84Service Manual – SC5000 20 - Drive System
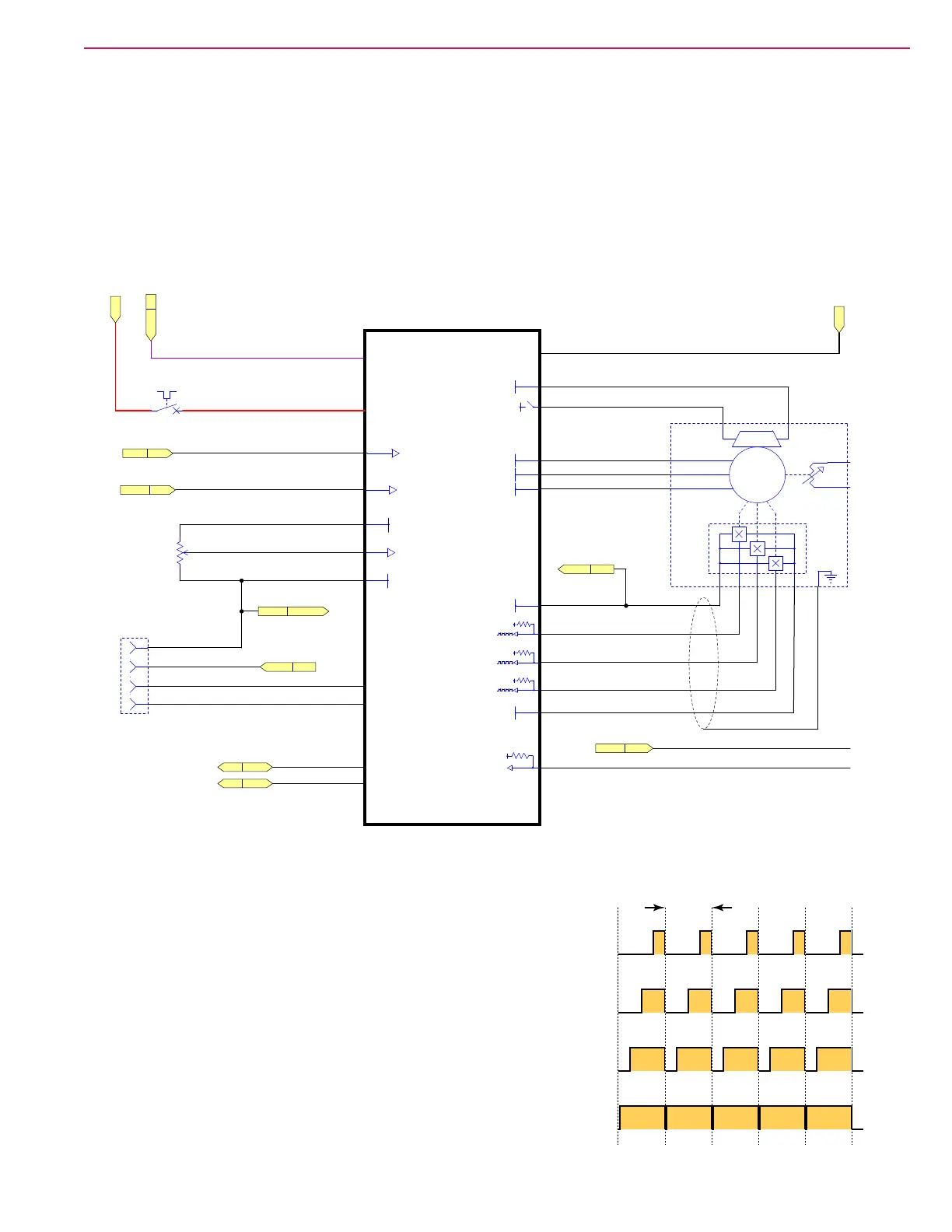
Drive Controller
The KSI relay provides logic power to the drive controller. When the main machine controller is not
energizing the KSI relay, the drive controller has no logic power. However, the drive controller has
unswitched power through the CB2 circuit breaker, which provides separate high-current power output
for the motor control. The drive controller also monitors the E-stop switch and seat switch, so that either
one can disable the drive output. Output is disabled if either the seat switch or E-stop is open. The drive
controller also receives many of its operating parameters from the main machine controller.
The motor contains an electromechanical brake, that releases only when power is present. The drive
controller releases the brake when the wheel motor is commanded to turn.
CB2
A4
Drive Controller
Pedal
Drive
EM Brake
Motor
Wheel
[BLDC]
Programmer
Connector
X219
RED/VIO
VIO
BLU
GRY
VIO/YEL
GRY
RED/VIO
PNK/BLU
PNK/YEL
YEL
BLU/GRY
BLU/YEL
VIO
RED
RED
RED
RED
RED
VIO/ORN
GRY
VIO/GRN
RED
BLK
J5-15
J5-9
J5-8
J5-12
J5-21
J5-20
J5-19
J5-18
J5-3
J5-2
J5-22
J5-4
J5-6
J5-13
J5-10
J5-1
B+ Lug
J4-1
J4-2
B- Lug
+5V
B-
15V
15V
15V
M
3Ø
U
Vcc Gnd
H
U
H
V
H
W
V
W
1 2 3 6
3
4
Encoder
4 5
Thermistor
M10
Y1
12
1 2
C
B
A
1
2
3
4
70 AMP
KSI
DATA
CL
EM BRAKE
U1
B-
E-Stop
TEMP SENSOR1
W
I/O GND
V1
WIPER
R4
W1
15V
5V
U
36V
Seat SW
V
CAN(1) L
CAN(1) H
B-
B+
KSI MMC
CAN1HMMC
CAN1LMMC
Batt+
E-Stop MMC
Seat SW MMC
Sig Gnd Thermistor
Sig Gnd DRIVE
15V Out DRIVE
15V Out PROG
Batt-
The drive motor is controlled from a Phoenix drive controller, which is a 3-phase motor controller for battery
operated equipment. The controller generates a square wave, 3-phase, pulse-width-modulated output to
the motor. The speed controller is designed specically for DC motors
with remote commutation. Pulse-width-modulation (PWM) is a form of
motor speed control that alters the power to a motor by rapidly turning
the power on and off. The ratio (also called “duty cycle”) between the
On and Off states determines how much power the motor receives. The
shorter the “off-time” the closer to full power the motor will receive. This
switching occurs so fast (15kHz for this controller) that the motor simply
sees it as a reduction in power (voltage) instead of the rapid on/off. PWM
is a standard motor control technique because it is easier to turn power
all the way on and all the way off, than it is to vary the magnitude of the
power. Varying the magnitude would create a lot of heat that would need
to be dissipated.
25% PWM Duty Cycle
50% PWM Duty Cycle
75% PWM Duty Cycle
100% PWM Duty Cycle
1-Cycle
(15kHz)

 Loading...
Loading...