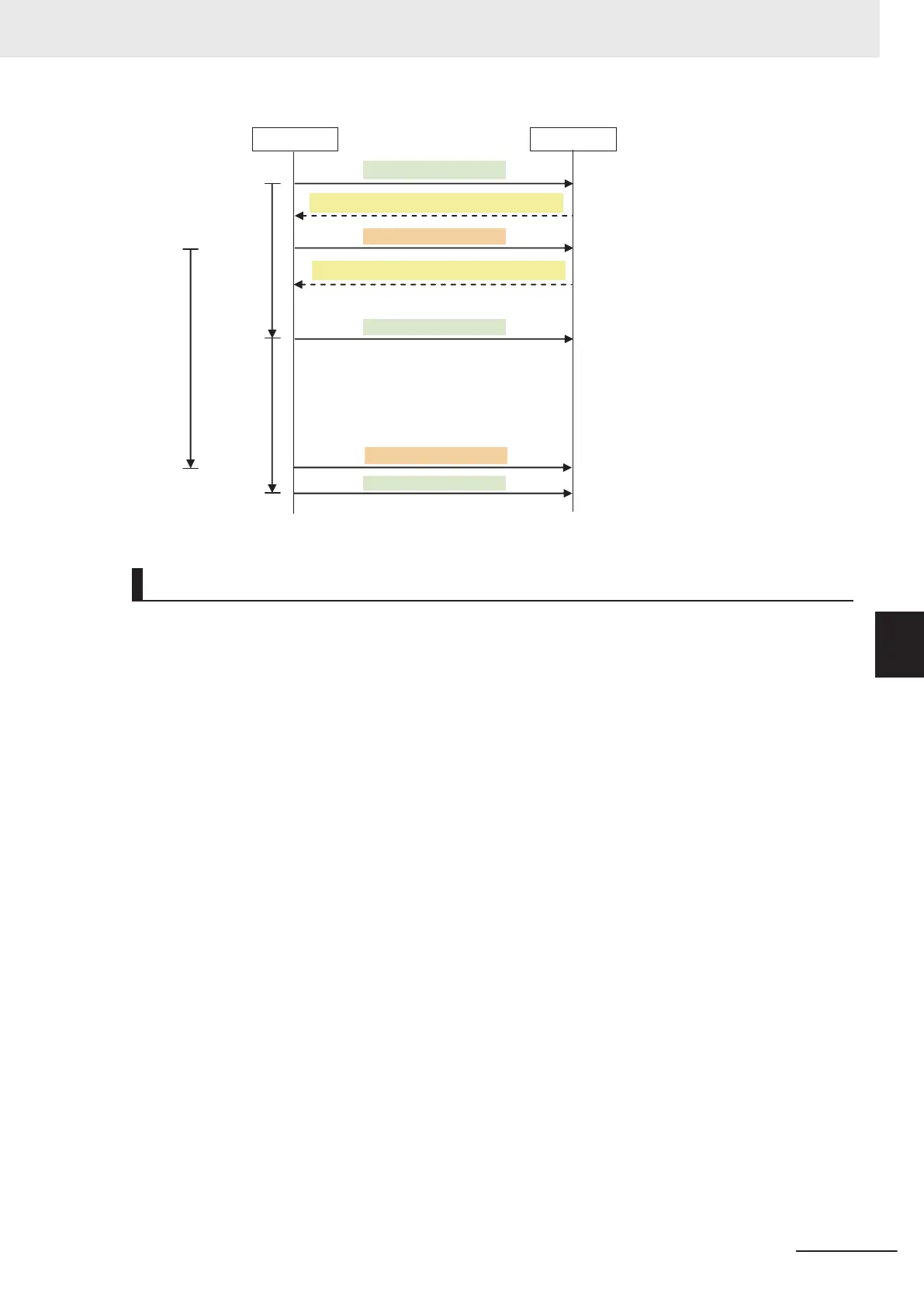
10 ms
15 ms
10 ms
100-ms interval
100-ms interval
Originator
Output data 1
Output data 2
Output data 1
Connection 2 heartbeat
Output data 2
Connection 1 heartbeat
Output data 1
Target
Node 2
Node 1
Requested Packet Interval (RPI) and Bandwidth Usage (PPS)
The number of packets transferred each second is called the used bandwidth, or PPS (packets per
second).
The PPS is calculated from the RPI and heartbeat for each connection as follows:
PPS for a connection (pps)
= (1,000/RPI (ms)) + (1,000/Heartbeat transmission period (ms))
Use the following equation to calculate the total number of packets transferred by each built-in Ether-
Net/IP port (Unit) in 1 second.
T
otal PPS for the built-in EtherNet/IP port = Total PPS of originator connections + Total PPS of target
connections (*)
* Connections set as target connections must be added, too.
The following shows the maximum number of packets that each CPU Unit can send and receive per
second via the built-in EtherNet/IP port through tag data links (i.e., the bandwidth allowed for the Unit).
You need to consider these values when configuring connections.
• NX701 CPU Unit: 40,000 pps
• NX102 CPU Unit: 12,000 pps
• NX1P2 CPU Unit: 3,000 pps
• NJ-series CPU Unit: 3,000 pps (*)
*Note that the bandwidth allowed for NJ-series CPU Units with unit version 1.00 to 1.02 is 1,000 pps.
Example)
Node 1 has an originator connection with the receive RPI of 500 ms, and two target connections with
the send RPIs of 200 ms and 2 ms.
Node 2 has three originator connections with the receive RPIs of 200 ms, 2 ms, and 5 ms.
15 Communications Performance and Communications Load
15-3
NJ/NX-series CPU Unit Built-in EtherNet/IP Port User’s Manual (W506)
15-1 Communications System
15
15-1-1 Tag Data Link Communications Method

 Loading...
Loading...