21-18
Cisco Security Appliance Command Line Configuration Guide
OL-10088-01
Chapter 21 Using Modular Policy Framework
Modular Policy Framework Examples
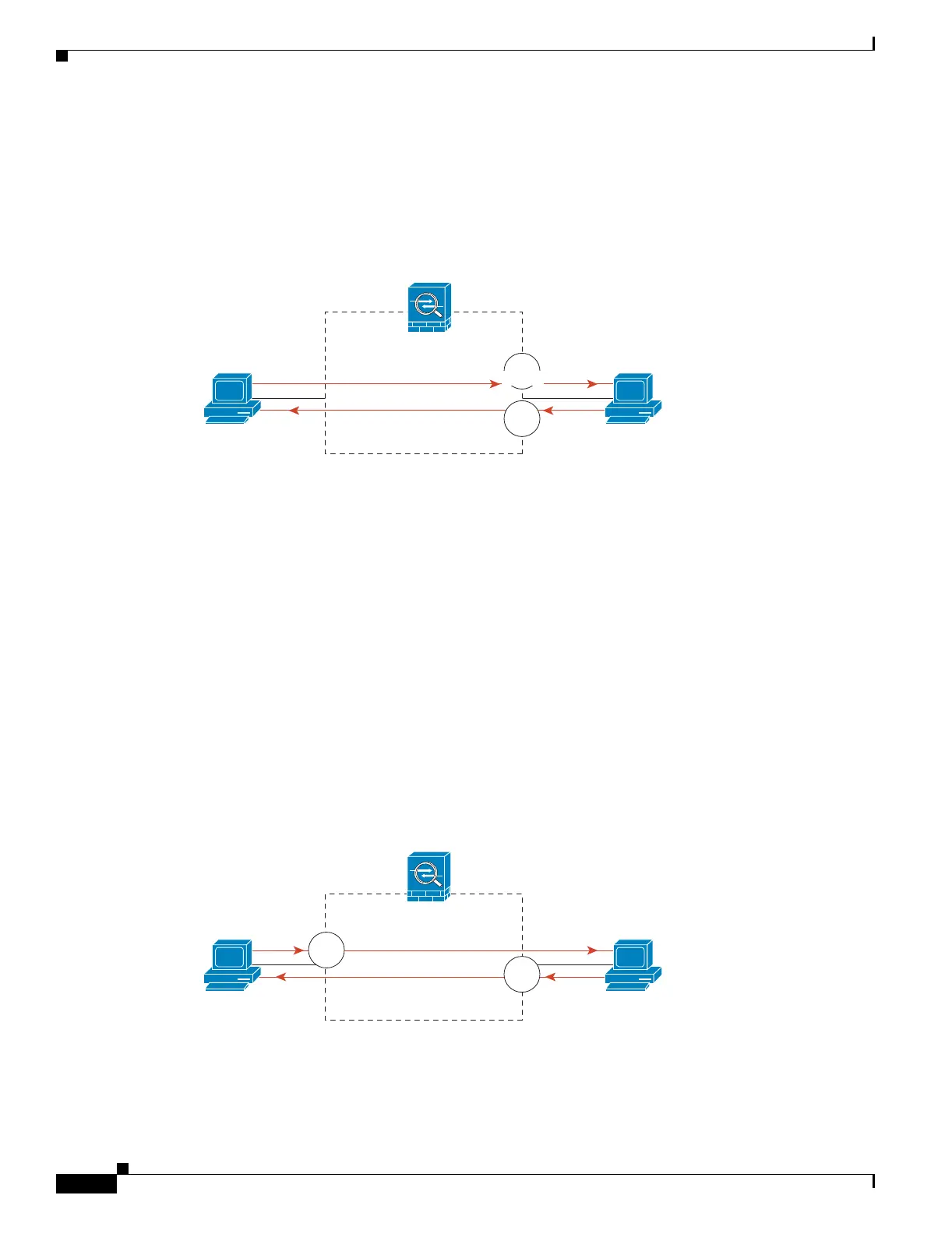
Applying Inspection and QoS Policing to HTTP Traffic
In this example (see Figure 21-1), any HTTP connection (TCP traffic on port 80) that enters or exits the
security appliance through the outside interface is classified for HTTP inspection. Any HTTP traffic that
exits the outside interface is classified for policing.
Figure 21-1 HTTP Inspection and QoS Policing
See the following commands for this example:
hostname(config)# class-map http_traffic
hostname(config-cmap)# match port tcp eq 80
hostname(config)# policy-map http_traffic_policy
hostname(config-pmap)# class http_traffic
hostname(config-pmap-c)# inspect http
hostname(config-pmap-c)# police output 250000
hostname(config)# service-policy http_traffic_policy interface outside
Applying Inspection to HTTP Traffic Globally
In this example (see Figure 21-2), any HTTP connection (TCP traffic on port 80) that enters the security
appliance through any interface is classified for HTTP inspection. Because the policy is a global policy,
inspection occurs only as the traffic enters each interface.
Figure 21-2 Global HTTP Inspection
See the following commands for this example:
hostname(config)# class-map http_traffic
hostname(config-cmap)# match port tcp eq 80
143356
inside
port 80
outside
A
Host A
Host B
port 80
Security
appliance
insp.
insp.
police
inside
port 80
outside
A
Host A
Host B
port 80
insp.
insp.
Security
appliance
143414

 Loading...
Loading...











