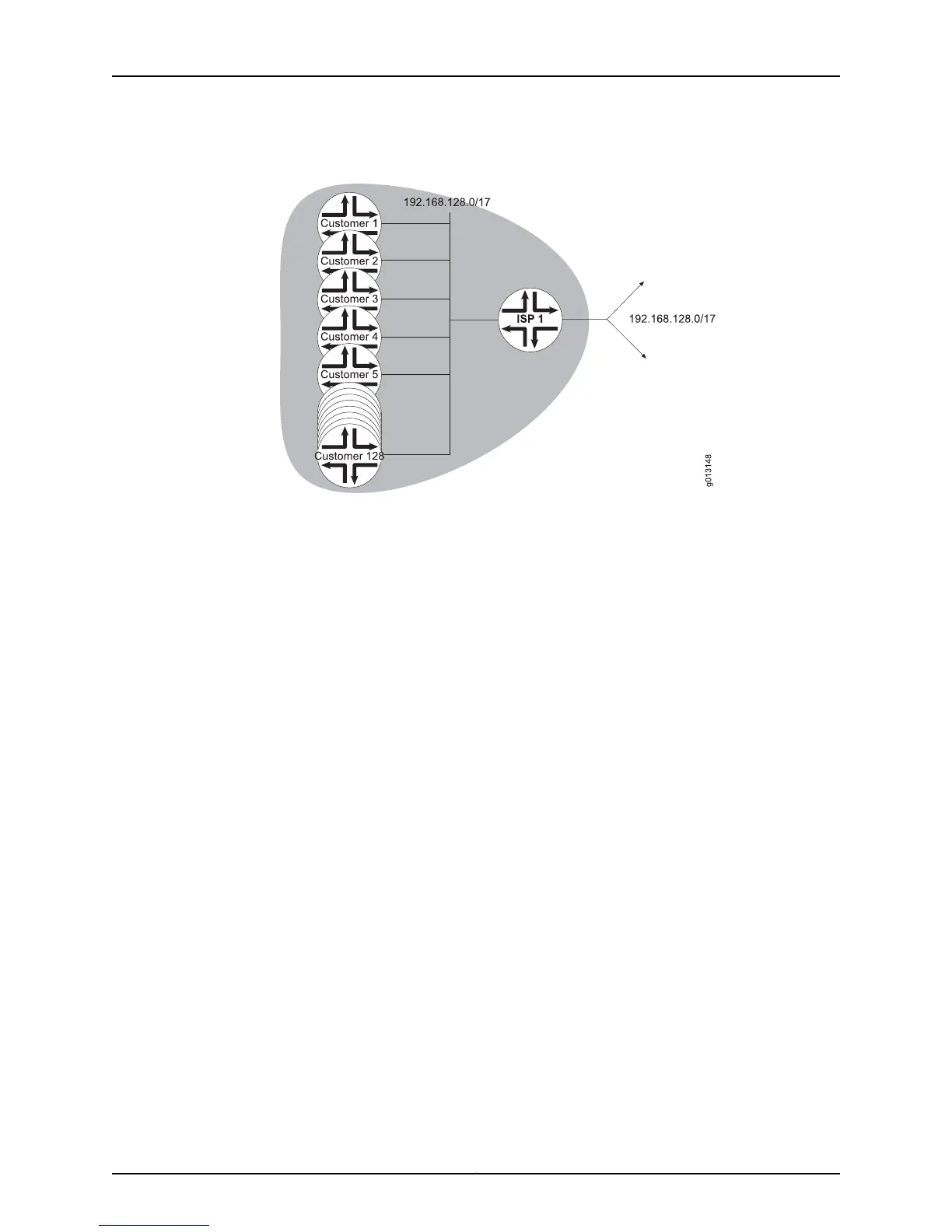
Figure 5: Routing with CIDR
Path Attributes
A path attribute provides some additional information about a route. If a BGP speaker
has more than one route to the same destination prefix, it selects one of those routes to
use (the “ best” route) based on the path attributes. BGP as implemented on the Juniper
Networks E Series Broadband Services Router specifies detailed and complex criteria
for picking the best route; this helps ensure that all routers will converge to the same
routing table, a necessary behavior to avoid routing loops. See “Selecting the Best Path”
on page 104 for more information.
The following are some of the most important path attributes:
•
AS-path specifies the sequence of autonomous systems that must be crossed to reach
a certain destination. This path attribute is used to avoid routing loops and to prefer
shorter routes over longer routes.
•
Next-hop specifies the IP address of the ingress router in the next autonomous system
on the path to the destination.
•
Local-pref and multiexit discriminator (MED) are metrics that administrators can tune
to ensure that certain routes are more attractive over other routes. The local-pref
attribute specifies a degree of preference that enables a router to select among multiple
routes to the same prefix. The MED is used for ASs that have more than one connection
to each other. The administrator of one AS sets the MED to express a degree of
preference for one link versus another; the BGP peer in the other AS uses this MED to
optimize traffic.
•
Originator-ID specifies the IP address of the router that originates the route. The router
ignores updates that have this attribute set to its own IP address.
•
Atomic-aggregate and aggregator inform peers about actions taken by a BGP speaker
regarding aggregation of routes. If a BGP speaker aggregates routes that have differing
path attributes, it includes the atomic-aggregate attribute with the aggregated prefix
to inform update recipients that they must not deaggregate the prefix. A BGP speaker
11Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Chapter 1: Configuring BGP Routing
 Loading...
Loading...