Outbound policies configured for peer groups are still inherited by peer group members,
but you cannot override this inherited outbound policy by configuring a different outbound
policy on individual members of that peer group with the following commands:
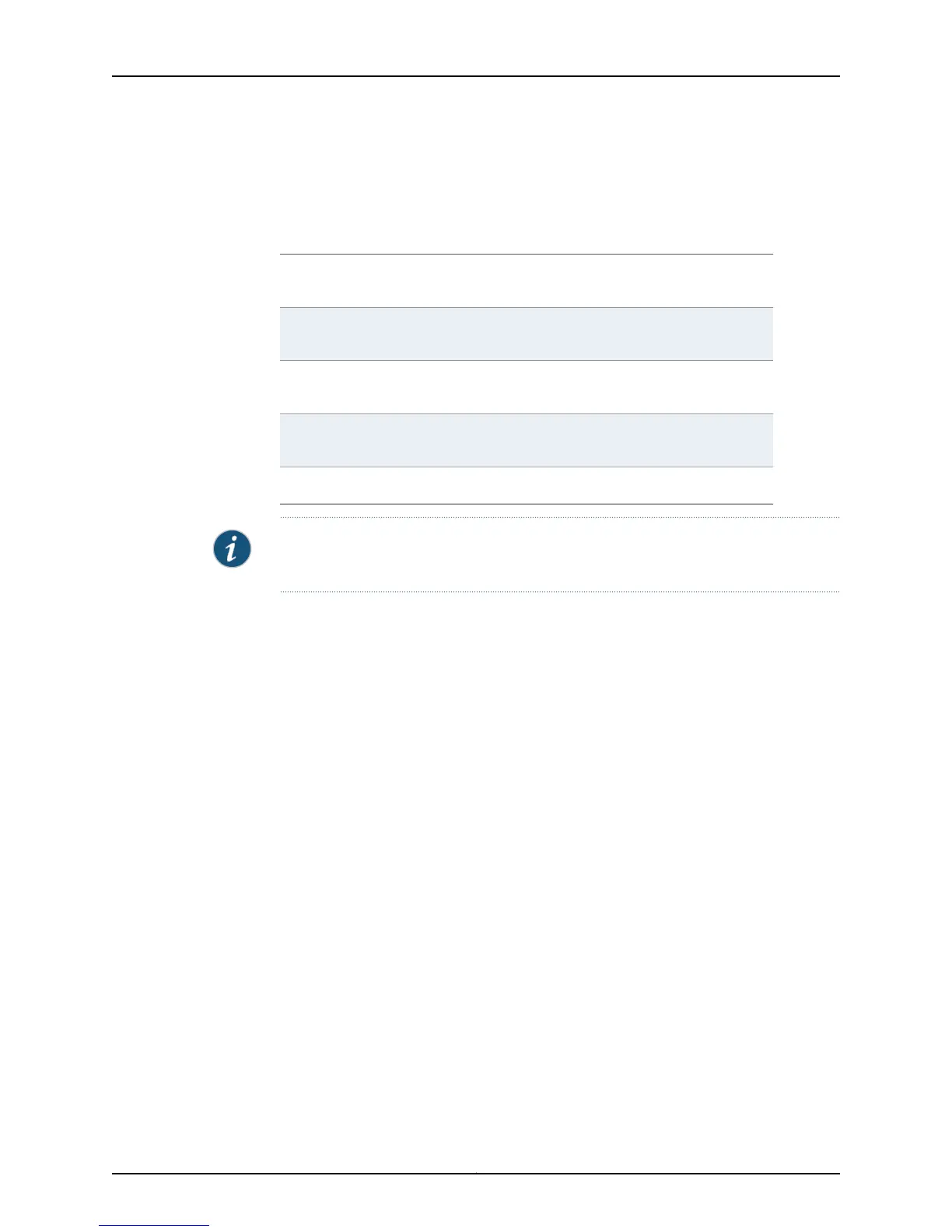
Table 12: Commands That Do Not Override Inherited Outbound Policy
neighbor route-map outneighbor
next-hop-unchanged
neighbor as-override
neighbor
route-reflector-client
neighbor prefix-list outneighbor
default-originate
neighbor send-communityneighbor prefix-tree outneighbor distribute-list
out
neighbor unsuppress-mapneighbor
remove-private-as
neighbor filter-list out
neighbor next-hop-self
NOTE: This restriction does not apply to inbound policy, which you can still override
per peer.
The update messages can vary for members of a peer group as follows:
•
The next hop can be different for each update sent to peer group members if the
members are all external peers.
•
The AS path can be different for each update sent to peer group members if the
members are all external peers if you have enabled AS override with the neighbor
as-override command.
Setting the BGP Identifier
By default, the router ID of the router is used as the BGP identifier. You can use the bgp
router-id command to configure an IP address as the BGP identifier.
bgp router-id
• Use to configure an IP address as the BGP identifier.
• Example
host1(config-router)#bgp router-id 10.25.1.1
• The new BGP identifier is used in open messages sent after you issue the command.
To use the new BGP identifier for sessions already in the established state, you must
use the clear ip bgp command to perform a hard clear.
• Use the no version to restore the router ID as the BGP identifier.
• See bgp router-id
25Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Chapter 1: Configuring BGP Routing

 Loading...
Loading...