Electrical Installation
3
3.14 Decrease Noise
SIEPYEUOQ2A01A AC Drive Q2A Technical Manual 107
3.14 Decrease Noise
Note:
The main circuit terminal block for the drive and the terminal block for the noise filter come in different shapes. Use caution when you
prepare the ends of the wires.
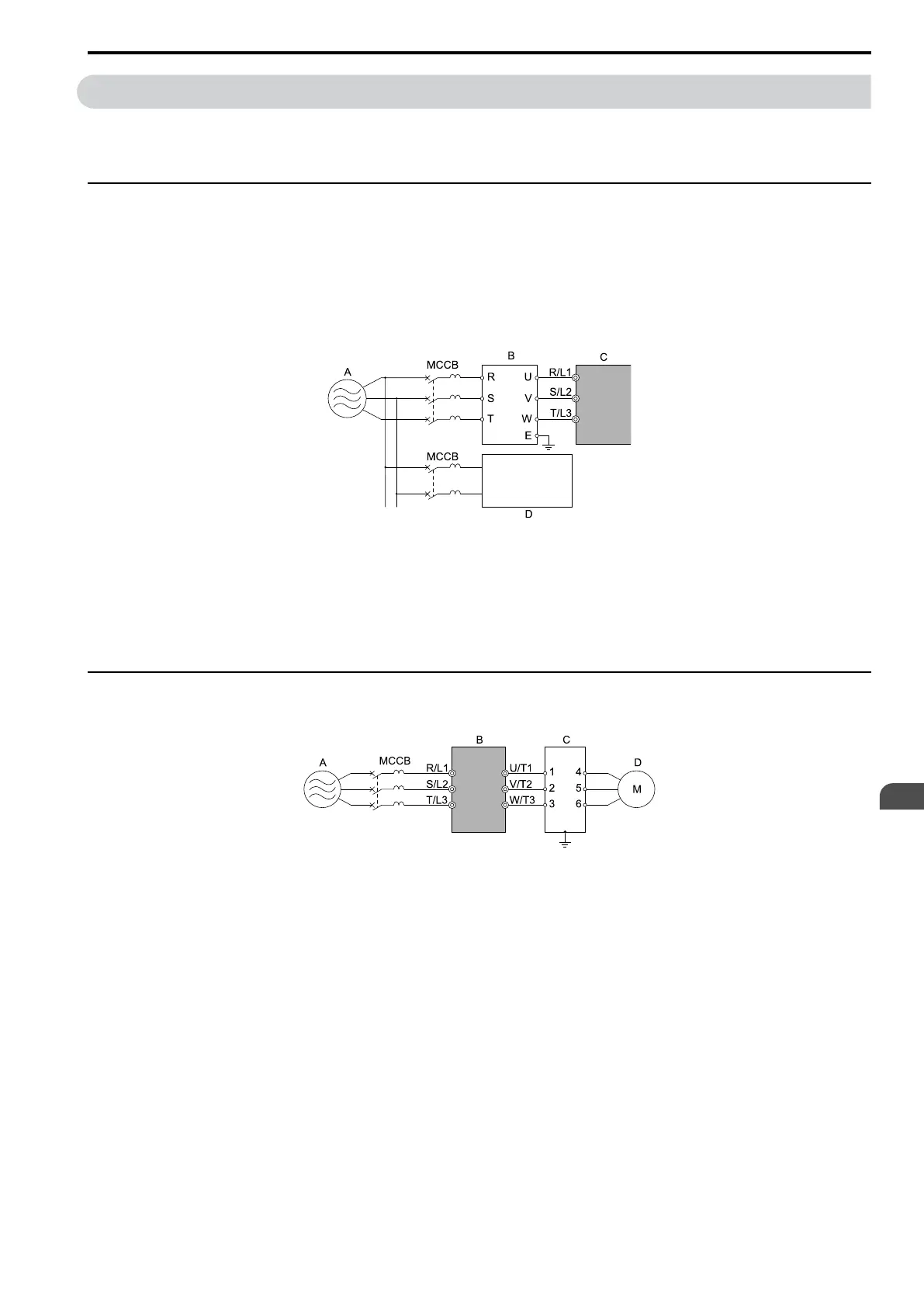
◆ Connect a Noise Filter to the Input Side (Primary Side)
High-speed switching makes noise in the drive output. This noise flows from the drive to the power supply, and
can possibly have an effect on other equipment. Install a noise filter to the input side of the drive to decrease the
quantity of noise that flows to the power supply. A noise filter also prevents noise from entering the drive from the
power supply.
• Use a noise filter specially designed for drives.
• Install the noise filter as close as possible to the drive.
A - Power supply
B - Input side (primary side) noise
filter
C - Drive
D - Other controller
Note:
The input side (primary side) noise filter model is LNFD-xx.
Figure 3.59 Example of Connecting the Noise Filter on the Input Side (Primary Side)
◆ Connect a Noise Filter to the Output Side (Secondary Side)
A noise filter on the output side of the drive decreases inductive noise and radio frequency interference.
A - Power supply
B - Drive
C - Noise filter on output side
(secondary side)
D - Motor
Figure 3.60 Example of Connecting the Noise Filter on the Output Side (Secondary Side)
NOTICE: Do not connect phase-advancing capacitors or LC/RC noise filters to the output circuits. Failure to obey can cause
damage to the drive, phase-advancing capacitors, LC/RC noise filters, and leakage breakers (ELCB, GFCI, or RCM/RCD).
Glossary
• Radio frequency interference:
Electromagnetic waves radiated from the drive and cables make noise through the full radio bandwidth that can
have an effect on nearby devices.
• Inductive noise:
The noise from electromagnetic induction can have an effect on the signal line and can cause the controller to
malfunction.

 Loading...
Loading...











