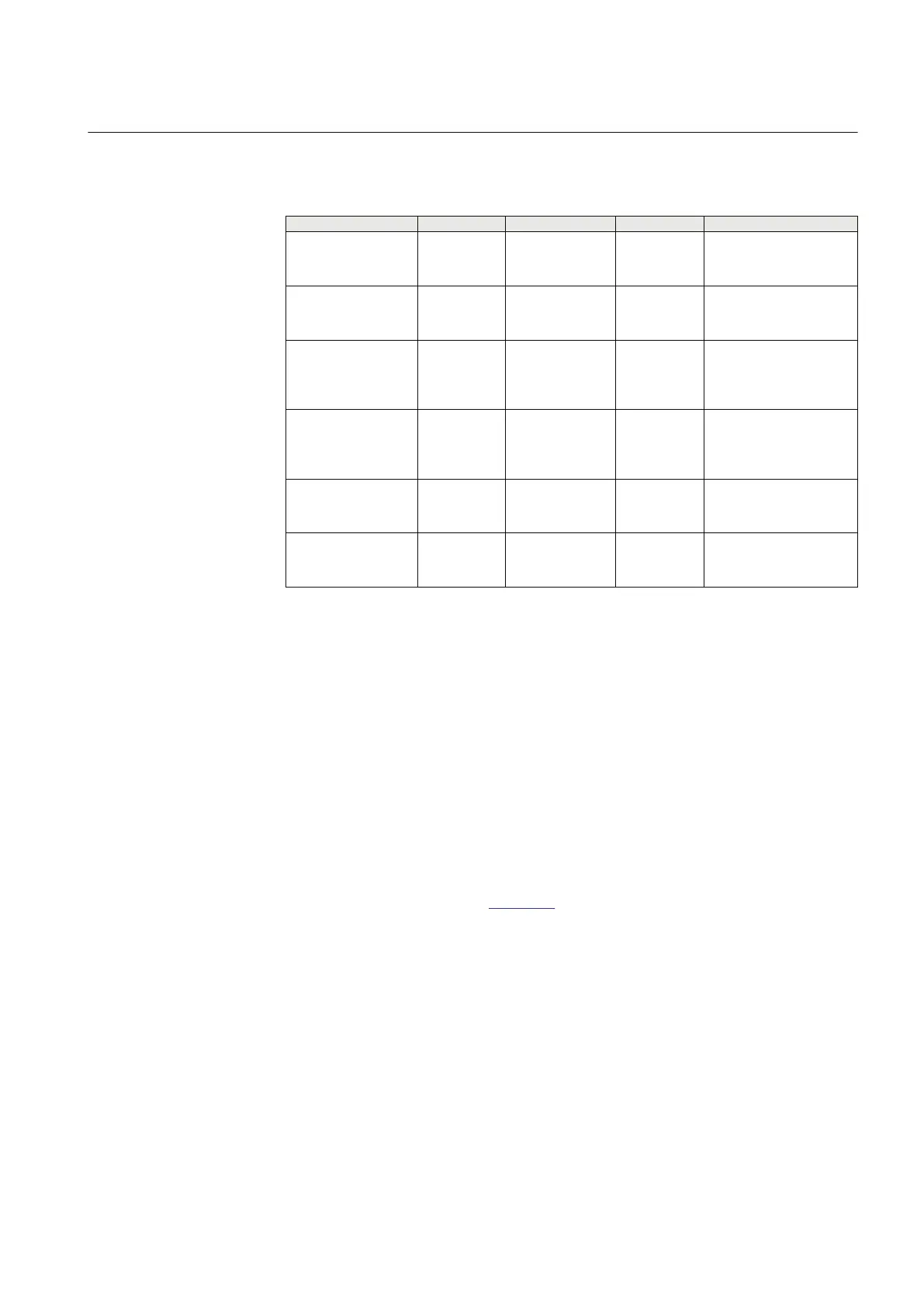
Table 76: OOSPPAM Monitored data
Name
Type Values (Range) Unit Description
VOLTAGE REAL - kV Magnitude of the
measured positive-
sequence voltage, in V
CURRENT
REAL - A Magnitude of the
measured positive-
sequence current, in A
R
REAL - % Real part of measured
positive-sequence
impedance % of UBase/
(sqrt(3)*IBase)
X
REAL - % Imaginary part of
measured positive-seq
impedance % of UBase/
(sqrt(3)*IBase)
ROTORANG
REAL - deg Rotor angle as estimated
by the out-of-step
function
UCOSPHI
REAL - kV Estimated Ucos(Phi)
voltage during pole slip,
in V
7.4.7 Operation principle
General
Under balanced and stable conditions, a generator operates with a constant rotor angle
(power angle), delivering active electrical power to the power system, which is
approximately equal to the input mechanical power on the generator axis, minus the
small losses in the generator. The currents and voltages are constant and stable. An
out-of-step condition is characterized by periodic changes in the rotor angle, that is,
the synchronizing power, rotational speed, currents and voltages. When displayed in
the complex impedance plane, these changes are characterized by a cyclic change in
the complex load impedance Z(R, X) as measured at the terminals of the generator, or
at the location of the voltage transformers of a power line connecting two power
subsystems. This is shown in
Figure 76.
1MRK 502 048-UEN A Section 7
Impedance protection
163
Technical manual

 Loading...
Loading...