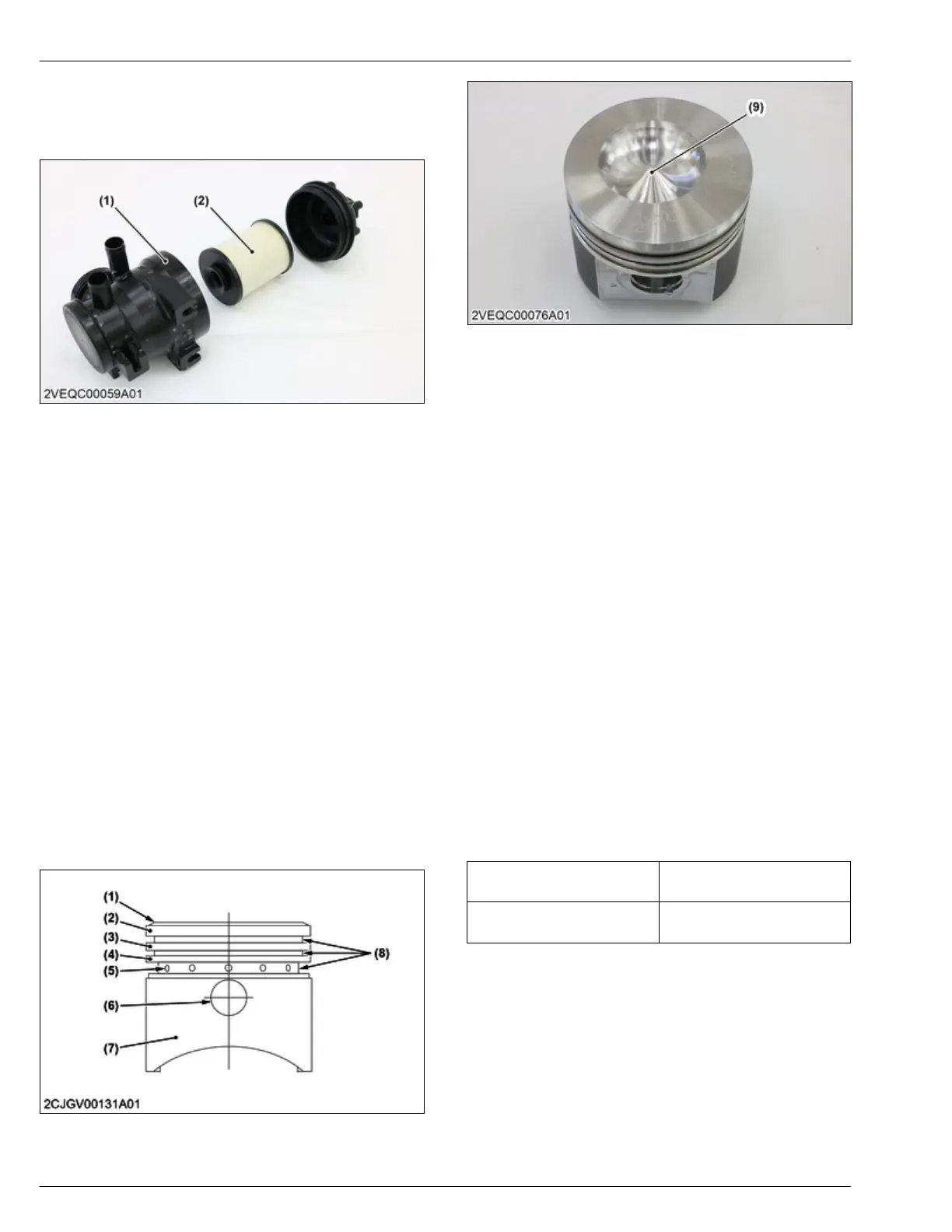
2.7.2 Structure of oil separator
The oil
separator is made up of a separator body and
element.
(1) Separator body (2) Element
2.7.3 Function of oil separator
The oil separator separates oil and gases in the blow-
by gases.
Part that returns oil to the oil pan.
The
blow-by
gas that escapes from the crankcase is
separated into oil and gases when it passes through
the element in the oil separator.
Separated oil is returned to the oil pan and the blow-by
gas is fed to the intake side hose.
The gas fed to the intake hose is re-combusted.
2.8 Piston
2.8.1 Outline of piston
The piston converts the explosive energy from
combustion to reciprocating motion.
2.8.2 Structure of piston
The piston is a re-entrant shape.
The piston skirt has a molybdenum coating.
(1) Piston head
(2) T
op land
(3) Second land
(4) Third land
(5) Oil return hole
(6) Piston pin hole
(7) Piston skirt
(8) Ring groove
(9) Piston profile (re-entrant
shape)
2.8.3 Function of piston
Along with the cylinder and cylinder head, the piston
forms the combustion chamber
.
In
addition, it reciprocates in the cylinder during each of
the intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust
strokes.
The first and primary role is to receive explosive energy
during combustion and transfer this to the crankshaft
via the connecting rod.
The piston surface is formed to provide swirl that
simplifies combustion of fuel injected from the injector.
Piston's skirt is coated with molybdenum disulfide,
which reduces the piston slap noise and thus the entire
operating noise.
Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2)
The molybdenum disulfide serves as a solid lubricant,
like a Graphite or Teflon.
This material helps resist metal wears even with little
lube oil.
2.8.4 Specification of piston
Piston diameter (D)
87.0 mm
3.43 in.
Oversize
+0.25 mm
+0.0098 in.
4. ENGINE
MECHANISM
2. Engine body
D1803-CR-E4,D1803-CR-TE4,D1803-CR-TIE4,V2403-CR-E4,V2403-CR-TE4,V2403-CR-TE4BG,V2403-CR-TIE4
 Loading...
Loading...