Program features 67
Notes:
• Actual motor shaft speed is not needed for motor control.
• Vector control also requires measurement of the DC voltage and two motor phase
currents.
The difference of vector control from the traditional control are:
- Torque control operates at the same time level as the power switch control.
- There is no separate voltage and frequency controlled PWM modulator.
- The output stage switching is based on the electromagnetic state of the motor.
- The best motor control accuracy is achieved by activating a separate motor.
identification run (normal ID run).
See also section Speed compensated stop (page 76).
Settings
• Main menu Motor data or Main menu Complete parameter list
parameter 99.04.
• Parameter 99.13 ID run requested (page 368).
Speed control performance figures
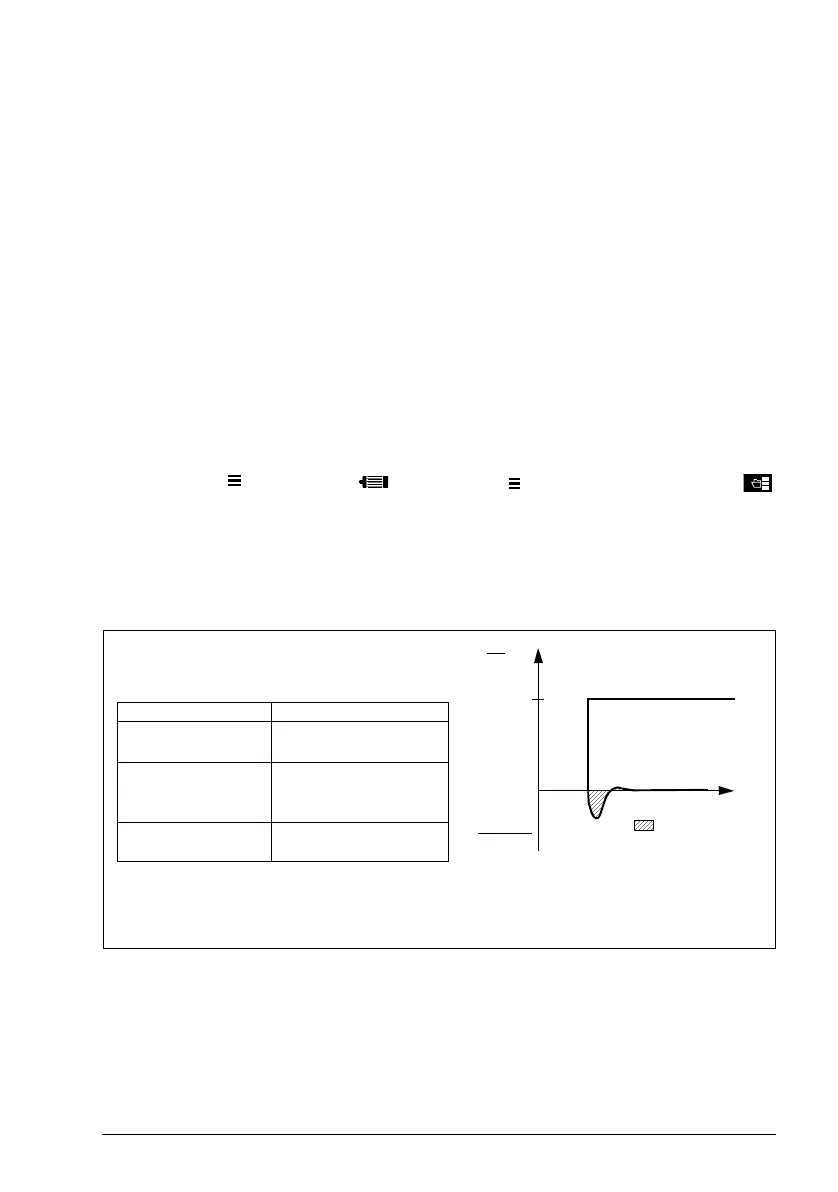
The table below shows typical performance figures for speed control.
100
t (s)
T
T
N
(%)
T
load
n
act
-n
ref
n
N
Area < 10% s
T
N
= rated motor torque
n
N
= rated motor speed
n
act
= actual speed
n
ref
= speed reference
Speed control Performance
Static accuracy 20% of motor nominal
slip
Dynamic accuracy < 10% s with 100%
torque step (with default
speed controller tuning)
Tuned speed
controller
< 2% s with 100%
torque step

 Loading...
Loading...