STUN is used for signaling and the media streams. STUN works with many existing NAT
types and does not require any special behavior.
STUN enables the device to discover the presence (and types) of NATs and firewalls
located between it and the public Internet. It provides the device with the capability to
determine the public IP address and port allocated to it by the NAT. This information is later
embedded in outgoing SIP / SDP messages and enables remote SIP user agents to reach
the device. It also discovers the binding lifetime of the NAT - the refresh rate necessary to
keep NAT ‘pinholes’ open.
On startup, the device sends a STUN Binding Request. The information received in the
STUN Binding Response (IP address:port) is used for SIP signaling. This information is
updated every user-defined period (NATBindingDefaultTimeout).
At the beginning of each call and if STUN is required (i.e., not an internal NAT call), the
media ports of the call are mapped. The call is delayed until the STUN Binding Response
(that includes a global IP:port) for each media (RTP, RTCP and T.38) is received.
Notes:
• STUN is applicable only to UDP connections (not TCP and TLS).
• STUN can’t be used when the device is located behind a symmetric NAT.
• Use either the STUN server IP address (STUNServerPrimaryIP) or
domain name (STUNServerDomainName) method, with priority to the
first one.
To enable STUN:
1. Open the Application Settings page (Configuration tab > System menu >
Application Settings).
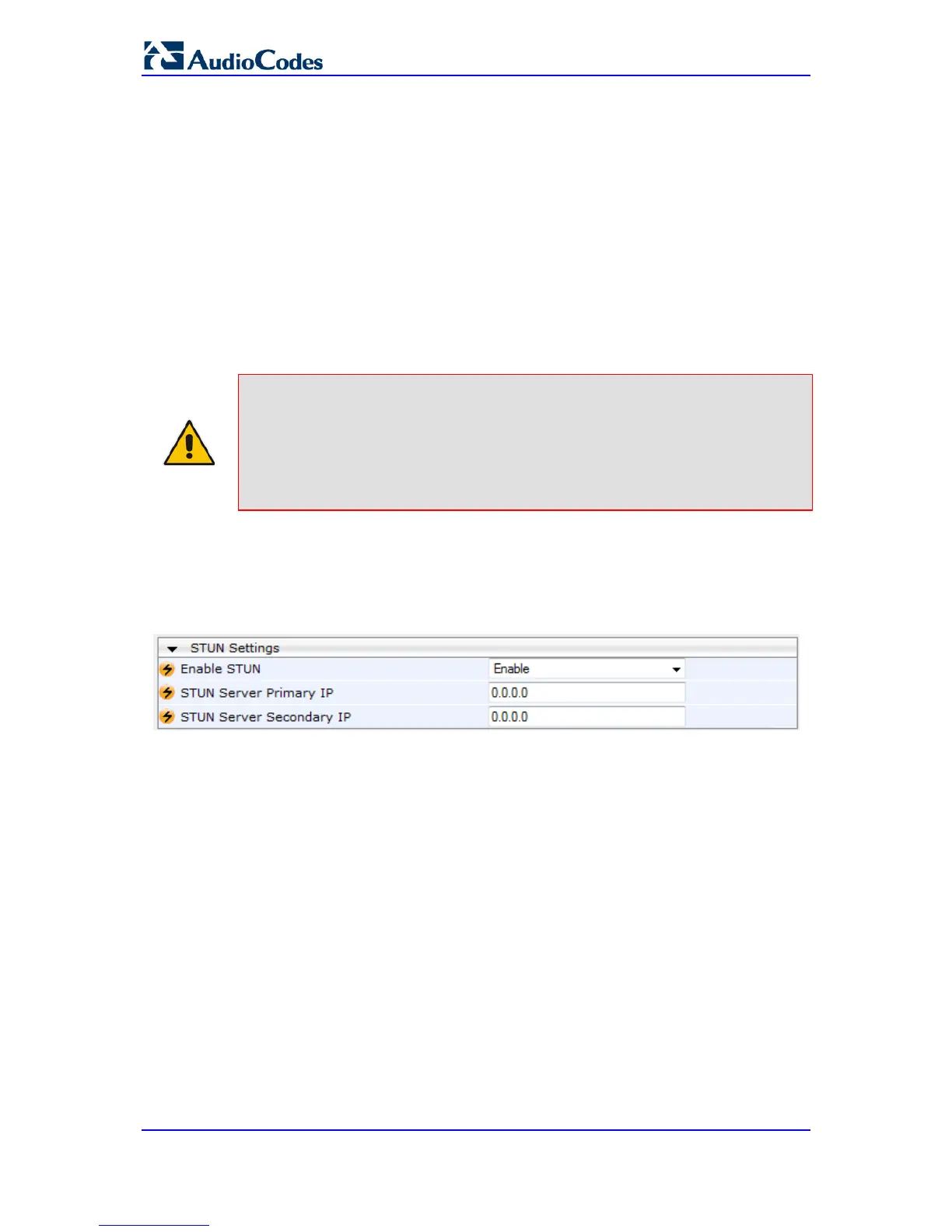
Figure 11-10: STUN Parameters in Application Settings Page
2. From the 'Enable STUN' (EnableSTUN) drop-down list, select Enable to enable the
STUN feature.
3. Configure the STUN server address using one of the following methods:
• Define the IP address of the primary and secondary (optional) STUN servers,
using the 'STUN Server Primary IP' field (STUNServerPrimaryIP) and 'STUN
Server Secondary IP' field. If the primary STUN server is unavailable, the device
attempts to communicate with the second server.
• Define the domain name of the STUN server using the ini file parameter,
STUNServerDomainName. The STUN client retrieves all STUN servers with an
SRV query to resolve this domain name to an IP address and port, sorts the
server list, and uses the servers according to the sorted list.
4. Configure the default NAT binding lifetime (in secondsUse) using the ini file
parameter, NATBindingDefaultTimeout. STUN refreshes the binding information after
this time expires.
11.8.1.2 Configuring a Static NAT IP Address for All Interfaces
You can configure a global (public) IP address of the router to enable static NAT between
the device and the Internet for all network interfaces. Thus, the device replaces the source

 Loading...
Loading...











