192
Table 102 Configuration items
Item Descri
tion
DNS Domain Name Suffix Configure a domain name suffix.
4. Click Apply.
Domain name resolution configuration example
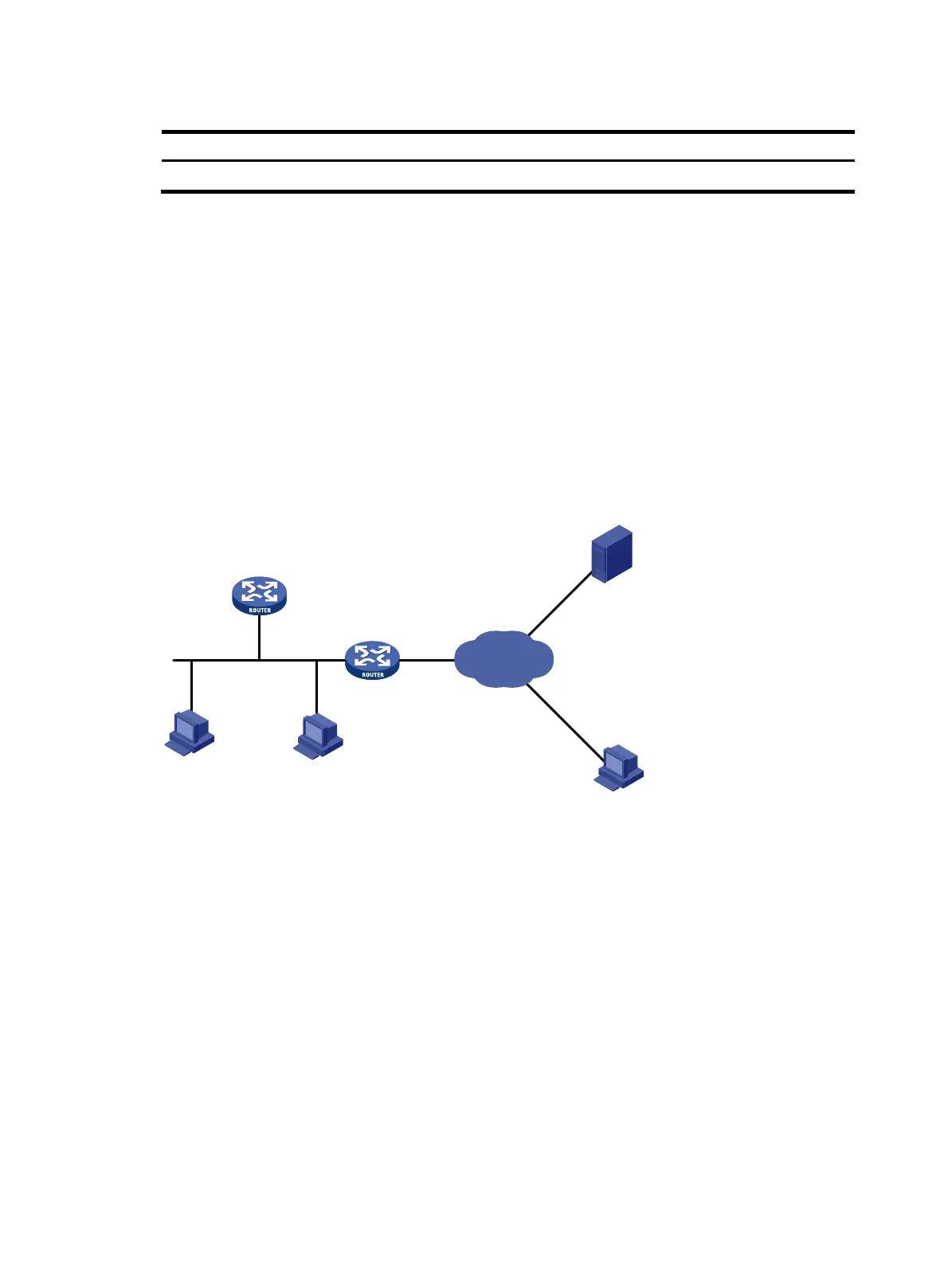
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 196, Router B serves as a DNS client and Router A is specified as a DNS server.
Dynamic domain name resolution and the domain name suffix are configured on Router B, and therefore
Router B can use domain name host to access the host with the domain name host.com and the IP
address 3.1.1.1/24.
Router A serves as the DNS proxy. The IP address of the actual DNS server is 4.1.1.1/24.
Router B performs domain name resolution through Router A.
Figure 196 Network diagram
Before performing the following configuration, make sure the device and the host are routable to each
other, and the IP addresses of the interfaces are configured as shown in Figure 196.
T
his configuration might vary with different DNS servers. The following configuration is performed on a
PC running Windows server 2000.
Configuring the DNS server
1. Select Start > Programs > Administrative Tools > DNS.
The page for configuring the DNS server appears.
2. Create zone com:
a. As shown in Figure 197, right-c
lick Forward Lookup Zones.
b. Select New Zone, and then follow the wizard to create a new zone named com.
3.1.1.1/24
host.com
Router B
DNS client
Router A
DNS proxy
IP network
DNS server
2.1.1.1/24
2.1.1.2/24 1.1.1.1/24
4.1.1.1/24
Host

 Loading...
Loading...