5 CLI-Based Management
This section provides an overview of the CLI-based management and configuration relating
to CLI management. The device's CLI-based management interface can be accessed
using the RS-232 serial port or by using Secure SHell (SSH) or Telnet through the Ethernet
interface.
Notes:
• For security, CLI is disabled by default.
• For information on accessing the CLI interface through the RS-232 port
interface, see 'CLI' on page 28.
• CLI is used only for debugging and mainly allows you to view various
information regarding device configuration and performance.
5.1 Enabling CLI using Telnet
The device's CLI can be accessed using Telnet. Secure Telnet using Secure Socket Layer
(SSL) can be configured whereby information is not transmitted in the clear. If SSL is used,
a special Telnet client is required on your PC to connect to the Telnet interface over a
secured connection; examples include C-Kermit for UNIX and Kermit-95 for Windows.
For security, some organizations require the display of a proprietary notice upon starting a
Telnet session. You can use the configuration ini file parameter, WelcomeMessage to
configure such a message (see Creating a Login Welcome Message on page 57).
To enable Telnet:
1. Open the Telnet/SSH Settings page (Configuration tab > System menu >
Management > Telnet/SSH Settings).
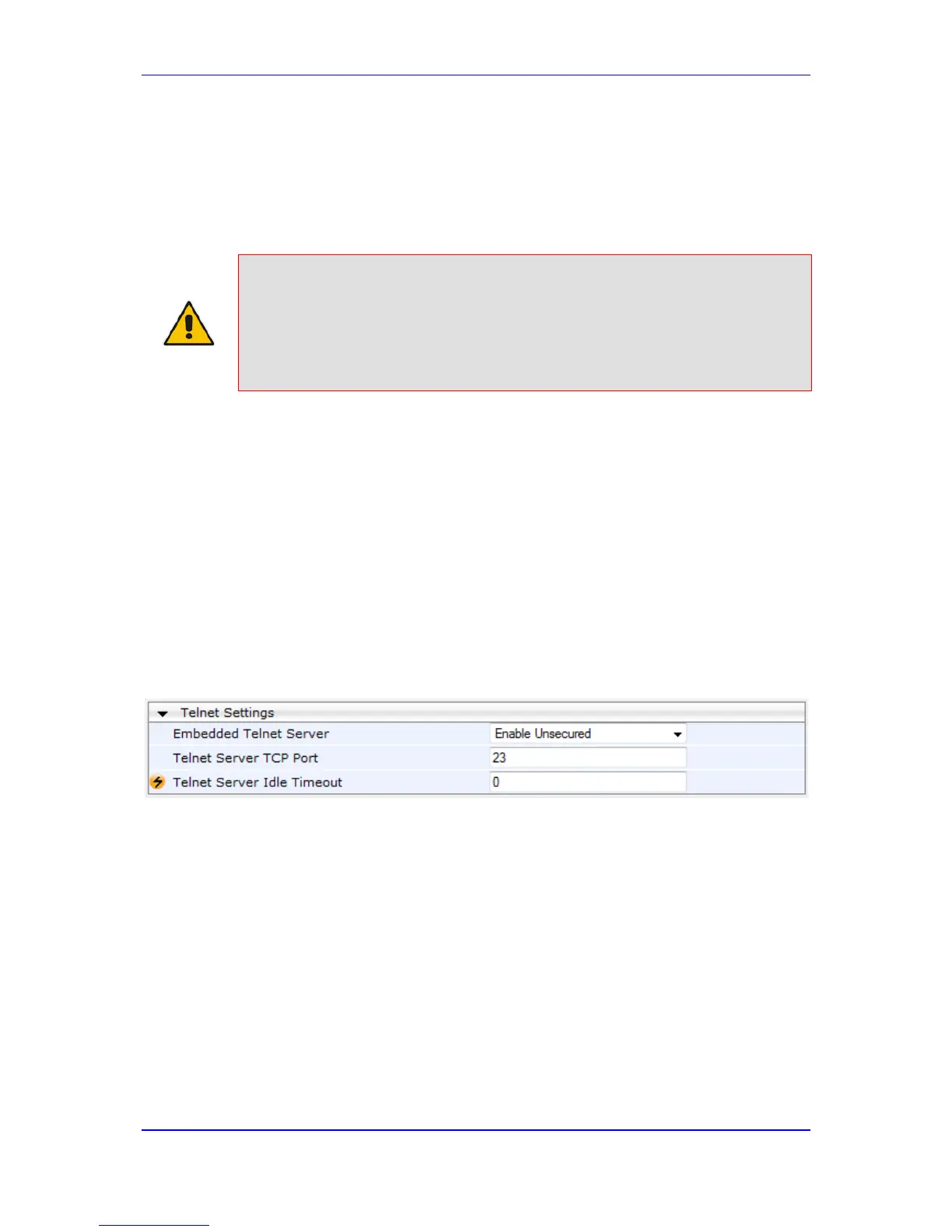
Figure 5-1: Telnet Settings on Telnet/SSH Settings Page
2. Set the ‘Embedded Telnet Server’ parameter to Enable Unsecured or Enable
Secured (i.e, SSL).
3. Configure the other Tenet parameters as required. For a description of these
parameters, see Telnet Parameters on page 434.
4. Click Submit.
5. Save the changes to flash memory with a device reset.
5.2 Enabling CLI using SSH and RSA Public Key
The device's CLI can be accessed using Telnet. However, unless configured for TLS,
Telnet is not secure as it requires passwords to be transmitted in clear text. To overcome
this, Secure SHell (SSH) is used, which is the de-facto standard for secure CLI. SSH 2.0 is
a protocol built above TCP, providing methods for key exchange, authentication,
encryption, and authorization.
SSH requires appropriate client software for the management PC. Most Linux distributions
have OpenSSH pre-installed; Windows-based PCs require an SSH client software such as

 Loading...
Loading...











