• Use the no version to restore the default, preventing the redistribution of default routes.
• See default-information originate.
Setting a Static Default Route
You might not want your routers to rely on dynamically learned default routes. Instead,
you might prefer to specify a static default route that your routers use to forward traffic
when they do not have a routing entry for a destination. Use the ip route command to
configure a default route on a router. The static route can point to a network number, an
IP address, or a physical interface. You can add a distance value to give preference to a
specific static route when multiple entries exist for the same route.
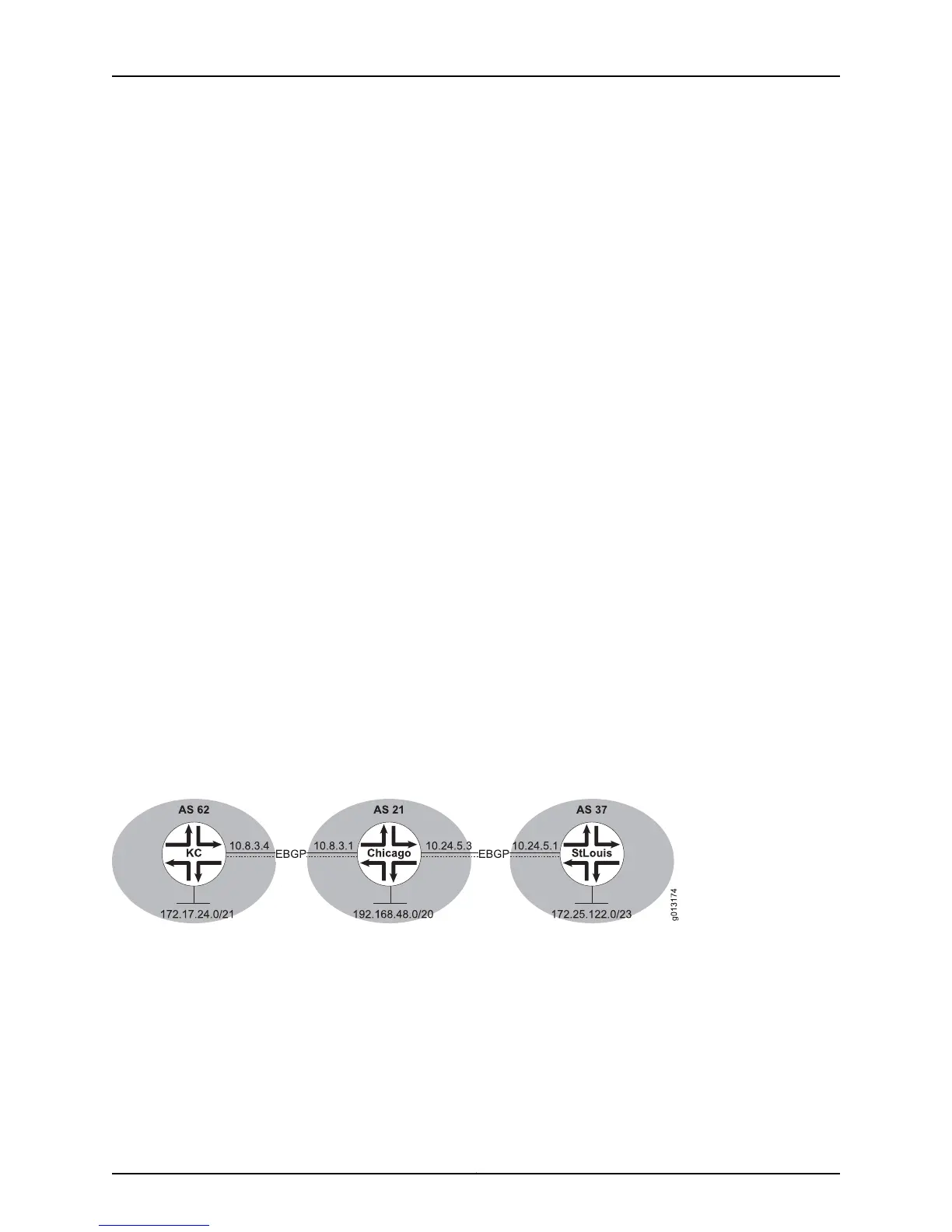
Suppose that in Figure 16 on page 57, router KC has been configured to advertise a default
route to router Chicago:
host1(config)#router bgp 62
host1(config-router)#network 172.17.24.0 mask 255.255.248.0
host1(config-router)#neighbor 10.8.3.1 remote-as 21
host1(config-router)#neighbor 10.8.3.1 default-originate
You prefer that router Chicago send traffic with unknown destinations to router StLouis,
so you configure a static default route on router Chicago:
host2(config)#router bgp 21
host2(config-router)#network 192.168.48.0 mask 255.255.240.0
host2(config-router)#neighbor 10.8.3.4 remote-as 62
host2(config-router)#neighbor 10.24.5.1 remote-as 37
host2(config-router)#exit
host2(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.25.122.0
Router StLouis is configured to advertise network 172.25.122.0/23 to router Chicago:
host3(config)#router bgp 37
host3(config-router)#network 172.25.122.0 mask 255.255.254.0
host3(config-router)#neighbor 10.24.5.3 remote-as 21
Figure 16: Setting a Static Default Route
ip route
Use to establish static routes.•
• Use the no version to remove static routes.
• See ip route.
57Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Chapter 1: Configuring BGP Routing

 Loading...
Loading...