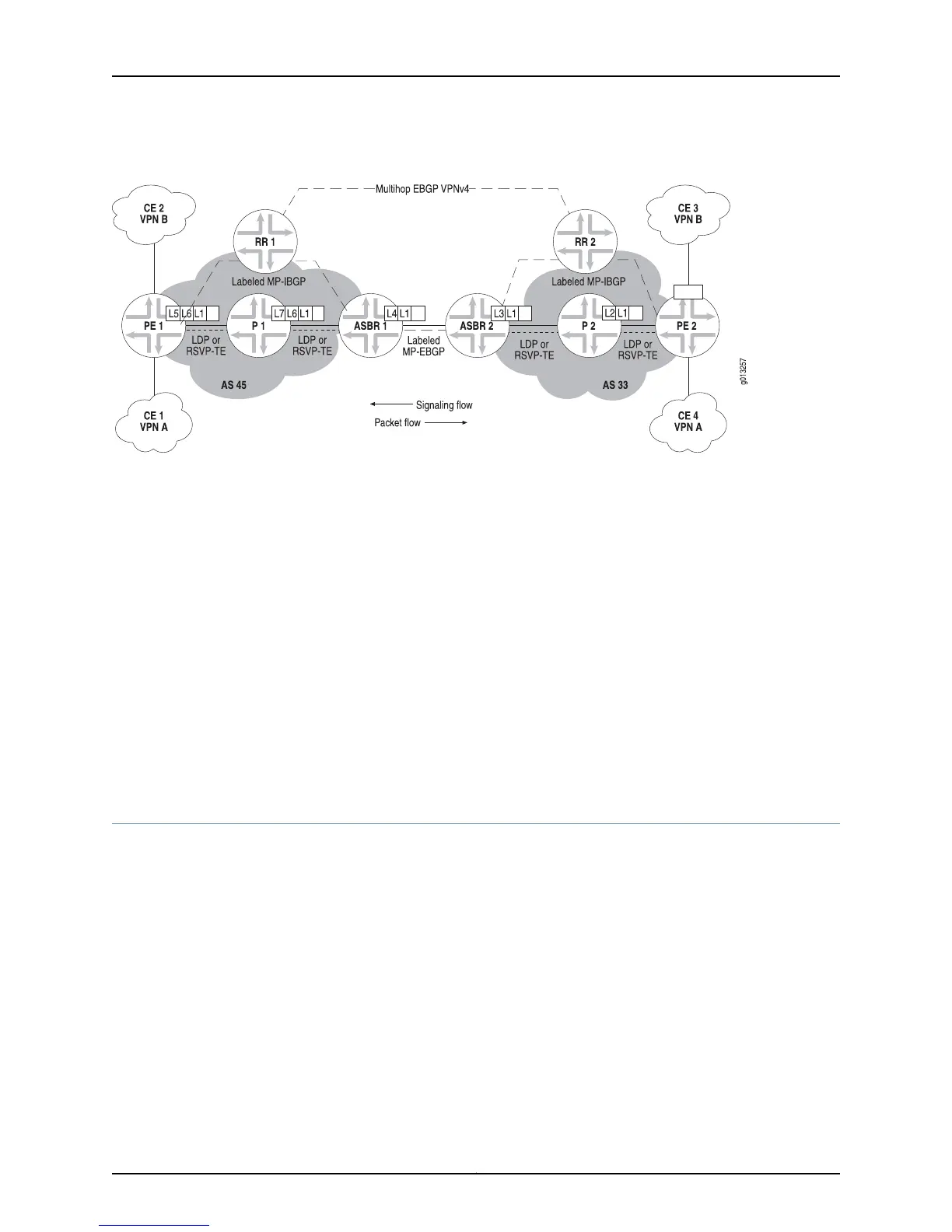
Figure 80: Topology for Inter-AS Option C with Route Reflectors
neighbor next-hop-unchanged
• Use to prevent BGP from modifying the next hop sent to the BGP peer.
• Outbound route maps take precedence over this command, enabling prefixes that
match the route map to be modified, regardless of this command.
• Takes effect immediately.
• Example
host1:vr1(config-router-af)#neighbor next-hop-unchanged 10.24.15.32
• Issuing this command automatically removes the neighbor next-hop-self configuration
(enabled or disabled) on the peer or peer group. Issuing the no or default version of
this command has no effect on the neighbor next-hop-self configuration.
• Use the no version to reenable BGP to modify the next hop.
• See neighbor next-hop-unchanged.
Providing IPv6 VPN Services Across Multiple Autonomous Systems
The JunosE Software supports inter-AS services for IPv6 VPNs in addition to IPv4 VPNs.
See “Providing IPv4 VPN Services Across Multiple Autonomous Systems” on page 401 for
more information about inter-AS services and IPv4 VPNs.
The JunosE Software currently supports only 2547bis option B for IPv6 VPNs. This
method—described in RFC 4364—BGP/MPLS IP Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
(February 2006)—uses BGP to signal VPN labels between the AS boundary routers
(Figure 81 on page 409). The base MPLS tunnels are local to each AS. Stacked tunnels
run from end to end between PE routers on the different ASs. This method enhances
scalability, because only the BGP RIBs store all the inter-AS VPN routes.
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.408
JunosE 11.2.x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide
 Loading...
Loading...