82 Rockwell Automation Publication MOTION-UM002E-EN-P - June 2016
Chapter 4 Configure an Articulated Independent Robot
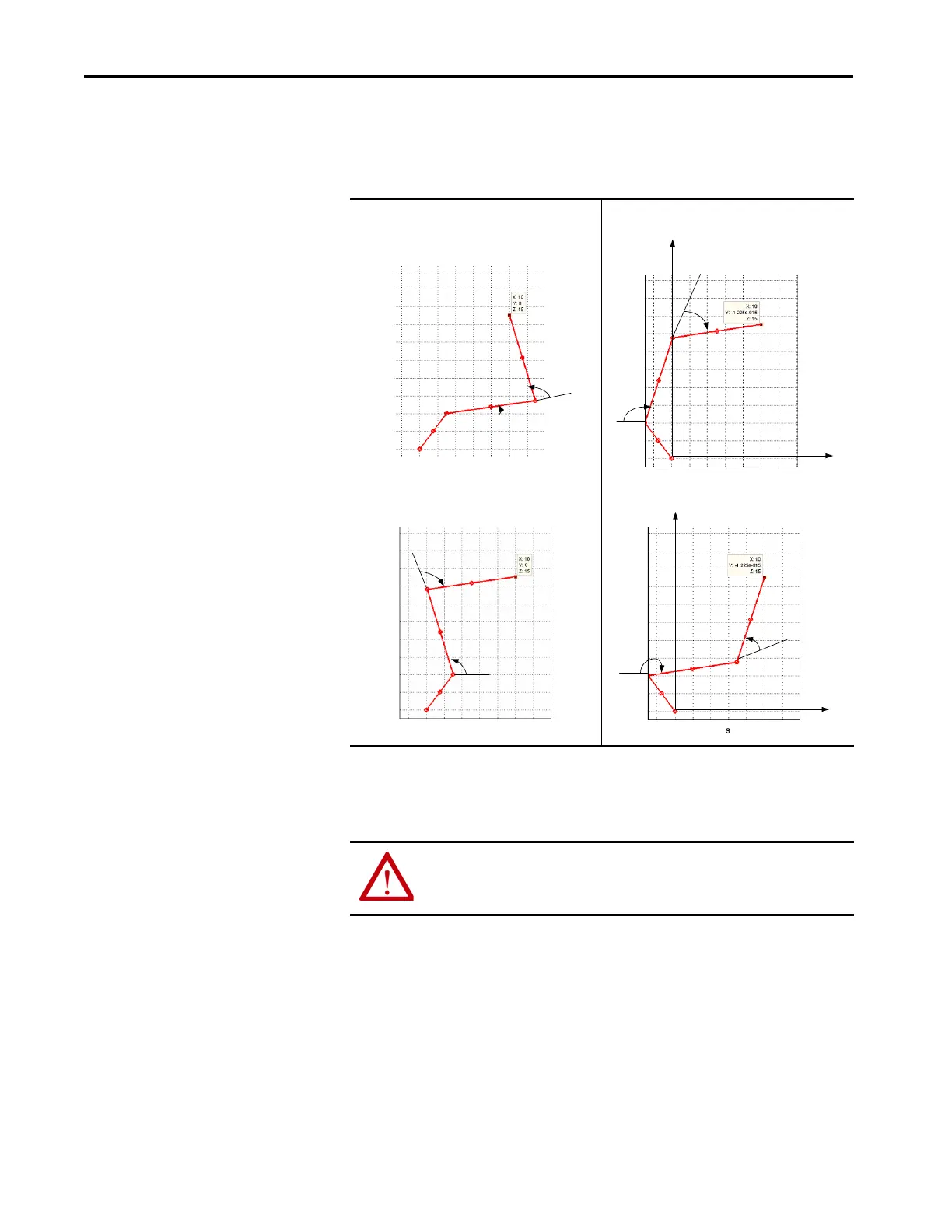
For example, consider the Cartesian point XYZ (10,0,15). The joint position
corresponding to this point has four joint solutions. Two of the solutions are
the same as the solutions for the two-dimensional case. The other two
solutions are mirror image solutions where J1 is rotated 180.
Activating Kinematics
Before activating Kinematics, configure the robot in a left-arm or right-arm
solution. The robot stays in the same configuration in which it was activated as
it is moved in Cartesian or source coordinate mode. If activated in a fully-
extended-arm mode (this is, neither a left-arm nor a right-arm solution), the
system chooses a left-arm solution.
Right-Arm
Left-Arm
Right-Arm Mirror
Left-Arm Mirror
ATTENTION: Be sure to choose an arm solution before activating the
Kinematic function. Failure to do so can result in machine damage and/or
serious injury or death to personnel.

 Loading...
Loading...











