The same address family identifier (AFI) and subsequent address family identifier (SAFI)
are used in the NLRI for VPWS and VPLS.
The VPWS NLRIs must be accompanied by a route-target extended community. PE
routers that receive VPN information can filter route advertisements with the route target
import lists and export lists. This route filtering enables the PE routers to control CE-to-CE
connectivity or full-mesh, hub-and-spoke, and overlapping VPNs as is done in L3VPNs.
A VPWS NLRI is uniquely identified by the route distinguisher, site ID (CE-ID), and the
label block offset.
In addition to the site ID and label block information, BGP also signals control flags that
indicate whether a control word is included in the encapsulation and whether packets
have a sequence number. If a control word mismatch occurs, the pseudowire remains in
a down state with a status of control word mismatch.
A control status vector is sent along with the other NLRI information. This vector carries
the operational state of the local layer 2 interfaces between the PE router and CE device
for a given VPWS instance. A TLV type of 1 is used currently to interoperate with Junos
OS.
Related Topics Configuring BGP-MPLS Applications on page 383•
• Configuring VPLS on page 589
VPWS Components Overview
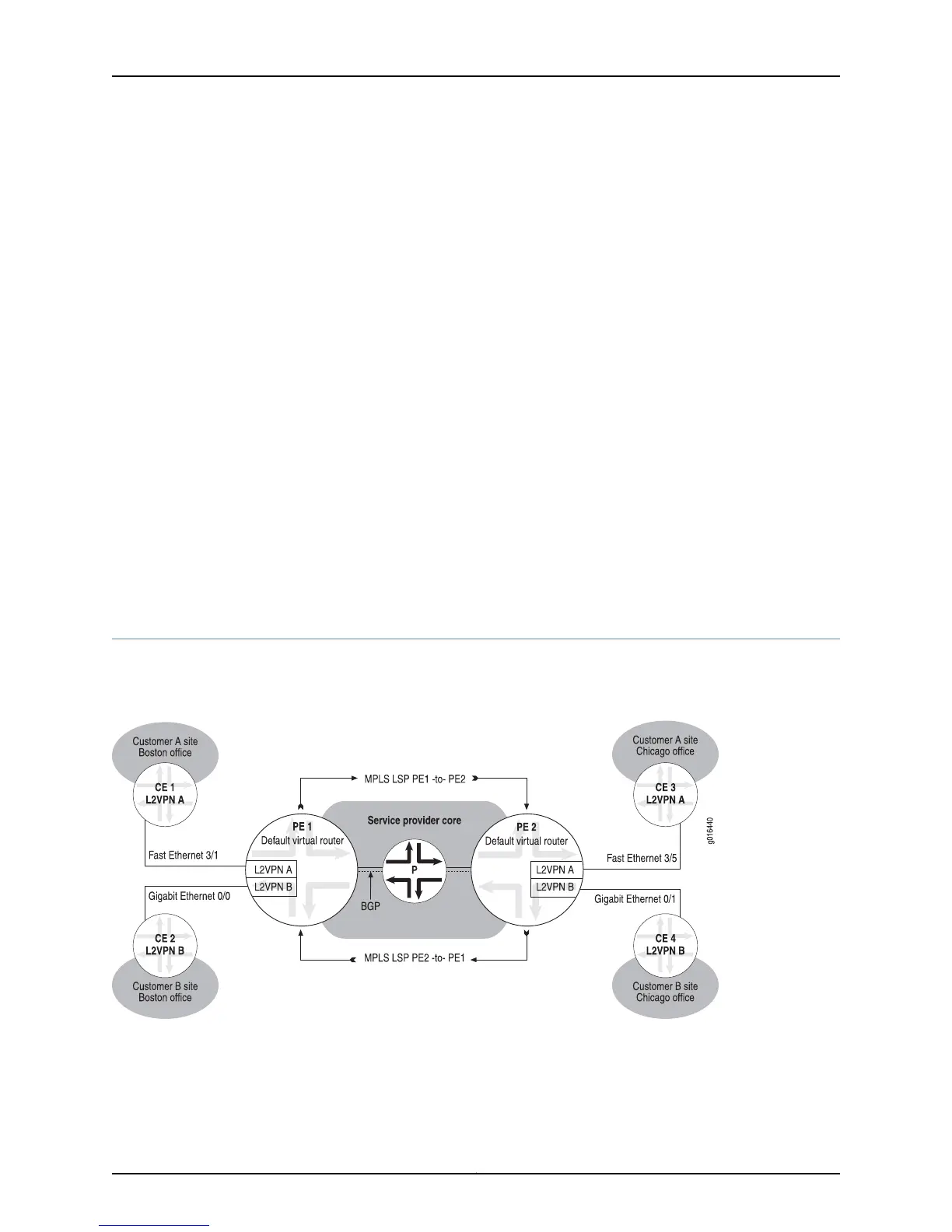
Figure 132 on page 642 shows the components of a typical VPWS L2VPN topology.
Figure 132: VPWS Components
•
VPWS Instances on page 643
•
Customer Edge Devices on page 643
•
VPWS Provider Edge Devices on page 643
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.642
JunosE 11.2.x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide
 Loading...
Loading...