•
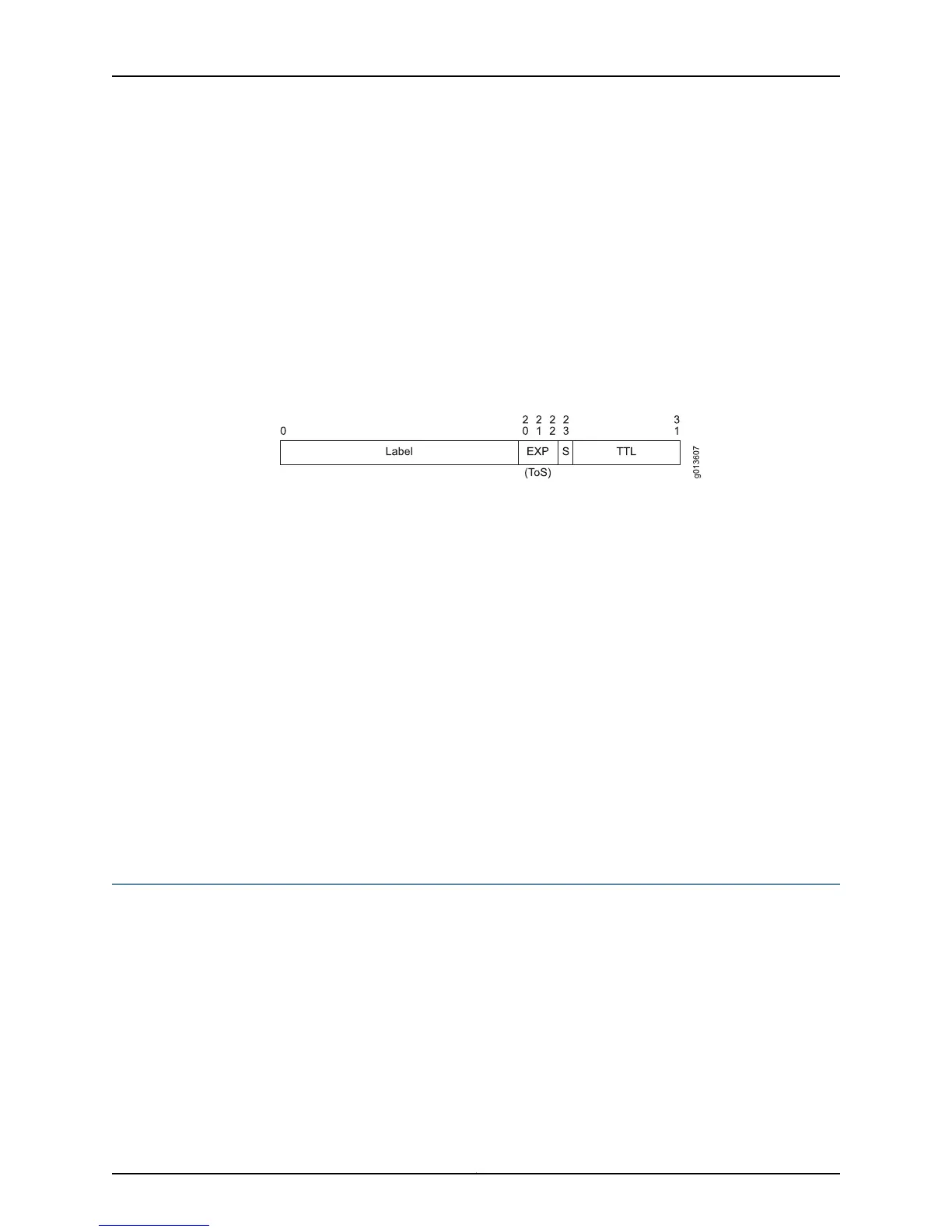
Label bits—Twenty bits
•
EXP bits—Three bits for class of service information; these bits are variously called the
experimental bits, class of service (CoS) bits, or type of service (ToS) bits. The EXP
bits are mapped from the IP packet at the ingress node and are mapped back into the
IP packet at the egress node.
•
S bit—One bit to indicate whether the label is on the bottom of the label stack.
•
TTL bits—Eight bits for a time-to-live indicator. The TTL bits are mapped from the IP
packet at the ingress node. The TTL bits in the shim header are decremented at each
hop. The bits are mapped back into the IP packet at the egress node. See“TTL
Processing in the Platform Label Space Overview” on page 222 for more information.
Figure 50: Shim Header
If you configure an MPLS interface to use the interface label space, the VPI/VCI
combinations are used as labels, so there is no need to place them within a shim header.
As the data travels along the LSP, the LSRs examine only the VPI/VCI combination. The
shim header is used only to carry the TTL bits to the egress, and is not visible to
intermediate LSRs. The ingress node learns the total hop count from signaling and then
uses that count to decrement the TTL to the correct final value. The TTL is then carried
in the shim header to the egress node without modification, arriving with the correct
count.
Related Topics MPLS Label Distribution Methodology on page 227•
• IP Data Packet Mapping onto MPLS LSPs Overview on page 229
• MPLS Forwarding and Next-Hop Tables Overview on page 233
• MPLS Interfaces and Interface Stacking Overview on page 236
• TTL Processing in the Platform Label Space Overview on page 222
• Topology-Driven LSPs Overview on page 255
TTL Processing in the Platform Label Space Overview
JunosE MPLS TTL processing is compliant with RFC 3443. The details of TTL processing
vary with the tunnel model that is configured for TTL processing, pipe or uniform.
To keep backward compatibility with earlier JunosE releases, you do not use the mpls
tunnel-model command to configure the tunnel model for TTL processing, That command
is used instead to configure the tunnel model for EXP bits processing. The default tunnel
model varies between TTL and EXP processing; for EXP processing, the default tunnel
model is pipe, while for TTL processing the default tunnel model is uniform.
You can issue the no mpls ip propagate-ttl command to change the TTL processing
tunnel model from the default uniform model to the pipe model. Issue the no mpls ip
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.222
JunosE 11.2.x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide
 Loading...
Loading...