S
WITCH
C
LUSTERING
3-243
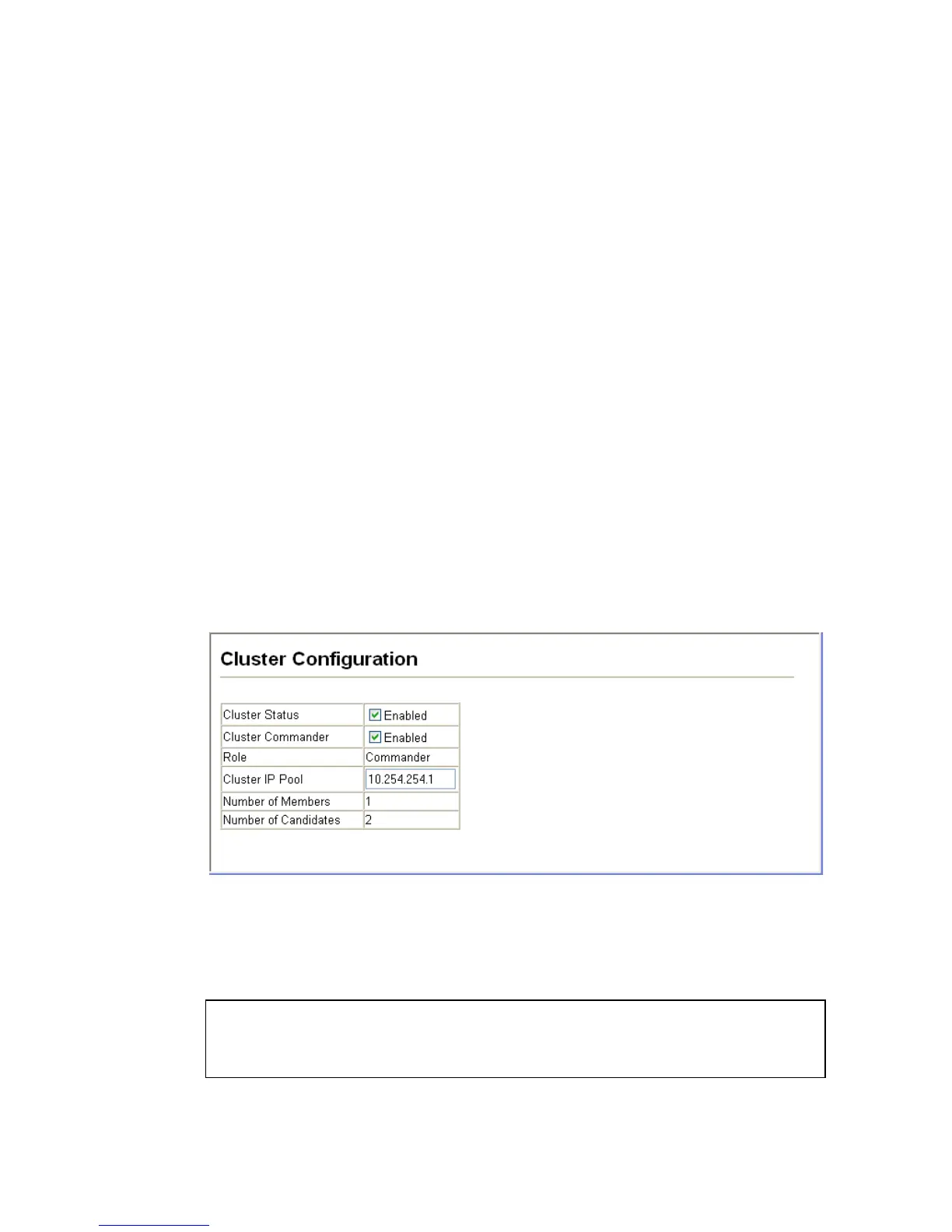
• Cluster Commander – Enables or disables the switch as a cluster
Commander.
• Role – Indicates the current role of the switch in the cluster; either
Commander, Member, or Candidate.
• Cluster IP Pool – An “internal” IP address pool that is used to assign
IP addresses to Member switches in the cluster. Internal cluster IP
addresses are in the form 10.x.x.member-ID. Only the base IP address
of the pool needs to be set since Member IDs can only be between 1
and 36. Note that you cannot change the cluster IP pool when the
switch is currently in Commander mode. Commandoer mode must
first be disabled.
• Number of Members – The current number of Member switches in
the cluster.
• Number of Candidates – The current number of Candidate switches
discovered in the network that are available to become Members.
Web – Click Cluster, Configuration.
Figure 3-114. Cluster Configuration
CLI – This example first enables clustering on the switch, sets the switch
as the cluster Commander, and then configures the cluster IP pool.
Console(config)#cluster 4-279
Console(config)#cluster commander 4-280
Console(config)#cluster ip-pool 10.2.3.4 4-281
Console(config)#

 Loading...
Loading...






