Electrical Installation
3
3.6 Control I/O Connections
SIEPYEUOQ2A01A AC Drive Q2A Technical Manual 93
3.6 Control I/O Connections
This section gives information about the settings for the listed control circuit I/O signals.
• MFDI (terminals DI1 to DI8)
• MFDO (terminals 2NO, 2CM, 3NO, 3CM, 4NO, and 4CM)
• Pulse train output (terminal PO)
• MFAI (terminals AI1 to AI3)
• PTC input (terminal AI3)
• MFAO (terminals AO1, AO2)
• Modbus communications (terminals RS485+, RS485-, A0V)
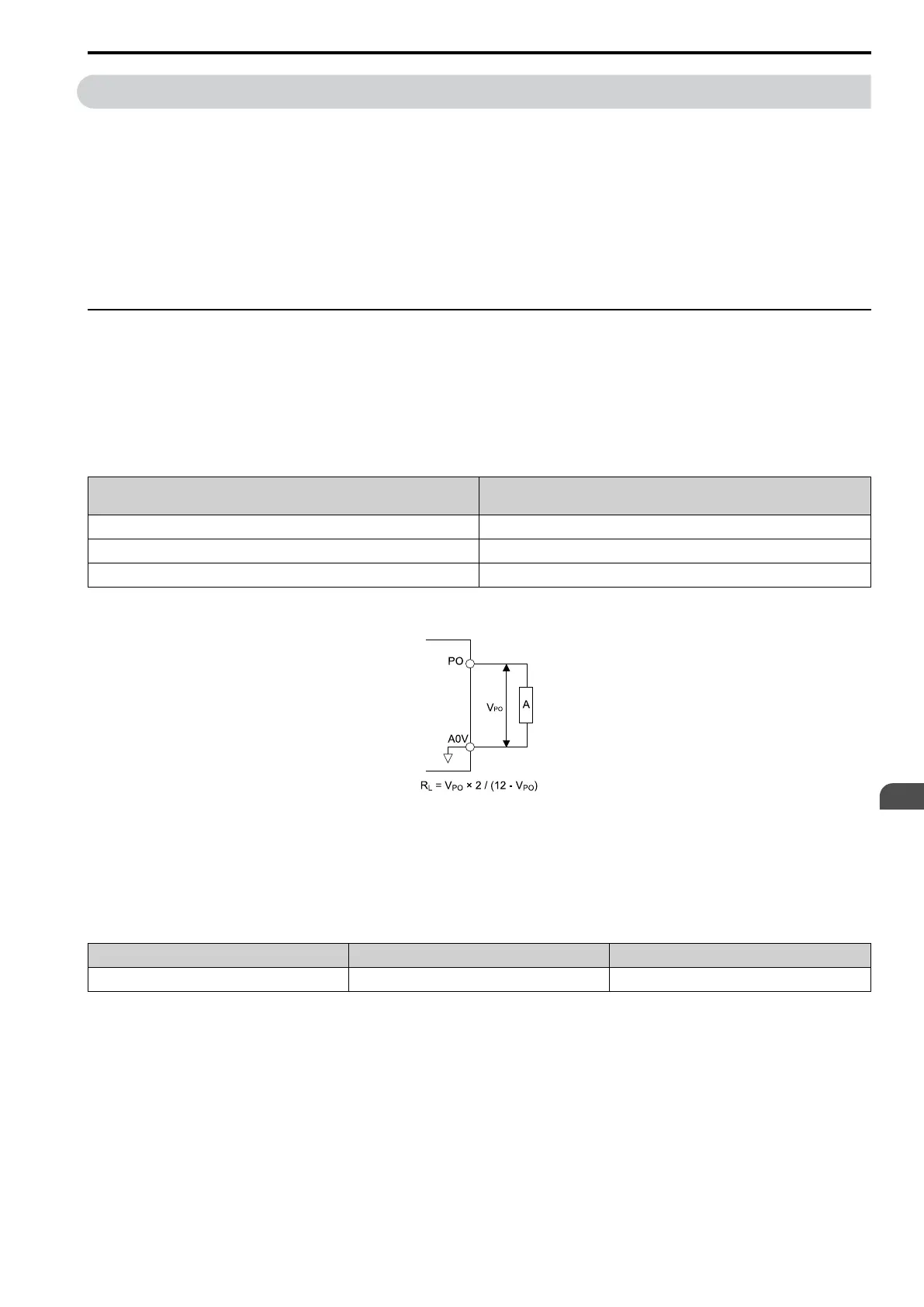
◆ Pulse Train Output (Terminal PO)
You can use pulse train monitor output terminal PO for sourcing mode or for sinking mode.
NOTICE: Connect peripheral devices correctly. Failure to obey can cause incorrect drive operation and damage to the drive or
connected circuits.
■ Use for sourcing mode
The load impedance changes the voltage level of the pulse train output signal.
Load Impedance
R
L
(kΩ)
Output Voltage
V
MP
(V)
1.5 kΩ or more 5 V or more
4.0 kΩ or more 8 V or more
10 kΩ or more 10 V or more
Note:
Use the formula in Figure 3.43 to calculate the necessary load resistance (kΩ) to increase output voltage (V)
MP
.
A - Load impedance
Figure 3.43 Wiring to Use Pulse Train Output in Sourcing Mode
■ Use in sinking mode
The external power supply changes the voltage level of the pulse train output signal. Keep the voltage from an
external source between 10.8 Vdc to 16.5 Vdc. Adjust the load impedance to keep the current at 16 mA or lower.
External Power Supply (V) Load Impedance (kΩ) Sinking Current (mA)
10.8 Vdc to 16.5 Vdc 1.0 kΩ or more 16 mA maximum

 Loading...
Loading...











