04/SHOCK ABSORBER, SWINGARM 22
6.1Adjusting the rebound damping of the shock absorber
Danger
Danger of accidents Disassembly of pressurized parts can lead to injury.
– The shock absorber is filled with high density nitrogen. Adhere to the description provided.
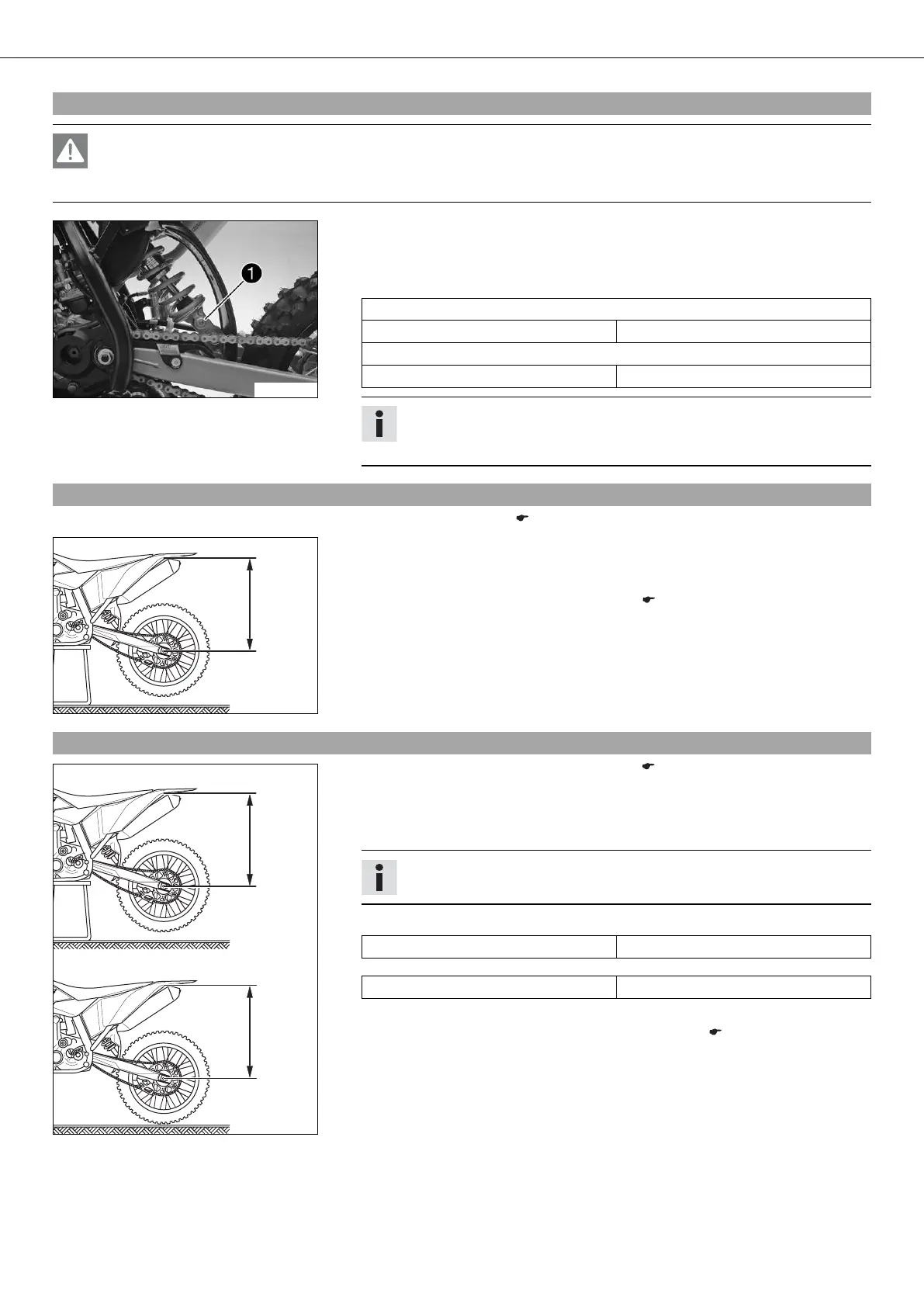
700476-01
– Turn adjusting screw clockwise up to the last perceptible click.
– Turn back counterclockwise by the number of clicks corresponding to the shock
absorber type.
Guideline
Rebound damping (50 SX)
Standard 10 clicks
Rebound damping (50 SX Mini)
Standard 12 clicks
Info
Turn clockwise to increase damping, turn counterclockwise to reduce damp-
ing.
6.2Measuring rear wheel sag unloaded
– Jack up the motorcycle. ( p. 7)
400220-10
– Measure the distance – as vertical as possible – between the rear axle and a fixed
point, for example, a mark on the side cover.
– Make a note of the value as measurement .
– Remove the motorcycle from the work stand. ( p. 7)
6.3Checking the static sag of the shock absorber
400221-10
– Measure distance of rear wheel unloaded. ( p. 22)
– Ask someone to help you by holding the motorcycle upright.
– Measure the distance between the rear axle and the fixed point again.
– Make a note of the value as measurement .
Info
The static sag is the difference between measurements and .
– Check the static sag.
Static sag (50 SX) 20 mm (0.79 in)
Static sag (50 SX Mini) 15 mm (0.59 in)
» If the static sag is less or more than the specified value:
– Adjust the spring preload of the shock absorber. ( p. 23)

 Loading...
Loading...











