37-21
Cisco Security Appliance Command Line Configuration Guide
OL-10088-01
Chapter 37 Configuring WebVPN
Configuring File Access
The Application Access window appears. Application Access is now enabled.
Configuring File Access
The Common Internet File System (CIFS) protocol provides users with network access to files, printers,
and other machine resources. Microsoft implemented CIFS for networks of Windows computers,
however, open source implementations of CIFS provide file access to servers running other operating
systems, such as Linux, UNIX, and Mac OS X.
WebVPN serves remote users with HTTPS portal pages that interface with a proxy CIFS client running
on the security appliance. Using this client, WebVPN provides users with network access to the files on
the network, to the extent that the users meet user authentication requirements and the file properties do
not restrict access. The client is transparent; the portal pages delivered by WebVPN provide the
appearance of direct access to the file systems.
When a user requests a list of files, WebVPN queries the server designated as the master browser for the
IP address of the server containing the list. The security appliance gets the list and delivers it to the
remote user on a portal page.
WebVPN lets the user invoke the following CIFS functions, depending on user authentication
requirements and file properties:
• Navigate and list domains and workgroups, servers within a domain or workgroup, shares within a
server, and files within a share or directory
• Create directories
• Download, upload, rename, move, and delete files
The security appliance requires a master browser or WINS server, typically on the same network as the
security appliance or reachable from that network, to query the network for a list of servers when the
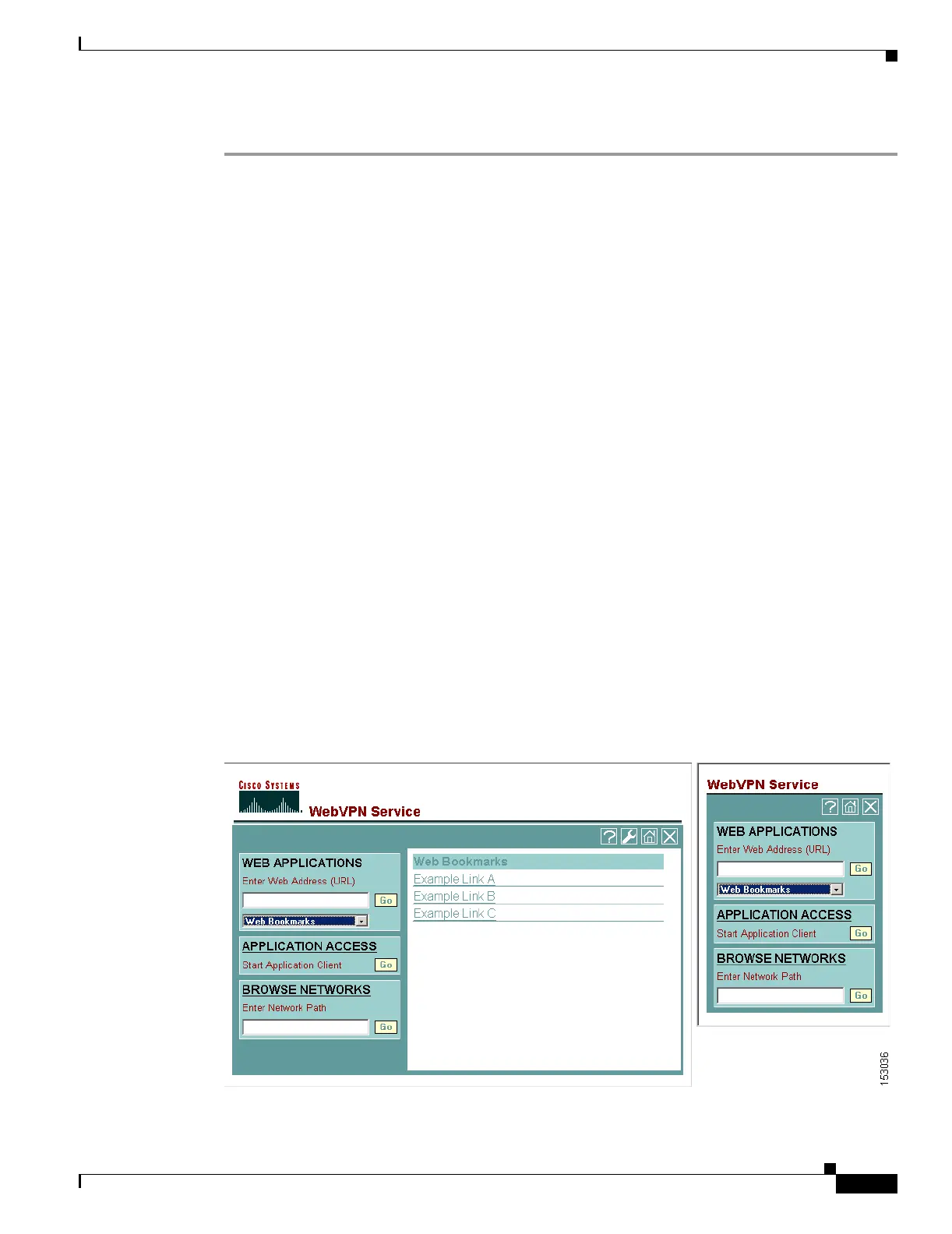
remote user clicks Browse Networks on the WebVPN home page or toolbar (Figure 37-5).
Figure 37-5 Browse Networks on the WebVPN Home Page and Floating Toolbar
 Loading...
Loading...











