Monitoring and Analyzing Switch Operation
Traffic Mirroring
■ You can reduce the risk of oversubscribing a single exit port by directing
traffic from different session sources to different exit ports
■ You can segregate traffic by type, direction, or source.
A given switch can operate as both a source and a destination for mirroring
sessions.
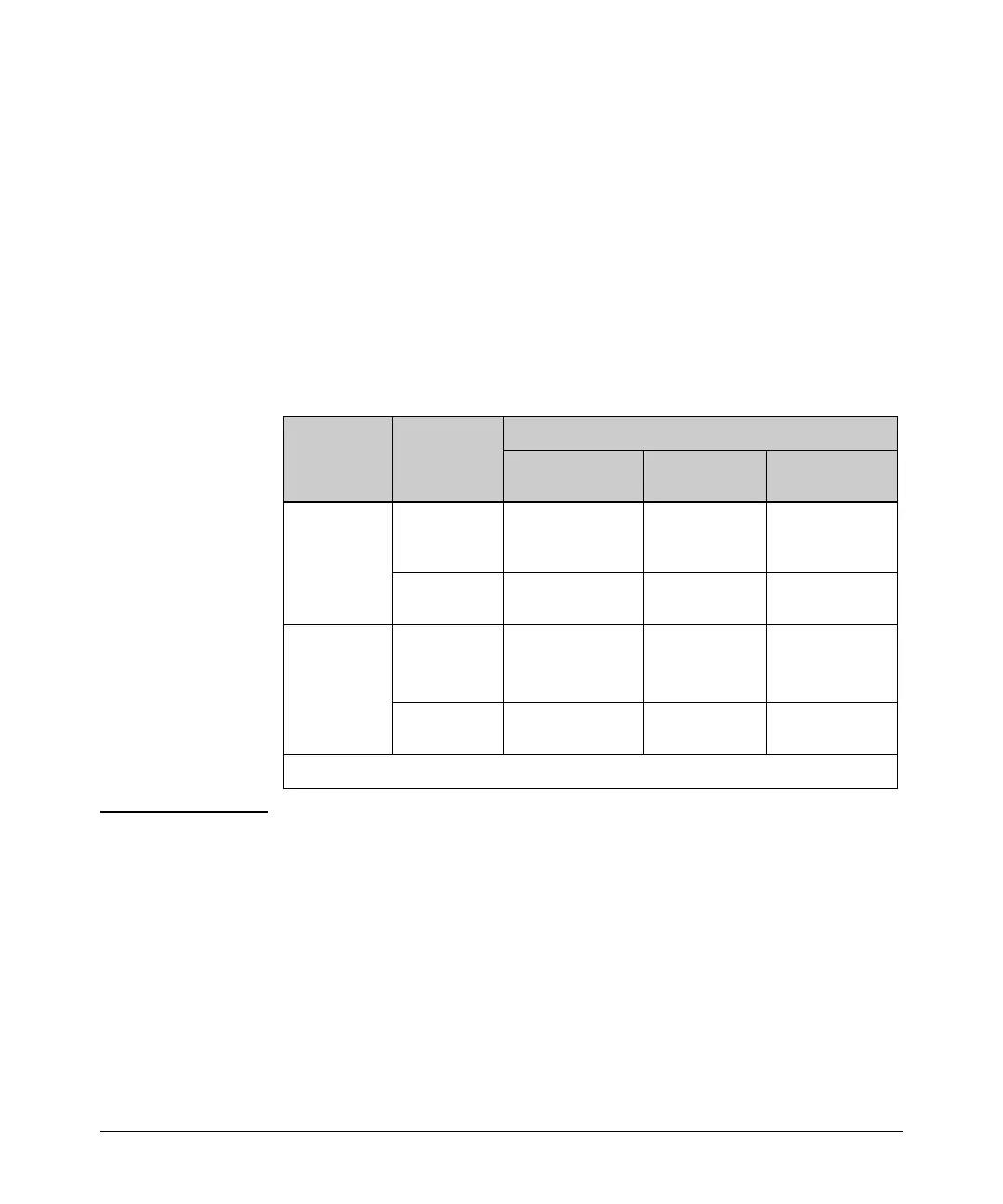
Configuration
Table B-1 lists the traffic mirroring configuration support available through
the CLI, Menu Interface, and SNMP methods.
Table B-1. Traffic Mirroring Configuration Options
Interface Monitor Traffic Direction
CLI Config Menu and Web
I/F Config
1
SNMP Config
VLAN all traffic inbound only, out-
bound only, or both
directions
inbound and
outbound
combined
inbound only, out-
bound only, or
both directions
ACL-selected
(IP) traffic
Inbound only n/a n/a
Port(s)
Trunk(s)
Mesh
all traffic inbound only, out-
bound only, or both
directions
inbound and
outbound
combined
inbound only, out-
bound only, or
both directions
ACL-selected
(IP) traffic
Inbound only n/a n/a
1
Configures only session 1, and only for local mirroring.
Note Using the CLI, you can access all mirroring capabilities on the switch. Using
the Menu or Web interfaces, you can configure and display only session 1 and
only as a local mirroring session for traffic in both directions on the specified
interface. If session 1 has been configured in the CLI for local mirroring for
inbound-only or outbound-only traffic, then using the Menu or Web interface
to change the session 1 configuration automatically reconfigures the session
to monitor both inbound and outbound traffic on the interface. (If session 1
has been configured in the CLI with an ACL or as a remote mirroring session,
then the Menu and Web interfaces cannot be used to configure a mirroring
session.) The CLI can configure sessions 1 - 4 for local or remote mirroring in
any combination, and can be used to override a Menu or Web interface
B-29
 Loading...
Loading...
















