375
Configuring GRE
You can configure GRE over IPv4 tunnels through the Web interface.
Overview
Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) is a protocol designed for encapsulating and carrying the packets
of one network layer protocol (for example, IP or IPX) over another network layer protocol (for example,
IP). GRE is a tunneling technology and serves as a Layer 3 tunneling protocol.
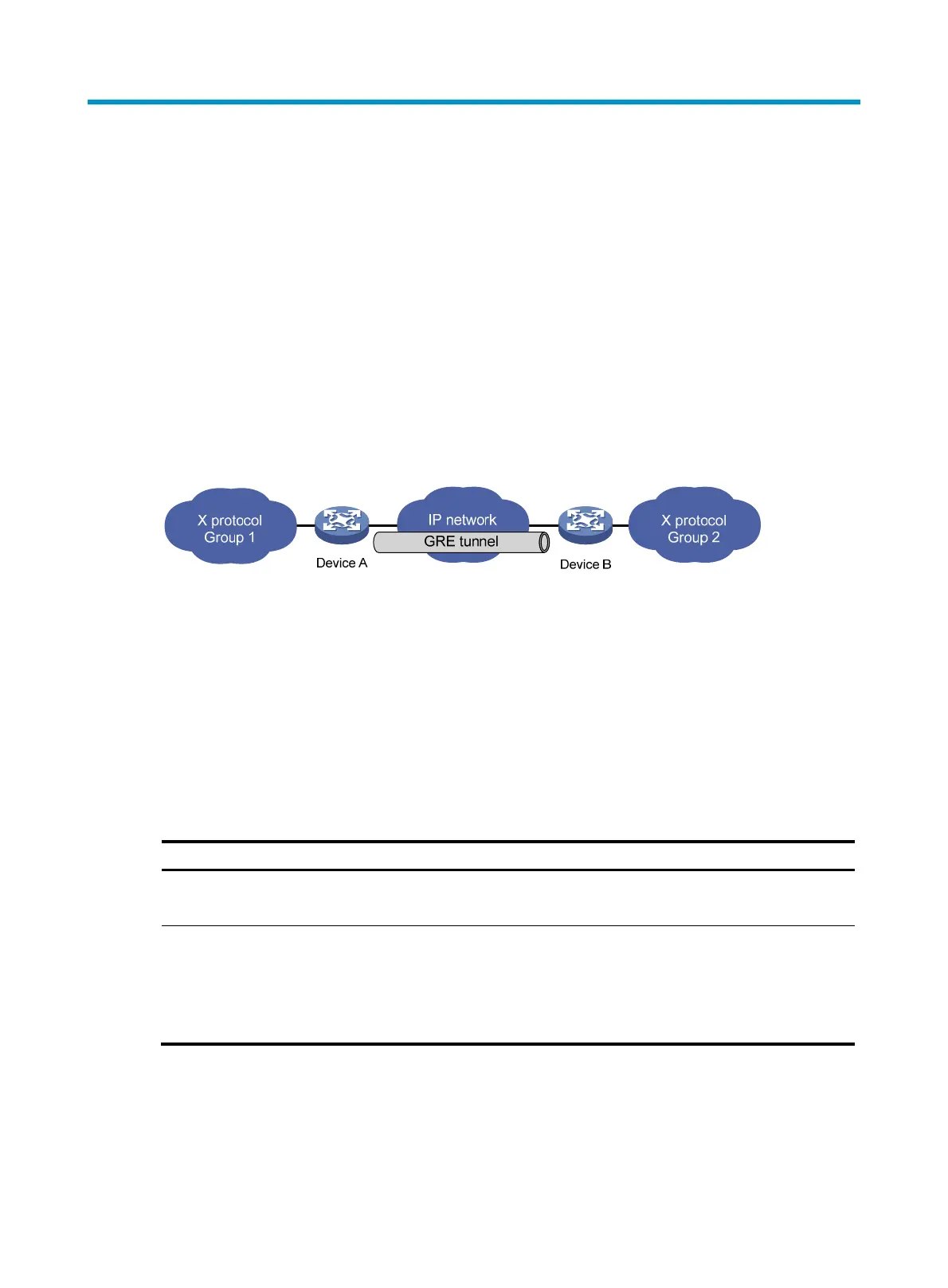
A GRE tunnel is a virtual point-to-point connection for transferring encapsulated packets. Packets are
encapsulated at one end of the tunnel and de-encapsulated at the other end. Figure 375 dep
icts the
encapsulation and de-encapsulation processes.
Figure 375 X protocol networks interconnected through the GRE tunnel
For more information about GRE, see Layer 3—IP Services Configuration Guide in HP MSR Router Series
Configuration Guides (V5).
Configuring a GRE over IPv4 tunnel
Before you configure a GRE over IPv4 tunnel, configure an IP address for the interface (such as a VLAN
interface, an Ethernet interface, or a Loopback interface) to be used as the source interface of the tunnel
interface.
Recommended configuration procedure
Task Remarks
1. Creating a GRE tunnel.
Required.
Create a tunnel interface and configure GRE tunnel related parameters.
2. Configure a route through
the tunnel.
Optional.
Each end of the tunnel must have a route (static or dynamic) through the
tunnel to the other end, so that GRE encapsulated packets can be forwarded
correctly.
For more information about route configuration, see "Configuring routes."
Creating a GRE tunnel
1. Select VPN > GRE from the navigation tree to enter the GRE tunnel configuration page, as shown
in Figure 376.

 Loading...
Loading...