Rockwell Automation Publication MOTION-UM002E-EN-P - June 2016 81
Configure an Articulated Independent Robot Chapter 4
Arm Solutions
A Kinematic arm solution is the position of all joints on the robot that
correspond to a Cartesian position. When the Cartesian position is inside the
workspace of the robot, then at least one solution always exists. Many of the
geometries have multiple joint solutions for a single Cartesian position.
• Two axis robots - two joint solutions typically exist for a Cartesian
position.
• Three axis robots - four joint solutions typically exist for a Cartesian
position.
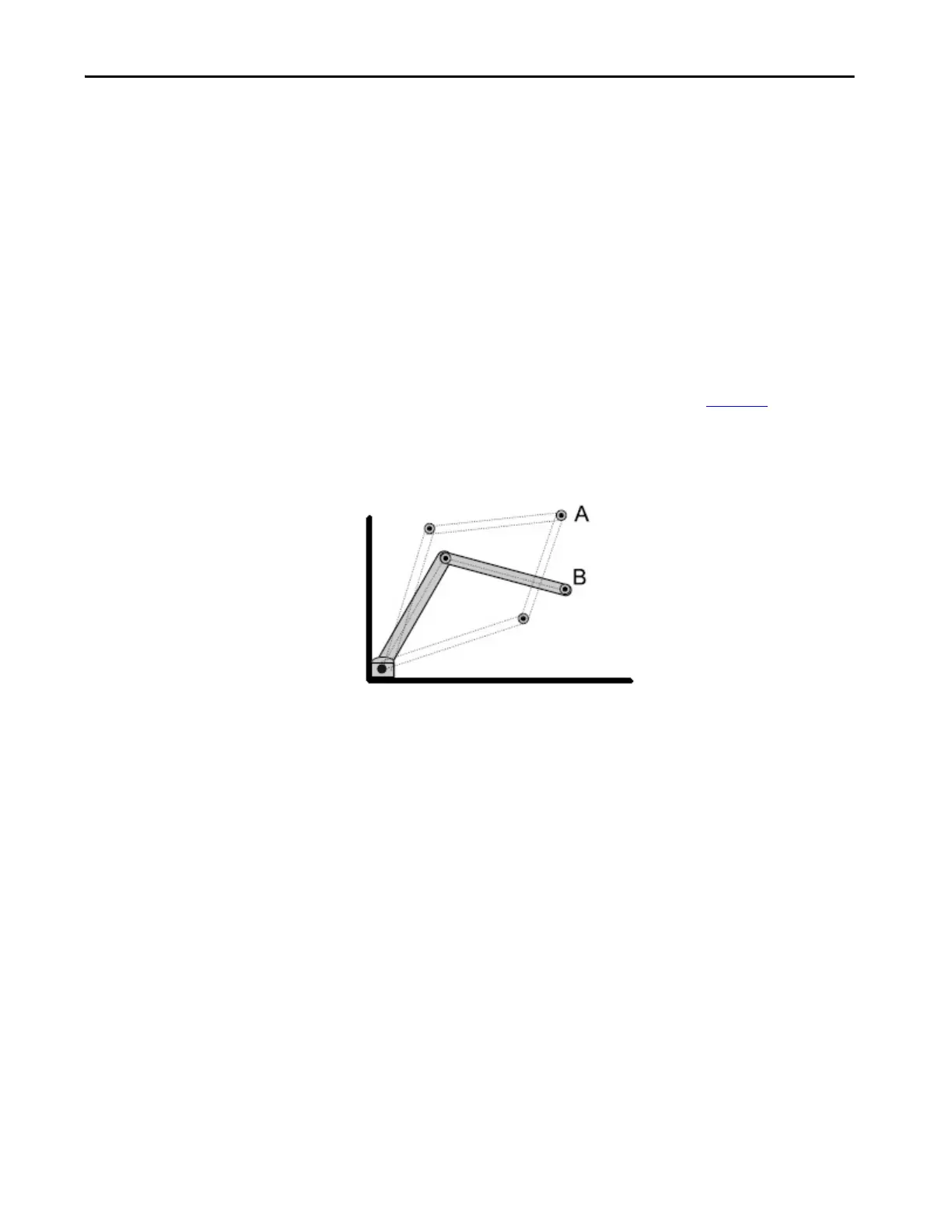
Left-Arm and Right-Arm Solutions for Two-Axes Robots
A robot having an arm configuration has two Kinematics solutions when
attempting to reach a given position (point A shown in Figure 33
). One
solution satisfies the equations for a right-armed robot, the other solution
satisfies the equations for a left-armed robot.
Figure 33 - Right Arm and Left Arm Solutions
Solution Mirroring for Three-dimensional Robots
For a three-dimensional Articulated Independent robot, there are four possible
solutions for the same point.
•Left-Arm
•Right-Arm
•Left-Arm Mirror
•Right-Arm Mirror
Left-Arm Solution
Right-Arm Solution

 Loading...
Loading...











